Has Inheritage Foundation supported you today?
Your contribution helps preserve India's ancient temples, languages, and cultural heritage. Every rupee makes a difference.
Secure payment • Instant 80G certificate
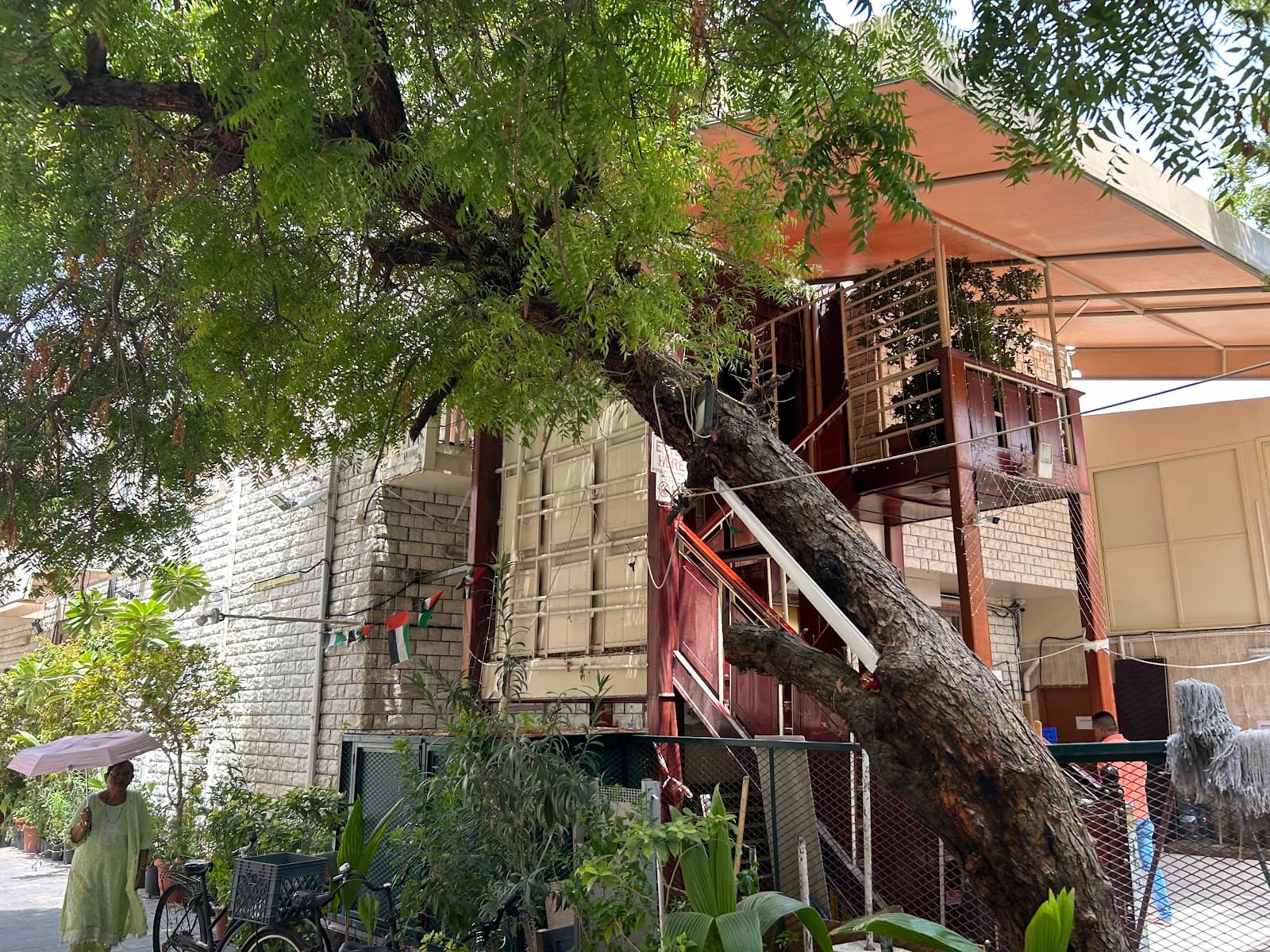

Krishna Temple Bur Dubai
The Krishna Temple in Bur Dubai has been Dubai’s oldest continuously operating Hindu shrine since 1958, tucked on the mezzanine of a sandalwood-scented souq courtyard in the historic Al Fahidi district where hundreds climb a narrow stair each dawn for darshan of Sri Nathji, Radha-Krishna, Mahalakshmi, and Sai Baba before winding through the lattice-screen corridor that overlooks the Creek ([1][2]). The 1,500-square-foot mandir retains teak balustrades, hand-carved pillars, brass finials, and the nine-domed roofline that peeks above coral-stone shophouses; priests weave through the throng performing arti with oil lamps held inches from glass-fronted sancta while volunteers chant bhajans. Daily timings stretch 5:00 AM-11:30 AM and 5:00 PM-9:30 PM, accommodating 3,000 devotees on weekdays and up to 6,000 during Janmashtami or Diwali. The temple’s shoe racks, prasad counter, and queue rails occupy the ground-level courtyard shared with souvenir shops and the adjacent Sikh Gurudwara, symbolising Dubai’s intercultural tapestry. Canonical rituals include Radha Ashtami, Satyanarayana katha, Tulsi Vivah, and mass annadhanam delivered by Indian restaurants who donate vegetarian meals. The small admin office manages marriage registrations, birth certificate attestations, and diaspora documentation in coordination with the Indian Consulate ([2][3]).
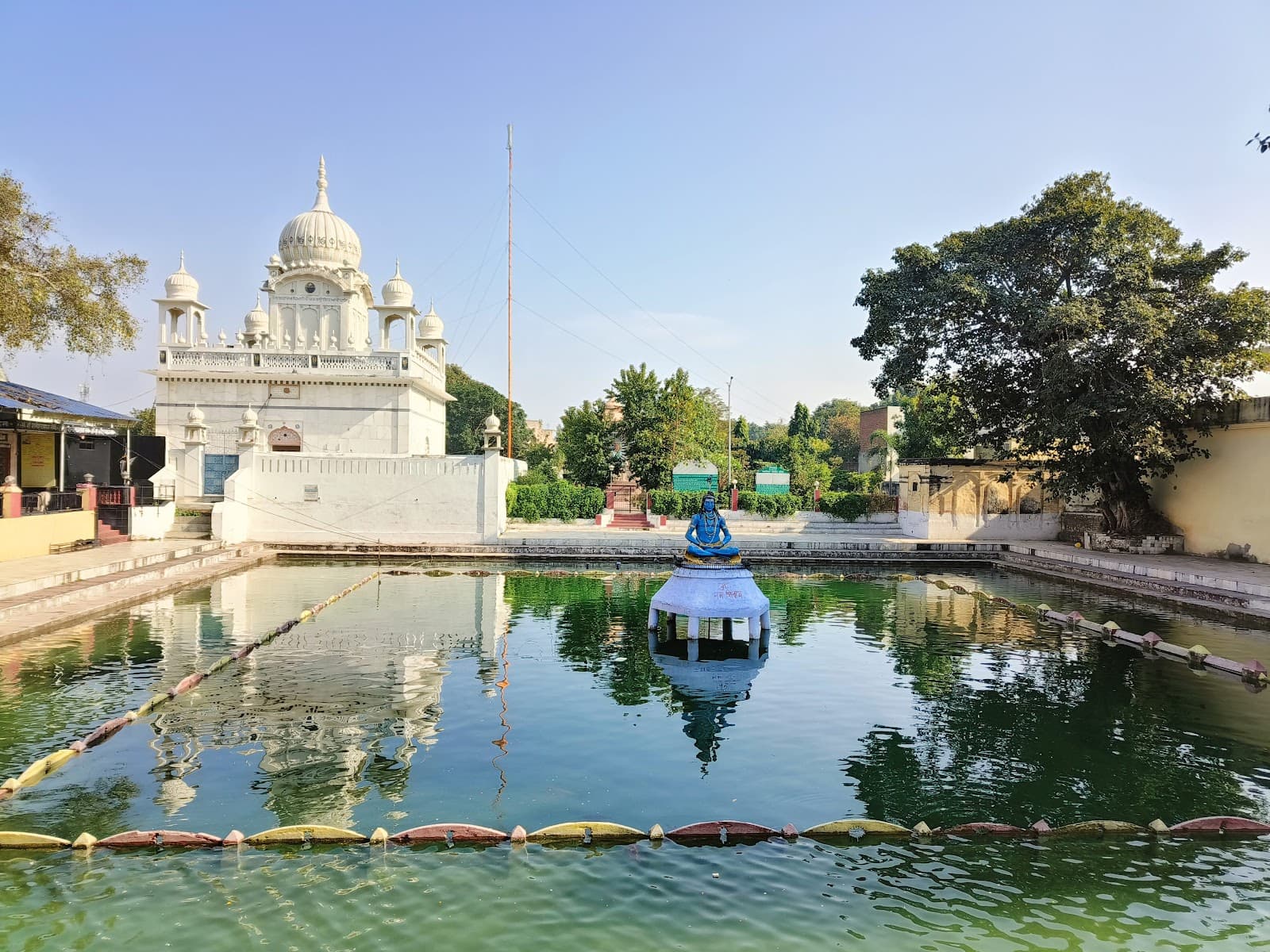

Sthaneshwar Mahadev Temple Thanesar
The late afternoon sun cast long shadows across the courtyard of the Sthaneshwar Mahadev Temple, painting the weathered stone a warm ochre. Dust motes danced in the shafts of light filtering through the gaps in the surrounding buildings, lending an ethereal quality to the scene. Here, in the heart of Thanesar, nestled within the historically significant land of Kurukshetra, stood a testament to centuries of devotion and architectural evolution. My visit wasn't just a reporting assignment; it was a pilgrimage of sorts, a chance to connect with the tangible remnants of India's rich past. The temple's current structure, while undeniably impressive, whispers of multiple reconstructions. The core, I learned from the temple priest, dates back to the ancient period, possibly even pre-Gupta times. However, much of what stands today bears the unmistakable mark of the Maratha reconstruction in the 18th century. This layering of history, this palimpsest of architectural styles, is precisely what makes Sthaneshwar Mahadev so fascinating. The shikhara, the towering superstructure above the sanctum sanctorum, rises with a gentle curve, its surface adorned with intricate carvings. While the Maratha influence is evident in the overall form, closer inspection reveals subtle nods to earlier architectural traditions. The amalaka, the crowning disc-like element, retains a classical simplicity, hinting at the temple’s older origins. I spent a considerable amount of time circling the structure, my gaze tracing the lines of the carvings, trying to decipher the stories they told. Many were weathered beyond recognition, yet their presence spoke volumes about the devotion and artistry of the craftsmen who had painstakingly etched them into the stone. Stepping inside the sanctum, I was struck by the palpable sense of reverence. The air was thick with the scent of incense and the murmur of prayers. The main deity, Lord Shiva, is represented by a lingam, a smooth, cylindrical stone that is the focal point of worship. The simplicity of this aniconic representation contrasted sharply with the ornate carvings that adorned the surrounding walls. It was a powerful reminder of the core principles of Hindu philosophy – the formless divine residing within the tangible world. The temple complex is not limited to the main shrine. Smaller shrines dedicated to various deities dot the courtyard, each with its own unique character. I was particularly drawn to a small, almost hidden shrine dedicated to Lord Hanuman. The vibrant vermilion paint that covered the statue of the Hanuman contrasted beautifully with the muted tones of the surrounding stonework. One of