Nagara Architecture Style Architecture in Jharkhand
This collection documents 13 heritage sites across jharkhand, representing profound expressions of Hindu civilization's architectural and spiritual heritage. These monuments exemplify the nagara architecture style architectural tradition, with some maintaining unbroken traditions spanning millennia. Our comprehensive documentation, developed in collaboration with Archaeological Survey of India archaeologists, conservation specialists, and scholarly institutions, preserves not merely physical structures but the sacred geometry, cosmological symbolism, and ritual spaces central to Dharmic worship. acknowledging their universal significance to human civilization. Through royal patronage and community devotion, these structures embody the timeless principles of Hindu cultural heritage, connecting contemporary devotees to ancient traditions through stone, sculpture, and sacred spaces that continue to inspire reverence and wonder.
13 Sites Found
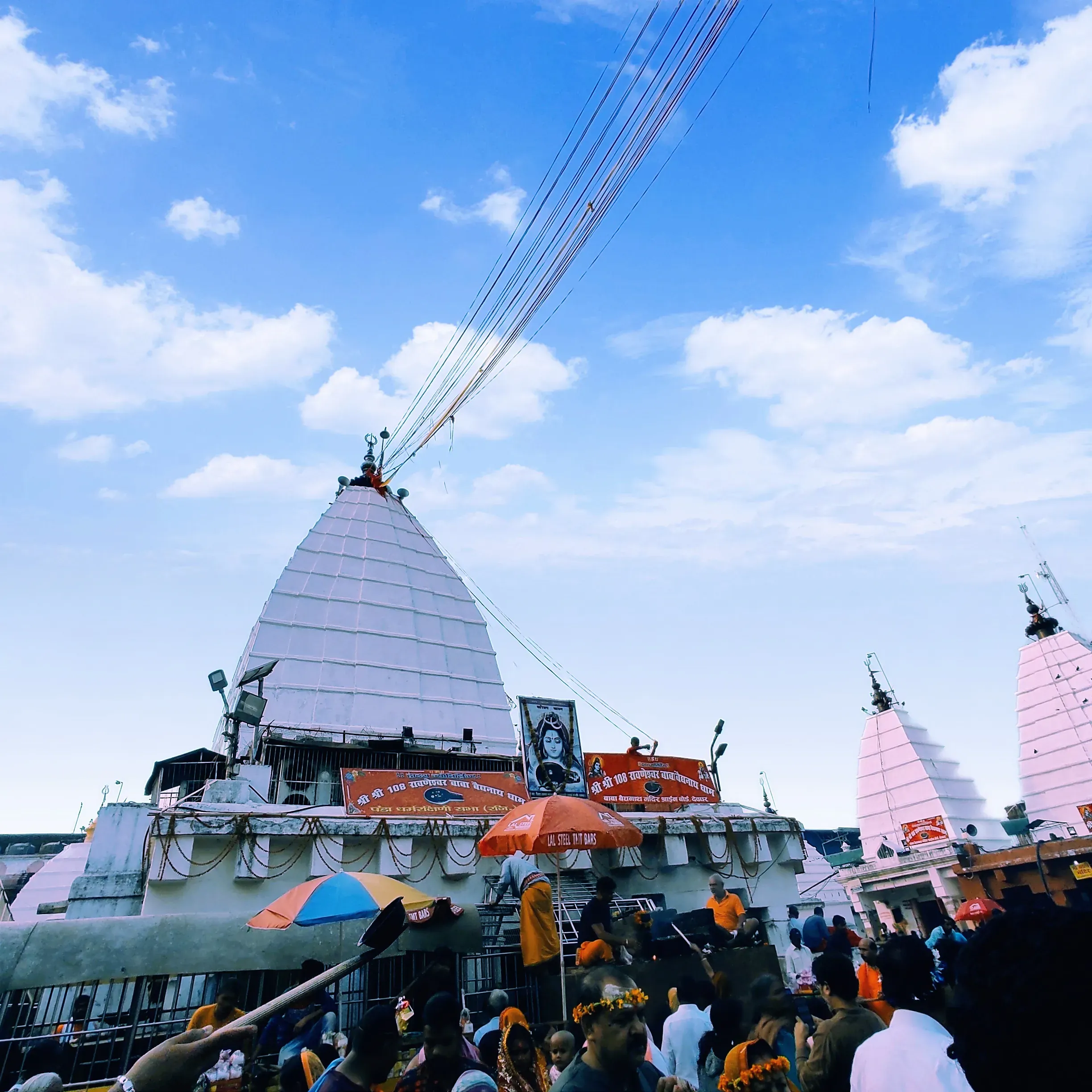

Encircled by formidable walls, the Baidyanath Temple in Deoghar, Jharkhand, is a sacred complex dedicated to Lord Shiva, attracting countless devotees ([1][2]). This cluster comprises twenty-two temples, each contributing to the spiritual ambiance ([1]). During the late medieval period, around 1650 CE, Raja Puran Mal commissioned the temple, adopting the Nagara style distinguished by curvilinear towers ([1][3]). Intricate carvings embellish the sandstone Shikhara (Spire), showcasing floral motifs, divine figures, and geometric patterns ([3]). These carvings display a restrained elegance, setting it apart from more exuberant regional styles ([1]). Stone, laterite, brick, and plaster were employed with sophisticated construction techniques throughout the complex ([1]). Vastu Shastra principles, the ancient Indian science of architecture, likely influenced the temple's layout and orientation, although specific textual references are not available ([2]). The temple reflects the architectural traditions prevalent during its time. Within the courtyard, the echoes of chants and the resonating bells create a vibrant atmosphere ([1]). Witnessing the rituals, offerings, and silent prayers of pilgrims fosters a profound sense of connection ([2][3]). Leaving the Baidyanath Temple, visitors gain a deeper appreciation for the fusion of architecture, faith, and human experience ([1]). This temple stands as an enduring symbol of faith, intertwining tangible and intangible elements ([2]). The Baidyanath Temple's construction in the 17th century showcases the architectural and artistic achievements of the period, reflecting the patronage of Raja Puran Mal and the enduring legacy of Nagara temple architecture in India ([1][3]). The temple continues to be a significant pilgrimage site, embodying the rich cultural and religious heritage of India ([2]).
Vibrating with spiritual energy, Basukinath Dham in Deoghar, Jharkhand, stands as a testament to India's rich temple-building heritage. Constructed in 1585 CE under the patronage of Raja Puran Mal ([1]), this sacred Shiva temple attracts devotees seeking authentic spiritual connection. Having explored many North Indian temples, Basukinath's architecture exemplifies the Nagara style, characterized by its curvilinear towers and stepped pyramidal structures ([2][3]). Intricate carvings, smoothed by centuries of devotion, adorn the temple's doorway, depicting scenes from Hindu mythology ([4]). The main shrine, dedicated to Lord Shiva, features a modest white structure adorned with prayer flags ([1]). Within the Garbhagriha (Sanctum), a vibrant tapestry of devotees gathers, the air filled with incense and the chanting of "Bol Bam" ([3]). This creates an immersive spiritual experience. Beyond the primary shrine, smaller temples dedicated to various deities enrich the complex ([5]). One such shrine, dedicated to Parvati, showcases remarkably preserved terracotta carvings, reflecting the region's artistic heritage ([5][6]). During the late medieval period, temple architecture flourished under royal patronage, blending regional styles with pan-Indian traditions ([7]). Stone platforms and foundations demonstrate the temple's enduring construction, utilizing locally sourced materials ([8]). The narrow lanes surrounding the temple bustle with stalls selling religious