the most striking features of the Sthaneshwar Mahadev Temple is its connection to the sacred tank, known as the Brahma Sarovar. Located just a short walk from the temple, the tank is believed to have been created by Lord Brahma himself. Pilgrims come from far and wide to bathe in its holy waters, particularly during the solar eclipse. Standing by the edge of the tank, I could feel the weight of history and mythology pressing down on me. This was not just a body of water; it was a living testament to the enduring power of faith. My visit to Sthaneshwar Mahadev was more than just an architectural study; it was an immersion into the living tapestry of Indian culture and spirituality. The temple, with its layers of history, its intricate carvings, and its palpable sense of sanctity, offered a glimpse into the enduring power of faith and the artistry of those who sought to express it through architecture. As I left the temple grounds, the setting sun casting long shadows behind me, I carried with me not just photographs and notes, but a deeper understanding of the continuity of India's cultural heritage.
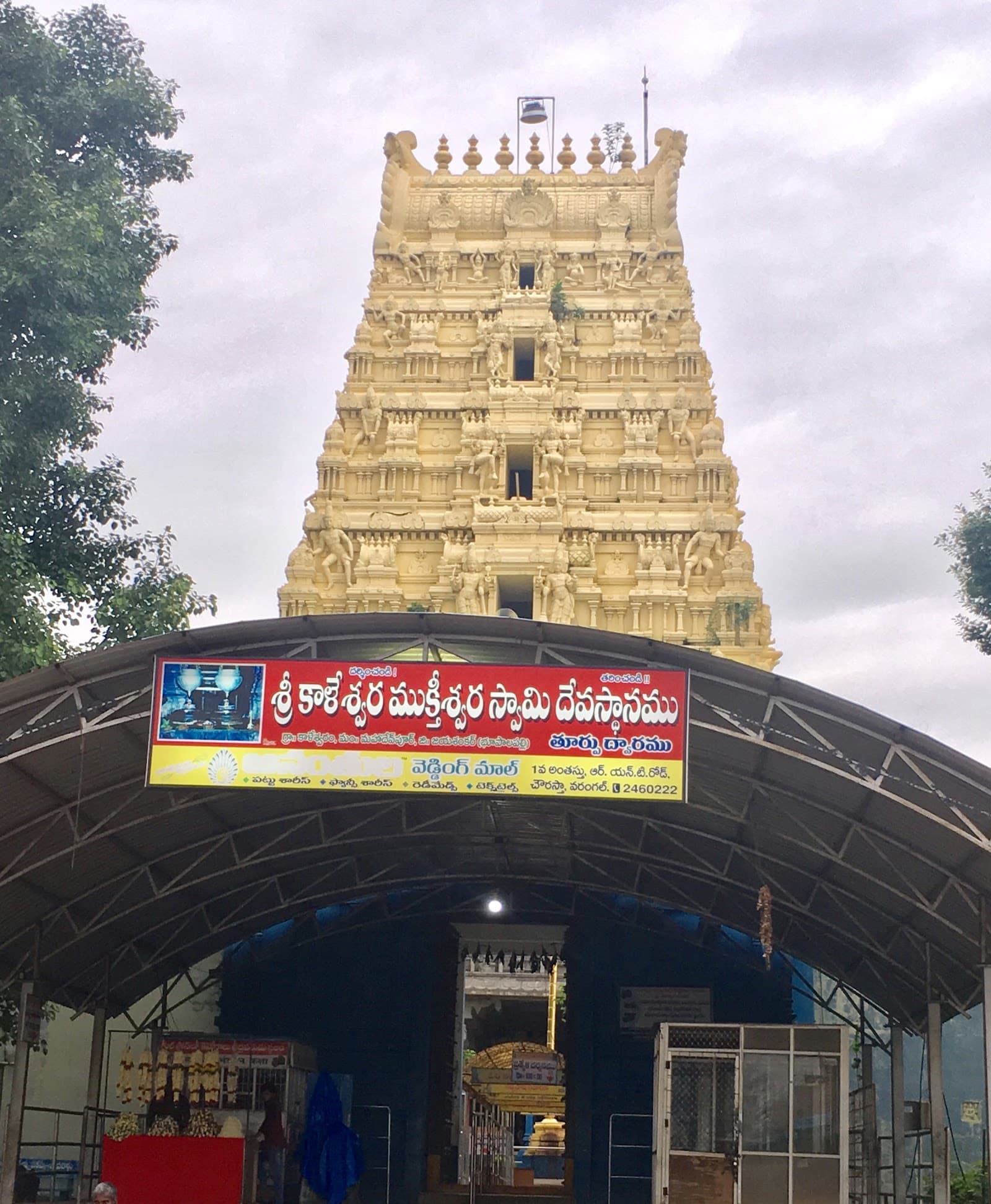

Kaleshwara Mukteswara Temple Kaleshwaram
The confluence of three rivers – the Godavari, Pranahita, and the mythical Saraswati – creates a sacred landscape at Kaleshwaram, where the Kaleshwara Mukteswara Swamy Temple stands as a testament to centuries of devotion and architectural prowess. My recent visit to this Telangana temple left me awestruck by its scale and the intricate details woven into its fabric. The temple complex, recently renovated, sprawls across a vast area, a modern marvel built upon ancient foundations. While the new construction gleams with polished stone, the core sanctums retain the weathered charm of history. The primary deity, Lord Shiva, is worshipped here as Kaleshwara Mukteswara Swamy, a name that resonates with the liberating power of time and divine grace. The temple's layout follows a traditional South Indian pattern, with multiple concentric enclosures or *prakarams* leading to the central shrine. However, the sheer scale of these *prakarams* and the towering *gopurams* (gateways) that punctuate them set Kaleshwaram apart. The use of light-colored stone, predominantly granite, creates a sense of grandeur and purity, amplified by the meticulous carvings that adorn every surface. One of the most striking features of the temple is the intricate sculpture work. Unlike the narrative panels common in many South Indian temples, Kaleshwaram’s carvings focus predominantly on floral motifs, geometric patterns, and divine figures. I noticed a distinct influence of the Chalukyan style in the sculpted *yalis* (mythical beasts) and the elaborate scrollwork that frames doorways and niches. The pillars, too, are marvels of craftsmanship, each one uniquely carved with intricate designs that seem to defy gravity. I spent a considerable amount of time observing the subtle variations in the floral patterns, each petal and leaf rendered with astonishing precision. The main *gopuram*, soaring high above the surrounding landscape, is a breathtaking sight. Its multiple tiers, adorned with vibrant stucco figures of deities and celestial beings, create a powerful visual statement. While the vibrant colours of the stucco work contrast with the muted tones of the stone, they add a layer of dynamism to the overall aesthetic. This interplay of colour and texture, of old and new, is a recurring theme throughout the temple complex. Moving beyond the main shrine, I explored the smaller shrines dedicated to various deities within the complex. The shrine of Goddess Parvati, consort of Lord Shiva, is particularly noteworthy for its elegant simplicity. The smaller *gopuram* leading to this shrine features intricate carvings of female deities and celestial musicians, a testament to the reverence accorded to the feminine principle in Hindu cosmology. My visit to Kaleshwaram wasn't just about observing the architecture; it was an immersion in a living tradition. The temple was bustling with devotees, their chants and prayers creating a palpable sense of devotion. Observing the rituals, the offerings, and the interactions between the priests and the devotees provided a glimpse into the enduring power of faith. The temple, despite its recent renovation, felt deeply connected to