items and local delicacies, adding to the sensory richness of the pilgrimage ([9]). Vastu Shastra principles, the ancient Indian science of architecture, likely guided the temple's layout and orientation, aligning it with cosmic energies ([10]). Basukinath Dham offers a profound connection to India's spiritual and architectural heritage, inviting visitors to experience its unique sanctity.
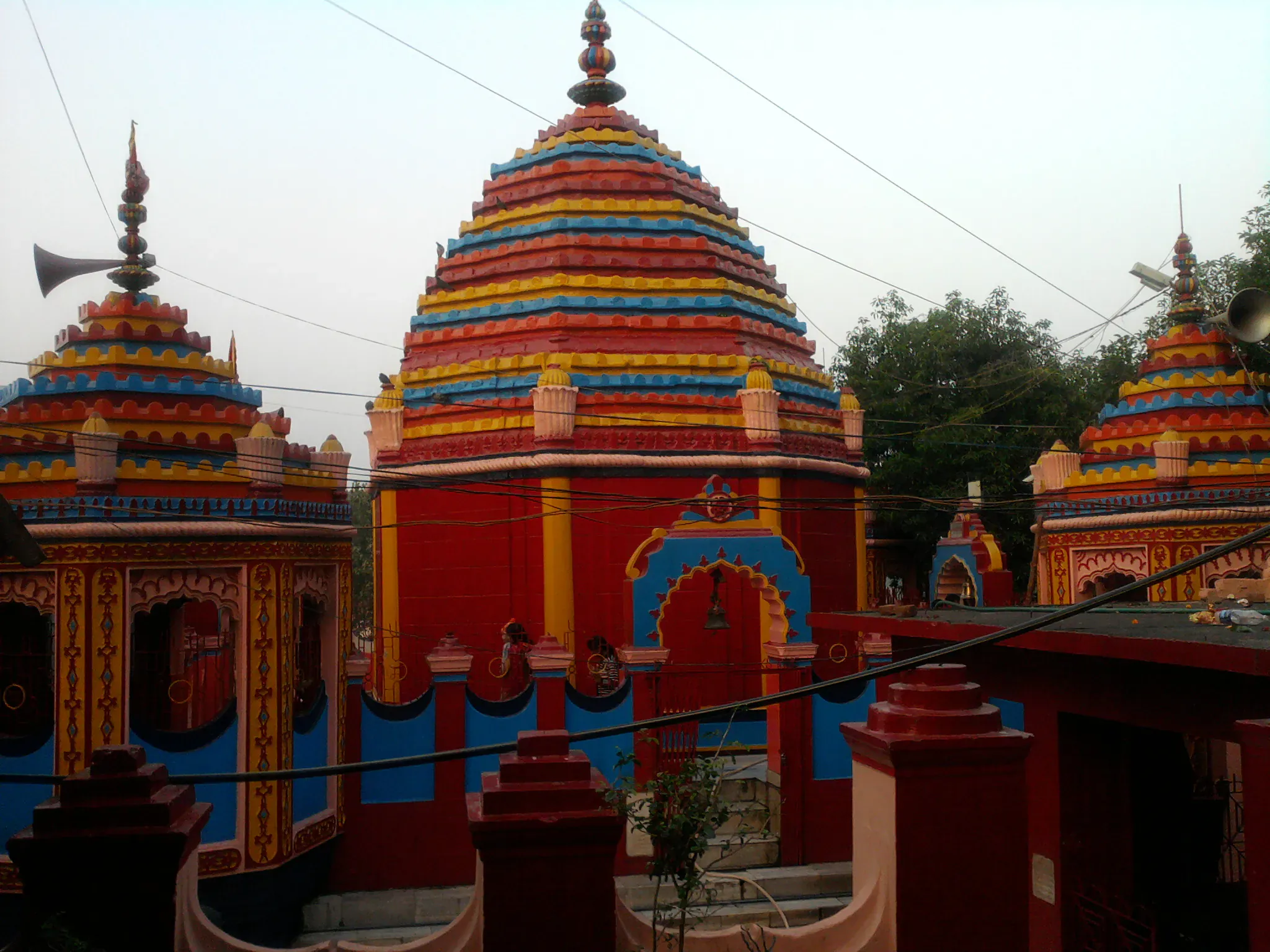

Nestled amidst the picturesque hills of Jharkhand, the Chhinnamasta Temple in Ramgarh provides a captivating glimpse into the region's rich architectural and spiritual heritage ([1][2]). Constructed around 1350 CE, during the Eastern Ganga Dynasty, this temple is dedicated to the unique tantric goddess Chhinnamasta, with patronage from the Chero Chiefs ([1][3]). The temple's architecture represents a fascinating Nagara-Kalinga hybrid style, showcasing the blending of distinct regional influences ([2][4]). Granite and sandstone blocks, meticulously carved by skilled artisans, constitute the primary building materials ([1][5]). The towering curvilinear Shikhara (spire), a defining feature of Nagara architecture, dominates the temple's skyline, rising majestically above the Garbhagriha (Sanctum) ([2][4]). Laterite stone, locally sourced, adds an earthy hue to the structure, contrasting with the intricate ornamentation that graces its surfaces ([3][5]). This harmonious blend of materials and styles reflects the architectural prowess of the Eastern Ganga period. Within the Garbhagriha, the striking iconography of the goddess Chhinnamasta takes center stage, depicting her self-decapitation as a profound symbol of self-sacrifice and cosmic renewal ([2][3]). The temple's design integrates tantric principles, emphasizing the interconnectedness of seemingly opposing forces, a concept deeply rooted in ancient Indian philosophy ([4][5]). Further, the temple exemplifies the enduring legacy of Indian temple architecture, seamlessly blending regional materials, artistic craftsmanship, and profound spiritual symbolism, offering a unique cultural experience ([1][2]). The Chhinnamasta Temple is a testament to India's architectural diversity.
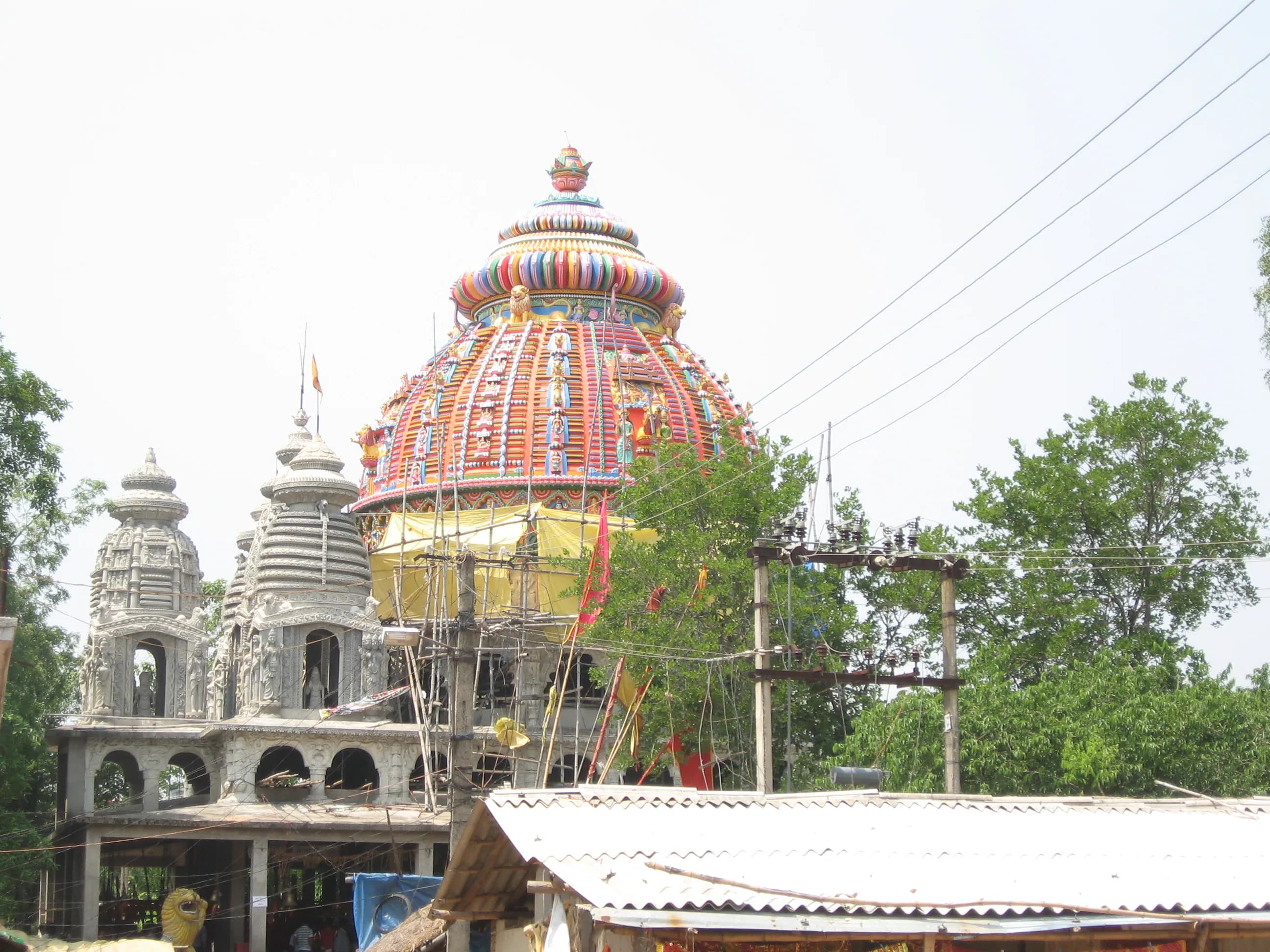

Amidst the verdant landscapes of Jharkhand stands Dewri Mandir, a unique testament to India's architectural heritage, built around 1750 CE during the British Colonial Period ([1][2]). This temple, dedicated to the Sun God Surya, showcases a captivating blend of Nagara style architecture with regional influences ([3]). The Nagvanshi King Pratap Karna's patronage shaped this sacred space, imbuing it with a distinct identity ([1]). Intricate carvings adorning the walls narrate tales from Hindu epics, the Ramayana and Mahabharata, rendered in terracotta, clay bricks and stone ([4]). This temple deviates from typical Nagara structures, evident in its curvilinear Shikhara (spire) reminiscent of Odishan architecture, yet embraces the terracotta artistry of Bengal ([3]). The temple's construction utilizes laterite stone, a common material in the region, adding to its unique character ([2]). Within the Garbhagriha (sanctum), the deities Shiva, Durga, and Ganesha are venerated, their iconography reflecting localized interpretations of pan-Indian traditions ([5]). Vastu Shastra principles, the ancient Indian science of architecture, likely guided the temple's layout, though specific textual references are yet to be definitively established ([6]). The use of vibrant colors, though faded with time, hints at the temple's former splendor, creating a visually stunning spectacle ([4]). Stone platforms and foundations demonstrate the enduring construction techniques employed, ensuring the temple's resilience through the centuries ([2]). This sacred site remains an active center of worship, where devotees gather to perform puja (prayers), bridging the past and present ([5]). Dewri Mandir stands as a reminder of India's diverse architectural traditions, inviting exploration and reverence. The temple is located on Dewri Mandir Road, Ranchi (835222), Jharkhand, India ([1]).