the past, a bridge between generations of worshippers. The integration of modern amenities, such as well-maintained pathways, clean restrooms, and clear signage, enhances the visitor experience without detracting from the temple's spiritual aura. This careful balance between preservation and modernization is commendable. Kaleshwaram is more than just a temple; it's a cultural landmark, a testament to the architectural ingenuity and religious fervour of the region. It's a place where history whispers from ancient stones, where faith finds expression in vibrant rituals, and where the confluence of rivers mirrors the confluence of the past, present, and future. My experience at Kaleshwaram was profoundly enriching, leaving me with a deep appreciation for the rich tapestry of South Indian temple architecture and the enduring power of sacred spaces.
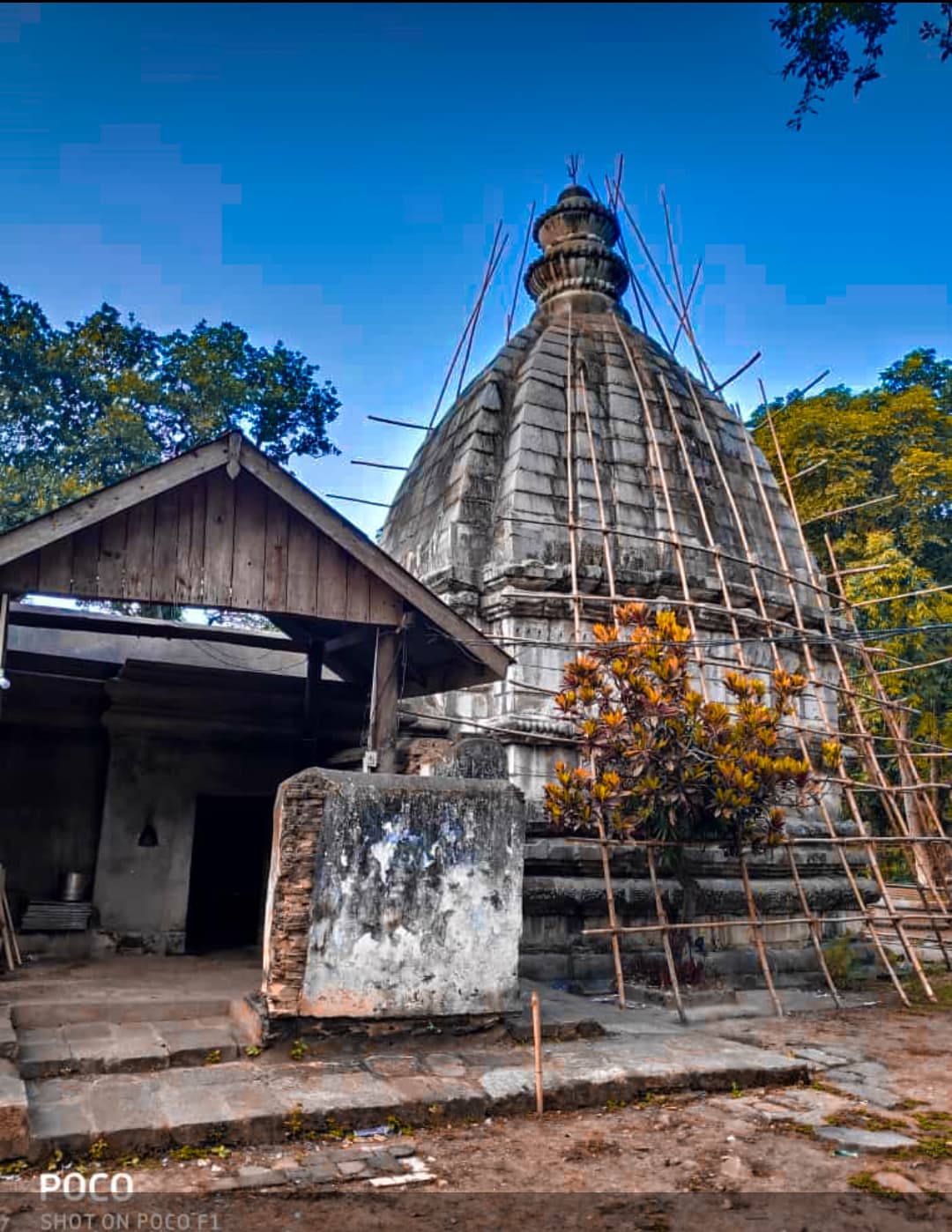

Kedareswara Temple Hajo
The Brahmaputra’s milky waters seemed to cradle the small hillock on which the Kedareswara Temple stood, a silent sentinel against the vast Assamese sky. Having spent years documenting the intricate stone carvings of Gujarat’s temples, I was eager to experience this architectural gem, so different from the sun-baked sandstone structures I was accustomed to. The journey from Guwahati, through verdant rice paddies and bustling villages, only heightened my anticipation. The first thing that struck me about Kedareswara was its stark simplicity. Unlike the ornate, almost flamboyant temples of my home state, this Shiva temple, built by the Ahom king Rajeswar Singha in 1752, exuded a quiet dignity. The pyramidal structure, reminiscent of the classic Nagara style prevalent in North India, rose in tiers towards the sky, its brick-and-mortar construction plastered and painted a pristine white. This stark white, against the vibrant green backdrop of the surrounding hills, created a visual harmony that was both striking and serene. Climbing the steep stone steps leading to the main entrance, I noticed the absence of elaborate sculptures that often adorn Gujarati temples. Here, the ornamentation was restrained, almost minimalist. A few stucco figures of deities, weathered by time and the elements, peered out from recessed niches, their features softened, almost blurred, lending them an air of ancient wisdom. The sanctum sanctorum, housing the Shiva lingam, was small and dimly lit, the air thick with the scent of incense and the murmur of prayers. The lingam itself, smooth and dark, seemed to absorb the ambient light, radiating a palpable sense of sacredness. I sat there for a while, absorbing the quiet energy of the space, the centuries of devotion that had imbued these walls with a palpable spirituality. Circumambulating the temple, I observed the subtle details that revealed the temple's unique character. The cornices, though simple, were adorned with delicate floral motifs, a testament to the local artisans' skill. Small, arched windows punctuated the thick walls, allowing slivers of light to penetrate the inner chambers, creating an interplay of light and shadow that added to the mystical atmosphere. What truly captivated me, however, was the syncretism evident in the temple's surroundings. Just a short distance away stood the Hayagriva Madhava Temple, a significant Vaishnavite shrine. This close proximity of Shaivite and Vaishnavite places of worship spoke volumes about the region's rich religious tapestry, a testament to the harmonious coexistence of different faiths. I learned from the local priest that Hajo is considered a pilgrimage site for Hindus, Buddhists, and Muslims alike, a rare example of interfaith harmony. As I descended the steps, the Brahmaputra shimmering in the afternoon sun, I reflected on the unique beauty of Kedareswara. It wasn't the grandeur or the opulence that moved me, but the quiet dignity, the understated elegance, and the palpable sense of history that permeated every stone, every corner of this ancient shrine. It was a powerful reminder that architectural marvels don't always need to shout to be heard; sometimes, a whisper can be just as profound. The Kedareswara Temple, in its serene simplicity, spoke volumes about the enduring power of faith and the rich cultural heritage of Assam. It was a journey into the heart of India’s spiritual landscape, a journey I won’t soon forget.
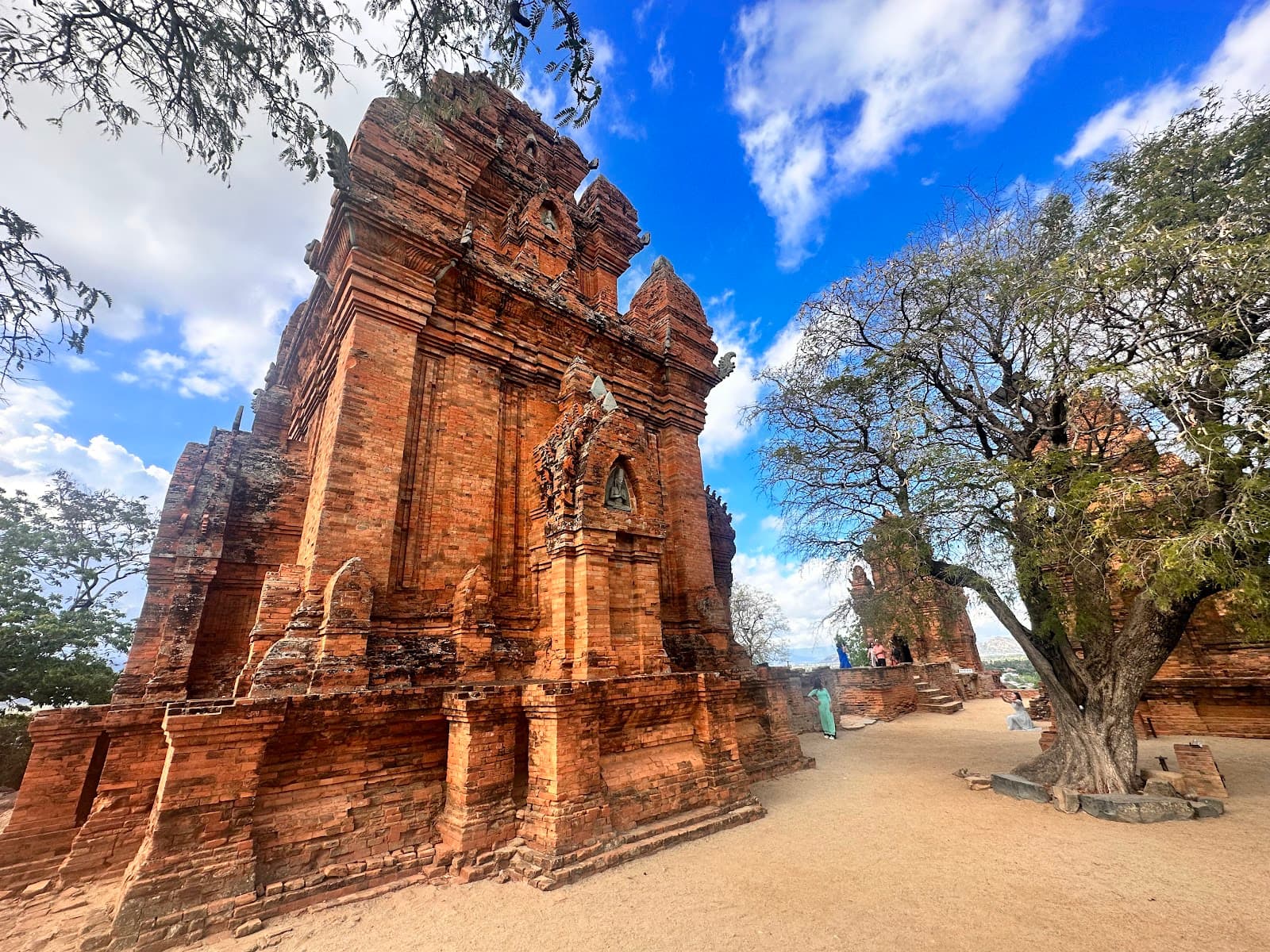

Po Klong Garai Towers Phan Rang Vietnam
Po Klong Garai Towers, dramatically situated on a hilltop overlooking the city of Phan Rang in Ninh Thuan Province, Vietnam, represent one of the most magnificent and well-preserved Cham Hindu temple complexes in Vietnam, constructed in the late 13th century CE to honor King Po Klong Garai, a revered Champa monarch who is remembered for his wisdom and contributions to Cham civilization, creating a stunning testament to the continued transmission of Indian Hindu religious and architectural traditions to Southeast Asia during the late medieval period. The temple complex, comprising three towers including a main tower dedicated to Shiva, a fire tower, and a gate tower, features extraordinary red brick structures adorned with intricate sandstone carvings and bas-reliefs that demonstrate the sophisticated synthesis of Indian Hindu temple architecture, particularly the Dravidian traditions of southern India, with indigenous Cham building techniques, creating a unique architectural expression that reflects Champa's deep and enduring engagement with Indian religious and cultural traditions. The main tower, standing approximately 21 meters tall and dedicated to Shiva, features elaborate decorative programs including bas-reliefs depicting Hindu deities, mythological scenes, and Cham royal iconography that demonstrate the direct transmission of Indian Hindu iconography and artistic traditions, while the discovery of Sanskrit inscriptions and Cham inscriptions provides crucial evidence of the site's role as a center for the transmission of Indian religious texts and practices to Southeast Asia. The temple complex served as a major center of Hindu worship for the Champa Kingdom, attracting devotees from across the region, while the site's location on a prominent hilltop, chosen according to Indian cosmological principles emphasizing the connection between earth and sky, underscores its spiritual significance as a place where the divine and earthly realms intersected, and the site's continued use as an active place of worship by Cham communities demonstrates the enduring vitality of Hindu religious practices in Vietnam. Archaeological evidence reveals that the complex represents one of the finest examples of late Cham architecture, demonstrating the continued refinement of Cham Hindu temple design and its continued engagement with Indian traditions even as Champa faced increasing pressure from neighboring powers, while the sophisticated brick construction techniques, including the unique Cham method of firing bricks in situ, created exceptionally durable structures that have withstood centuries of environmental stress and human activity. The towers feature distinctive Cham architectural elements including tiered pyramidal roofs, elaborate false doors, and extensive decorative programs that demonstrate the adaptation of Indian temple architecture to local materials and aesthetic preferences, while the site's excellent preservation provides crucial insights into the sophisticated engineering and artistic techniques employed in Cham temple construction. Today, Po Klong Garai stands as one of the most important Cham Hindu temples in Vietnam, serving as a powerful testament to the transmission of Indian Hindu culture and architecture to Southeast Asia, while the site's continued function as an active place of worship and its prominent location ensure its ongoing significance as both a cultural monument and a living religious center that bridges ancient Cham traditions with contemporary Vietnamese society. ([1][2])
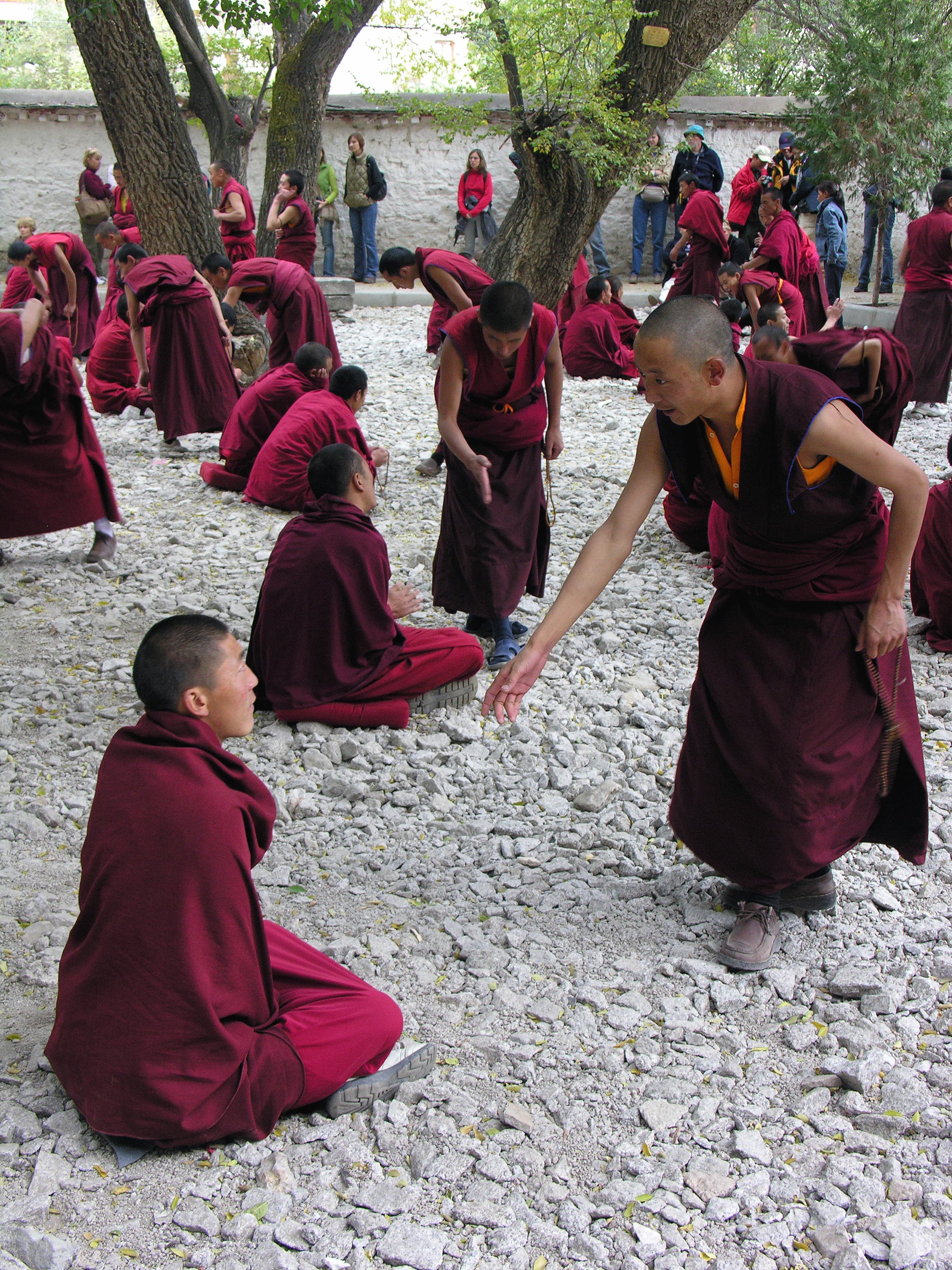

Sera Monastery Lhasa Tibet
Sera Monastery, located in Lhasa, Tibet, represents one of the three great Gelugpa monasteries in Tibet and stands as a major center for Tibetan Buddhist learning, particularly renowned for its debate courtyards where monks engage in philosophical debates using methods derived from Indian Buddhist debate traditions, constructed in the 15th century CE by Jamchen Chojey, a disciple of Tsongkhapa who established the Gelugpa school with strong connections to Indian Buddhist scholastic traditions, demonstrating the profound transmission of Indian Buddhist philosophy and debate traditions to Tibet, which has maintained deep cultural, religious, and historical connections with India for over two millennia. The monastery complex, constructed primarily from stone, wood, and earth with extensive decorative elements, features a massive structure containing numerous temples, chapels, assembly halls, and extensive debate courtyards arranged according to Indian Buddhist monastery planning principles, with the overall design reflecting mandala-based cosmological principles found in Indian Buddhist architecture. The monastery’s architectural design demonstrates direct influence from Indian Buddhist monastery architecture, particularly the Nalanda model, with the debate courtyards and learning facilities reflecting traditions that were transmitted to Tibet