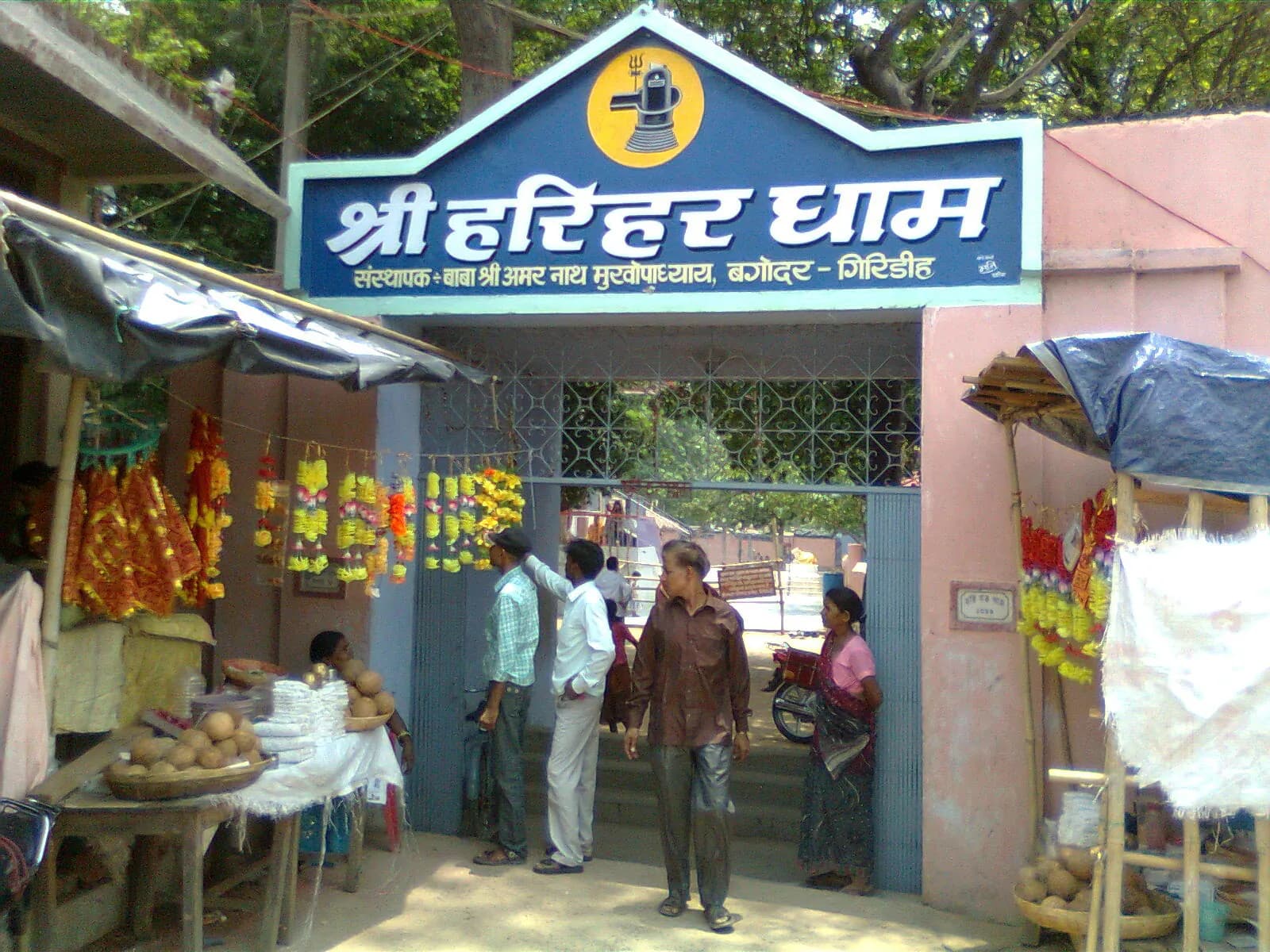

The air hung heavy with the scent of incense and marigold garlands as I approached Harihar Dham, a sprawling temple complex nestled amidst the rolling hills of Giridih, Jharkhand. The sheer scale of the site was immediately striking. Towering shikharas, reminiscent of the Nagara style prevalent in my home state of Madhya Pradesh, pierced the sky, their sandstone surfaces gleaming a warm ochre under the late afternoon sun. Unlike the intricate carvings that adorn many Madhya Pradesh temples, these shikharas possessed a certain stark elegance, their smooth surfaces punctuated only by rhythmic projections and a simple amalaka crowning each spire. My lens immediately gravitated towards the main temple dedicated to Harihar, the combined form of Vishnu (Hari) and Shiva (Har). The structure, a blend of North and South Indian architectural styles, showcased a fascinating interplay of influences. The curvilinear shikhara, a hallmark of the Nagara style, dominated the skyline, while the square mandapa, with its sturdy pillars and pyramidal roof, hinted at a Dravidian influence. This fusion, rarely seen in such a pronounced manner, spoke volumes about the region's rich cultural crossroads. As I circled the main temple, I noticed intricate carvings adorning the doorway. Depictions of deities, celestial beings, and scenes from Hindu mythology unfolded in meticulous detail. The sandstone, weathered by time and the elements, lent these carvings a unique patina, a testament to the temple's enduring presence. I spent a considerable amount of time documenting these narrative panels, each one a window into the rich tapestry of Hindu beliefs. Beyond the main temple, the complex sprawled across a vast area, encompassing smaller shrines dedicated to various deities. A particularly captivating structure was the temple dedicated to Radha-Krishna. Its smaller scale and ornate carvings provided a stark contrast to the imposing grandeur of the Harihar temple. The delicate latticework screens, known as jalis, allowed for a play of light and shadow within the sanctum, creating an ethereal atmosphere. I captured the interplay of light filtering through these jalis, highlighting the intricate carvings of the divine couple. One aspect that truly captivated me was the presence of numerous smaller shrines scattered throughout the complex, almost like miniature echoes of the main temple. Each shrine, though smaller in scale, possessed its own unique architectural character, showcasing variations in shikhara design and decorative