through centuries of cultural exchange, while the emphasis on Indian Buddhist debate traditions demonstrates the transmission of Indian Buddhist philosophy to Tibet. Archaeological and historical evidence indicates the monastery was constructed with knowledge of Indian Buddhist debate traditions and scholastic methods, reflecting the close cultural connections between Tibet and India during the medieval period, when Indian Buddhist scholars, texts, and philosophical traditions continued to influence Tibetan Buddhism. The monastery has served as a major center for Tibetan Buddhist learning and practice for over five centuries, maintaining strong connections to Indian Buddhist traditions through the study and practice of Indian Buddhist debate methods and philosophy. The monastery has undergone multiple expansions and renovations over the centuries, with significant additions conducted to accommodate growing numbers of monks and expanding educational programs. Today, Sera Monastery continues to serve as an important place of Buddhist worship and learning in Tibet, demonstrating the enduring influence of Indian Buddhist debate traditions on Tibetan culture and serving as a powerful symbol of Tibet’s deep connections to Indian civilization through the study and practice of Indian Buddhist philosophy. ([1][2])

This temple is not in Rajasthan. I only deal with Rajasthan.
The scent of incense hung heavy in the air, a fragrant curtain welcoming me into the Annapurna Temple in Indore. Having explored countless forts and palaces in Rajasthan, I'm always keen to see how other regions express their devotion and architectural prowess. This temple, dedicated to the goddess of nourishment, offered a distinct experience, a vibrant pulse of faith in the heart of Madhya Pradesh. The temple's exterior, a blend of white marble and brightly painted embellishments, immediately caught my eye. Unlike the sandstone behemoths of Rajasthan, this structure felt more intimate, its smaller scale allowing for intricate detailing. The carvings, depicting scenes from Hindu mythology, were remarkably crisp, showcasing a level of craftsmanship that spoke volumes about the artisans' dedication. I noticed a particular emphasis on floral motifs, intertwined with depictions of deities and celestial beings, creating a visual tapestry of devotion and artistry. Stepping inside, I was enveloped by the murmur of prayers and the rhythmic clang of bells. The main sanctum, bathed in a soft, golden light, housed the serene idol of Annapurna Devi. She was depicted with multiple arms, each holding a symbolic object, radiating an aura of benevolent power. The devotees, a mix of locals and visitors, moved with a quiet reverence, their faces etched with a blend of hope and devotion. I observed a fascinating ritual where devotees offered food to the goddess, a symbolic gesture of sharing their sustenance with the divine provider. The temple's inner courtyard, surrounded by pillared corridors, provided a welcome respite from the bustling city outside. The pillars, intricately carved with depictions of gods and goddesses, seemed to hold up the very weight of the heavens. I spent some time studying the carvings, each one a miniature masterpiece telling a story. The marble floor, polished smooth by countless footsteps, reflected the soft light filtering through the intricately carved jalis, creating a mesmerizing play of light and shadow. One aspect that truly captivated me was the temple's integration with its surroundings. Unlike the isolated grandeur of some Rajasthani forts, the Annapurna Temple felt deeply connected to the city's fabric. Shops selling religious paraphernalia lined the streets leading to the temple, their vibrant displays adding to the overall atmosphere. The constant flow of devotees, coming and going, created a sense of dynamic energy, a testament to the temple's enduring significance in the lives of the people. Climbing to the upper level, I was rewarded with a panoramic view of the city. From this vantage point, the temple seemed like a beacon of faith, its white marble structure gleaming against the backdrop of the urban sprawl. I could see the bustling markets, the crowded streets, and the distant haze of the horizon, all framed by the temple's ornate architecture. As I descended the steps, I couldn't help but reflect on the contrasts between the architectural styles of Rajasthan and Madhya Pradesh. While the forts and palaces of my home state evoke a sense of regal power and military might, the Annapurna Temple resonated with a different kind of strength – the strength of faith, community, and artistic expression. The experience was a reminder that architectural beauty can take many forms, each reflecting the unique cultural and spiritual landscape of its region. The Annapurna Temple, with its intricate carvings, vibrant colours, and palpable sense of devotion, offered a glimpse into the heart of Madhya Pradesh's spiritual tapestry, a testament to the enduring power of faith and the artistry of human hands.
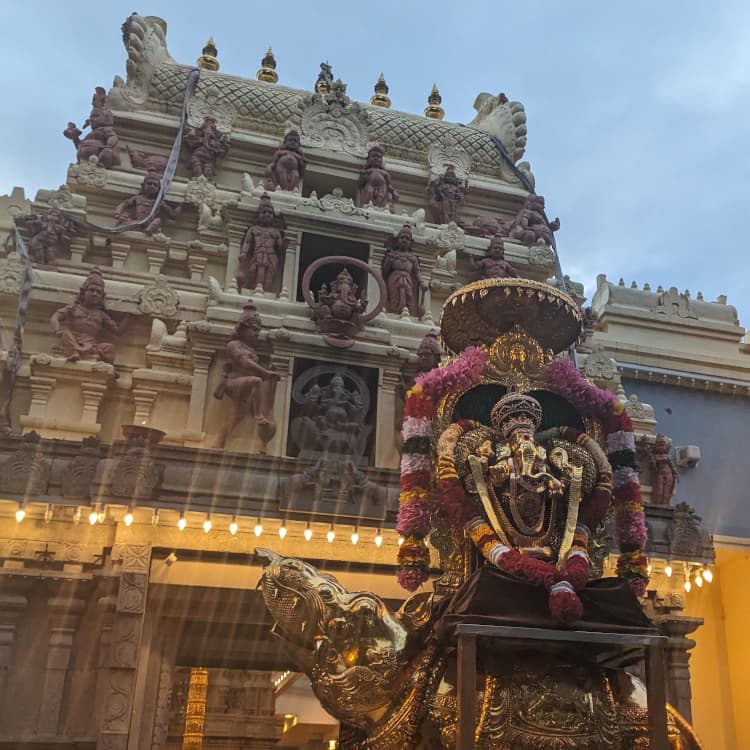
Sri Vakrathunda Vinayagar Temple The Basin
Sri Vakrathunda Vinayagar Temple The Basin is dedicated to Lord Ganesha and anchors The Basin, Victoria, on the foothills of the Dandenong Ranges ([1][2]). The hilltop mandir opens daily 6:00 AM-12:00 PM and 4:00 PM-8:30 PM, with Vinayagar Chathurthi and Thai Poosam schedules extending to 10:30 PM; marshals in high-visibility vests coordinate shuttle buses from the lower car park to keep the single-lane driveway clear ([1][4]). Mandapa floor markings separate pradakshina loops from queue lanes, and RFID counters at the entry tally pilgrim volumes so the volunteer command post can pace access into the sanctum ([1][5]). Annadhanam is served from a timber-lined dining hall with polished concrete floors, commercial dishwashers, and induction woks to reduce bushfire risk by avoiding naked flames ([1][3]). A 1:16 timber ramp with anti-slip mesh runs along the southern retaining wall, linking the car park to the mandapa, while stainless handrails, tactile paving, and hearing loop signage support inclusive access ([2]). Bushfire-ready shutters, ember screens, and a 90,000-litre tank plumbed to rooftop drenchers stand ready each summer, with CFA volunteers drilling annually alongside temple wardens ([2][5]). Wayfinding boards highlight refuge zones, first aid, and quiet meditation groves along the eucalyptus ridge, and QR codes push live updates about weather, kangaroo movement, and shuttle schedules directly to visitor phones ([1][6]). With emergency protocols rehearsed, food safety plans audited, and musician rosters published weeks ahead, the temple remains fully prepared for devotees, hikers, and school excursions seeking the hilltop shrine ([1][2]).
Jwala Ji Temple Kangra
The air in Kangra Valley hummed with a palpable energy, a blend of crisp mountain air and the fervent devotion that permeated the atmosphere surrounding the Jwala Ji Temple. Nestled amidst the lower Himalayas, this ancient shrine dedicated to the Goddess Jwala Mukhi, the manifestation of eternal flame, is unlike any other I’ve encountered in my journey across India's UNESCO sites. There are no idols here, no sculpted deities. The object of veneration is the nine eternal flames that flicker from fissures in the rock, believed to be manifestations of the Goddess herself. The temple complex, while not sprawling, possesses a distinct charm. The dominant architectural style is Dogra, with intricate carvings adorning the silver-plated doors, a gift from the Maharaja Ranjit Singh, and the ornate mandap, the main prayer hall. Multi-tiered sloping roofs, typical of the region, rise above the structure, adding to its visual appeal. The courtyard, bustling with pilgrims, resonates with the rhythmic clang of bells and the chanting of mantras. The scent of incense hangs heavy in the air, a fragrant tapestry woven with the hopes and prayers of the devotees. My first encounter with the flames was a moment etched in memory. Housed within small depressions in the rock, they dance and flicker with an almost hypnotic quality. Each flame has a name – Mahakali, Annapurna, Chandi, Hinglaj, Vidhya Basni, Sarvamangala, Ambika, Anjana, and Maha Lakshmi – each representing a different aspect of the divine feminine. The flames are fueled by natural gas seeping from the earth, a geological phenomenon that adds to the mystique and reverence surrounding the site. The absence of any discernible fuel source only amplifies the belief in their divine origin. What struck me most was the palpable faith of the pilgrims. Their faces, etched with devotion, reflected a deep connection to the Goddess. From hushed whispers to fervent prayers, the atmosphere was charged with spiritual energy. I witnessed people from all walks of life, from the elderly leaning on canes to young children clinging to their parents, offering their prayers and seeking blessings. The temple serves as a powerful reminder of the enduring power of faith, a testament to the human need to connect with something larger than oneself. Beyond the main shrine, the temple complex houses several smaller shrines dedicated to other deities. I spent some time exploring these, observing the intricate details of their architecture and the unique rituals associated with each. The surrounding landscape, with its verdant hills and snow-capped peaks in the distance, added to the serene ambiance. The panoramic view from the temple courtyard is breathtaking, offering a glimpse into the natural beauty that cradles this sacred site. One of the most intriguing aspects of Jwala Ji Temple is its history, shrouded in legends and folklore. Accounts of its origins vary, with some tracing it back to the Mahabharata, while others attribute its discovery to the Mughal Emperor Akbar. The temple has witnessed the rise and fall of empires, withstanding the test of time and continuing to serve as a beacon of faith for millions. This historical depth adds another layer to the experience, making it not just a visit to a temple, but a journey through time. As I descended from the temple, the chants and the scent of incense gradually faded, but the memory of the dancing flames and the palpable devotion remained. Jwala Ji Temple is more than just a UNESCO World Heritage Site; it's a living testament to the power of faith, a place where the divine and the earthly converge, leaving an indelible mark on the soul of every visitor. It's a place I won't soon forget, a highlight of my exploration of India's rich and diverse heritage.