elements. This decentralized approach to temple architecture created a sense of exploration and discovery, inviting visitors to wander through the complex and uncover hidden gems. The presence of a large water tank, or kunda, added another layer to the site's spiritual significance. Devotees were performing ritual ablutions in the kunda, their chants and prayers resonating through the air. The reflection of the towering shikharas in the still water of the kunda created a mesmerizing visual, a perfect blend of the built and natural environment. I captured this scene, aiming to convey the serene atmosphere and the deep spiritual connection that permeated the site. My experience at Harihar Dham was more than just a photographic documentation; it was an immersion into a vibrant spiritual landscape. The architectural nuances, the intricate carvings, and the palpable devotion of the pilgrims all contributed to a profound sense of place. As I packed my equipment, I felt a deep sense of gratitude for the opportunity to witness and document this remarkable testament to India's rich cultural heritage. The images I captured, I hope, will serve as a window into this sacred space, allowing others to glimpse the beauty and spiritual significance of Harihar Dham.
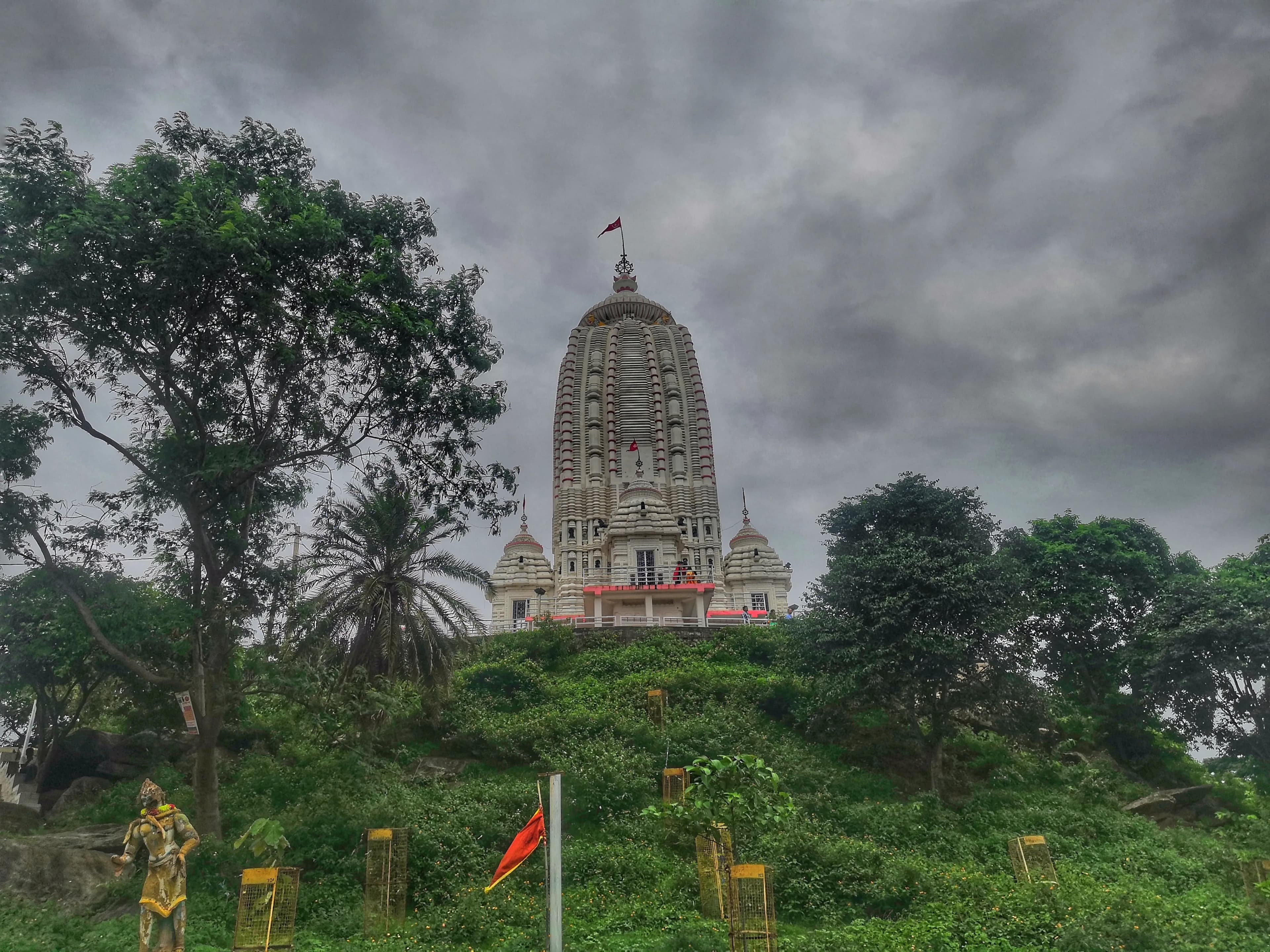

The crisp Jharkhand air, a welcome change from Maharashtra's humidity, carried the scent of incense as I approached the Jagannath Temple in Ranchi. Perched atop a small hillock, the temple’s pristine white shikhara, reminiscent of Odisha's famed Puri Jagannath Temple, dominated the skyline. Having explored countless caves and temples across Maharashtra, I was eager to see how this architectural marvel compared to the familiar terrain of my home state. The climb to the temple was a pilgrimage in itself. A wide flight of stairs, flanked by vendors selling everything from religious trinkets to local delicacies, led to the main entrance. The vibrant energy of the place was palpable, a blend of devotion and everyday life that is so characteristic of India's sacred spaces. Unlike the often chaotic scenes at Maharashtra's popular temples, there was a sense of calm order here, perhaps influenced by the temple's elevated position. The temple's architecture is a striking blend of traditional Odishan and contemporary styles. The shikhara, with its curvilinear silhouette and intricate carvings, is undoubtedly the highlight. While echoing the style of the Puri temple, it possesses a unique character, perhaps due to the use of locally sourced laterite