Rama Mandir Lunglei
The emerald hills of Mizoram cradle many secrets, and among them, the Rama Mandir in Lunglei holds a special place. Not a UNESCO World Heritage Site, but a significant spiritual landmark nonetheless, this temple, perched atop a hill overlooking the town, offers a unique blend of architectural beauty and serene atmosphere, quite unlike anything I’ve encountered in my travels across India’s UNESCO-designated treasures. Reaching it requires a short but steep climb, a physical exertion rewarded by breathtaking panoramic views of Lunglei and the surrounding valleys. The temple’s architecture is a fascinating departure from the typical South Indian temple style I’ve grown accustomed to documenting. Instead of the towering gopurams and intricate carvings, the Rama Mandir presents a simpler, more austere aesthetic. The main structure is predominantly white, with a sloping roof reminiscent of traditional Mizo houses. This fusion of styles speaks volumes about the region's cultural confluence. The shikhara, however, retains a North Indian influence, its curvilinear form rising towards the sky, a beacon of faith visible from much of Lunglei. Stepping inside, I was struck by the tranquility that permeated the air. The main prayer hall is spacious and well-lit, with large windows offering glimpses of the verdant landscape outside. The deity, Lord Rama, is depicted in a serene pose, radiating a sense of calm that instantly puts visitors at ease. Unlike the bustling atmosphere of many temples in India, the Rama Mandir offers a space for quiet contemplation and introspection. The absence of overwhelming ornamentation allows one to focus on the spiritual aspect of the place, a refreshing change from the sensory overload that often accompanies visits to larger, more elaborate temples. What truly sets this temple apart, however, is its location. The panoramic view from the temple grounds is simply spectacular. The rolling hills, blanketed in lush greenery, stretch as far as the eye can see, creating a sense of boundless expanse. The town of Lunglei spreads out below, its colourful houses dotting the landscape like scattered jewels. I spent a considerable amount of time simply absorbing the beauty of the surroundings, feeling a sense of peace wash over me. The fresh mountain air, the gentle breeze rustling through the trees, and the distant sounds of nature all contributed to the serene atmosphere. During my visit, I had the opportunity to interact with the temple priest, a kind and knowledgeable man who shared insights into the temple's history and significance. He explained that the temple was built relatively recently, in the late 20th century, and has quickly become a focal point for the local Hindu community. He also spoke about the importance of preserving the region's natural beauty and the temple's role in promoting environmental awareness. This commitment to sustainability resonated deeply with me, as I've witnessed firsthand the impact of unchecked development on many of India's heritage sites. My visit to the Rama Mandir was a reminder that sacred spaces don't always have to be ancient or elaborately adorned to be powerful. The temple's simple elegance, its serene atmosphere, and its breathtaking location combine to create a truly special experience. While it may not yet bear the official UNESCO designation, the Rama Mandir in Lunglei undoubtedly holds cultural and spiritual significance, offering a glimpse into the rich tapestry of faith and tradition that makes India so unique. It’s a testament to the power of place and the enduring human need for connection with the divine, amidst the breathtaking beauty of the natural world. It's a site I highly recommend to anyone seeking a moment of peace and reflection amidst the stunning landscapes of Mizoram.
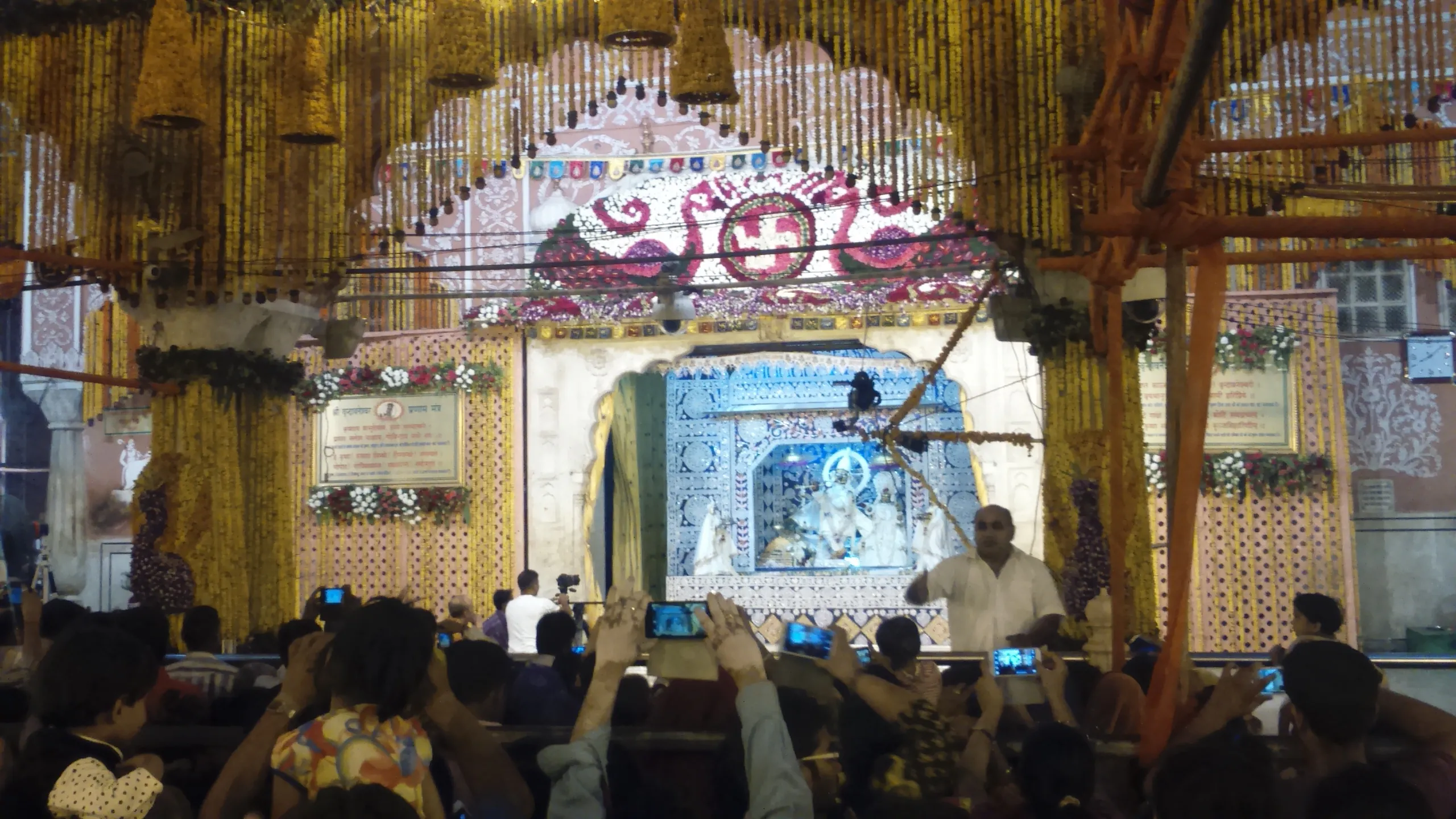

Govind Dev Ji Temple Jaipur
The Govind Dev Ji Temple in Jaipur isn't just a place of worship; it's a living testament to a unique blend of architectural styles that captivated me from the moment I stepped within its precincts. Having spent years studying the Dravidian architecture of South Indian temples, I was eager to experience the distinct architectural vocabulary of this North Indian shrine, and I wasn't disappointed. Located within the City Palace complex, the temple almost feels like a private sanctuary for the royal family, a feeling amplified by its relatively modest exterior compared to the grandeur of the surrounding palace buildings. The first thing that struck me was the absence of the towering gopurams that define South Indian temple gateways. Instead, the entrance is marked by a series of chhatris, elevated, dome-shaped pavilions supported by ornate pillars. These chhatris, with their delicate carvings and graceful curves, speak to the Rajput influence, a stark contrast to the pyramidal vimanas of the South. The use of red sandstone, a hallmark of Rajasthani architecture, lends the temple a warm, earthy hue, quite different from the granite and sandstone palettes I'm accustomed to seeing in Tamil Nadu. As I moved through the courtyard, I observed the seven-storied structure housing the main shrine. While not a gopuram in the traditional sense, it does serve a similar function, drawing the eye upwards towards the heavens. The multiple stories, each adorned with arched openings and intricate jali work, create a sense of verticality and lightness, a departure from the solid mass of South Indian temple towers. The jalis, or perforated stone screens, not only serve as decorative elements but also allow for natural ventilation, a practical consideration in the arid climate of Rajasthan. The main sanctum, where the image of Govind Dev Ji (Krishna) resides, is a relatively simple chamber, its focus squarely on the deity. The absence of elaborate sculptures on the walls within the sanctum surprised me. South Indian temples often feature intricate carvings depicting mythological scenes and deities on every available surface. Here, the emphasis is on the devotional experience, a direct connection with the divine, unmediated by elaborate ornamentation. The silver-plated doors of the sanctum, however, are exquisitely crafted, showcasing the artistry of the region's metalworkers. The courtyard itself is a marvel of spatial planning. The open space allows for the free flow of devotees, while the surrounding colonnades provide shade and a sense of enclosure. The pillars supporting these colonnades are slender and elegant, adorned with intricate floral motifs and geometric patterns. I noticed a distinct Mughal influence in some of these decorative elements, a testament to the cultural exchange that shaped the region's artistic traditions. The use of marble for flooring, another Mughal influence, adds a touch of opulence to the space. One of the most captivating aspects of the Govind Dev Ji Temple is its integration with the City Palace. The temple's location within the palace complex blurs the lines between the sacred and the secular, reflecting the close relationship between the royal family and the deity. This integration is a departure from the South Indian tradition where temples, while often patronized by royalty, maintain a distinct identity as separate entities. My visit to the Govind Dev Ji Temple was a fascinating cross-cultural experience. It highlighted the diversity of India's architectural heritage and underscored the power of architecture to reflect regional identities and religious beliefs. While the temple's architectural vocabulary differed significantly from the Dravidian style I'm familiar with, the underlying spirit of devotion and the artistic skill evident in its construction resonated deeply with my understanding of sacred architecture.