stone. This reddish-brown stone, so different from the basalt and black stone I’m accustomed to seeing in Maharashtra’s temples, lends the structure a warm, earthy hue. The carvings, though weathered by time and elements, still retain a remarkable level of detail, depicting scenes from Hindu mythology and showcasing the skill of the artisans who crafted them. Stepping inside the main sanctum, I was greeted by the imposing idols of Jagannath, Balabhadra, and Subhadra. The atmosphere was thick with the fragrance of sandalwood and the murmur of prayers. The deities, with their distinctive large eyes and cylindrical forms, exuded a powerful aura. While smaller than their counterparts in Puri, they held the same captivating presence. I observed the rituals with fascination, noting the distinct regional variations compared to the temple practices I’ve witnessed in Maharashtra. The rhythmic chanting of the priests, the clanging of bells, and the flickering of oil lamps created a mesmerizing sensory experience. Beyond the main shrine, the temple complex houses several smaller shrines dedicated to various deities. I was particularly drawn to the intricate carvings adorning the walls of these smaller structures. They depicted a fascinating array of mythological figures, celestial beings, and floral motifs. The level of detail was astonishing, each carving a testament to the artistic prowess of the craftsmen. I spent a considerable amount of time studying these panels, drawing parallels and contrasts with the sculptural traditions of Maharashtra. The panoramic view from the temple grounds was breathtaking. The sprawling city of Ranchi lay spread out below, a tapestry of green and grey punctuated by the occasional glint of sunlight reflecting off a distant building. The cool breeze carried the sounds of the city, a gentle hum that blended seamlessly with the temple’s serene atmosphere. It was a moment of quiet contemplation, a chance to reflect on the journey that had brought me to this sacred place. Leaving the Jagannath Temple, I carried with me not just photographs and memories, but a deeper understanding of India's rich architectural and spiritual heritage. The temple, a testament to the enduring power of faith and artistry, stands as a beacon of hope and devotion, offering solace and inspiration to all who visit. While my heart remains rooted in the ancient caves and temples of Maharashtra, the Jagannath Temple of Ranchi has carved a special place in my travelogue, a reminder of the diverse and captivating tapestry of India's sacred landscape.