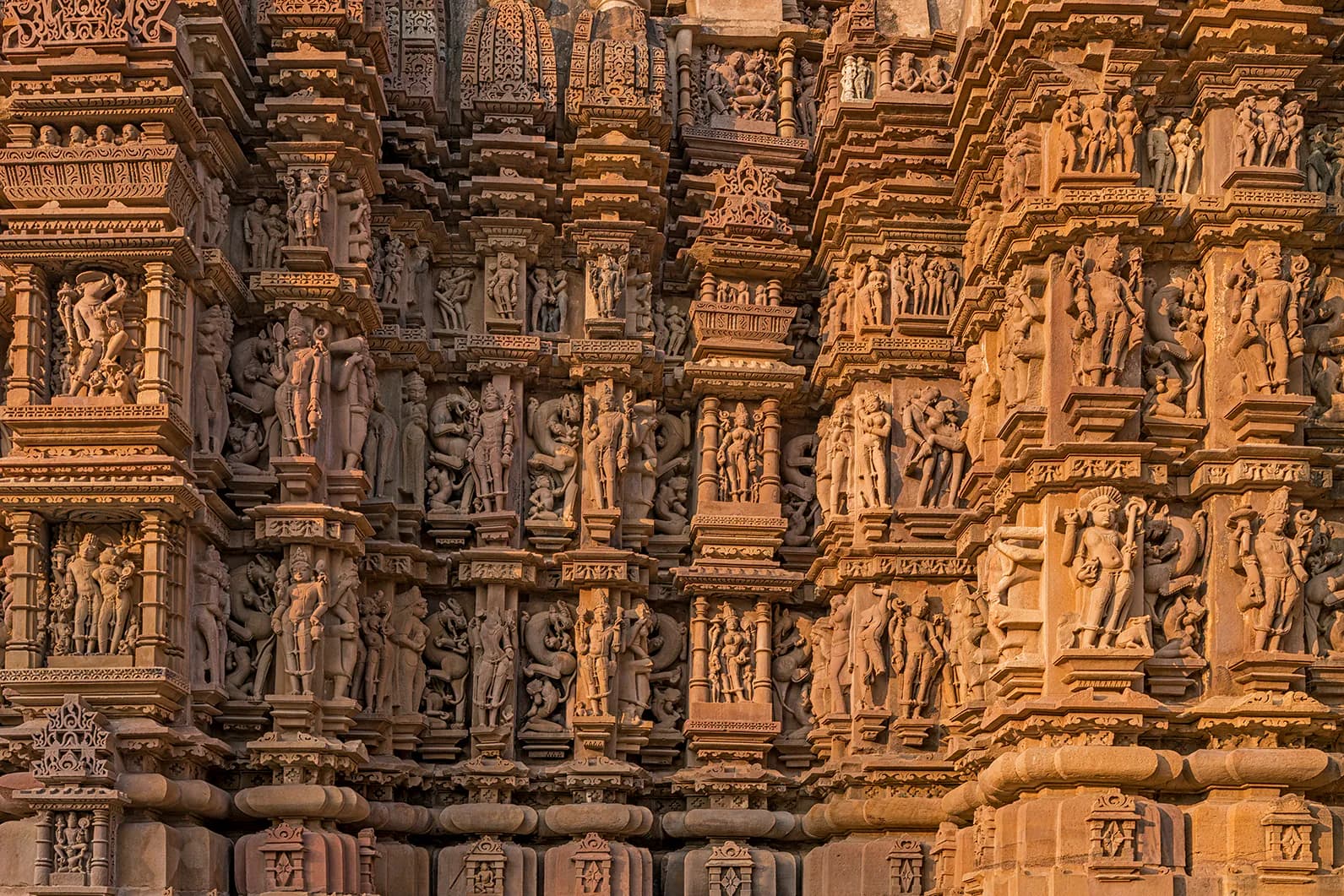

Khajuraho Temples Khajuraho
The first rays of dawn painted the sandstone a soft gold, illuminating the intricate carvings of the Kandariya Mahadeva Temple. Standing before this magnificent edifice, the largest of the Khajuraho group, I felt a palpable connection to the Chandela dynasty’s artistic zenith. Having explored countless temples across North India, from the snow-capped Himalayas to the plains of the Ganges, I can confidently say that Khajuraho holds a unique place, a testament to a time when art and spirituality were seamlessly interwoven. The sheer scale of the Kandariya Mahadeva is breathtaking. Its towering shikhara, a mountain of sculpted stone, reaches towards the heavens, a symbol of Mount Meru, the sacred abode of the gods. As I circumambulated the temple, my eyes traced the intricate friezes depicting celestial beings, mythical creatures, and scenes of everyday life. The level of detail is astonishing; every inch of the sandstone seems to pulsate with life. Noticeably, the erotic sculptures, often the focus of casual visitors, form only a small fraction of the overall artwork. They are integrated into the narrative, representing the cycle of creation and the celebration of life in all its forms. Moving beyond the Kandariya Mahadeva, I explored the western group of temples, each with its own distinct character. The Lakshmana Temple, dedicated to Vishnu, captivated me with its elegant proportions and the dynamic energy of its sculptures. I spent a considerable amount of time studying the narrative panels, deciphering the stories from the Ramayana and the Mahabharata etched into the stone. The sheer mastery of the Chandela sculptors is evident in the way they captured movement and emotion, breathing life into these ancient epics. The Chitragupta Temple, dedicated to Surya, the sun god, offered a different perspective. Its towering chariot, drawn by seven horses, is a powerful symbol of the sun’s journey across the sky. Inside, the sanctum houses a magnificent image of Surya, radiating an aura of divine power. The architectural style here subtly shifts, showcasing the evolution of the Chandela aesthetic over time. Venturing into the eastern group of temples, I found myself in a quieter, more intimate setting. The Parsvanatha Temple, a Jain temple, exudes a sense of serenity. Its polished sandstone surfaces gleam in the sunlight, reflecting the surrounding landscape. The intricate carvings here are more delicate, focusing on floral motifs and geometric patterns. The absence of the elaborate narratives found in the western group creates a different atmosphere, one of contemplation and inner peace. The Javari Temple, though smaller in scale, is a gem of architectural ingenuity. Its ornate doorway, adorned with celestial nymphs and intricate scrollwork, is a masterpiece of Chandela craftsmanship. I was particularly struck by the graceful curves and the delicate detailing of the sculptures, showcasing the artists' ability to manipulate the hard stone into forms of exquisite beauty. My exploration of Khajuraho wasn't just about admiring the architecture and sculptures. It was about experiencing the spirit of the place, imagining the artisans who toiled for decades to create these masterpieces, and the devotees who thronged these temples centuries ago. The air is thick with history, and as I walked through the temple grounds, I felt a profound sense of connection to India's rich cultural heritage. Khajuraho is more than just a collection of temples; it's a living testament to the artistic genius of a bygone era, a place that whispers stories of faith, devotion, and the celebration of life. It’s a must-see for anyone seeking to understand the depth and complexity of Indian art and history.
Quick Links
Plan Your Heritage Journey
Get personalized recommendations and detailed visitor guides