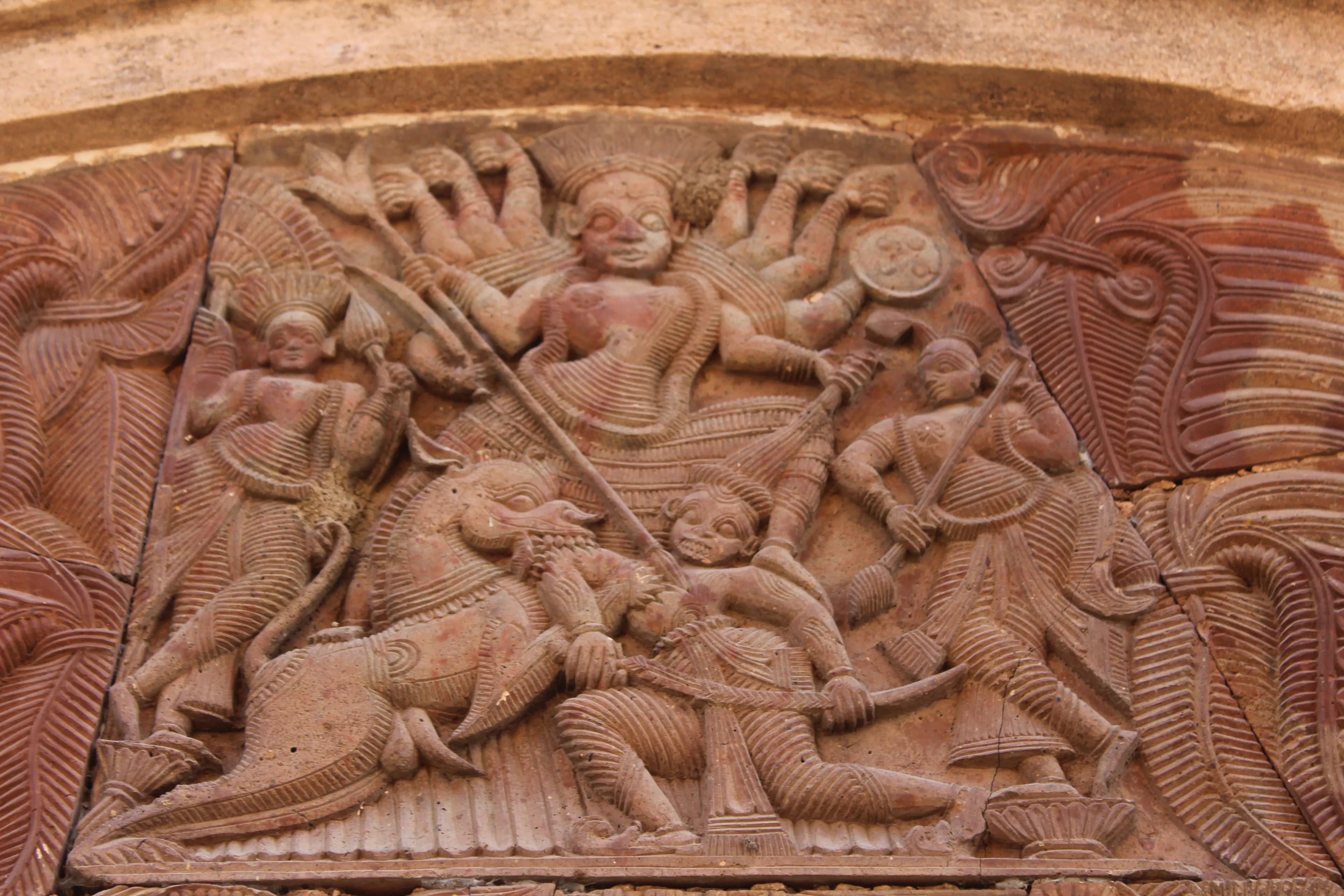

The terracotta temples of Maluti rise from the Jharkhand plains like an army of baked-earth sentinels, their intricate surfaces a stark contrast to the verdant rice paddies surrounding them. Having explored the sandstone grandeur of Rajasthan's forts and palaces for years, I was eager to witness this unique cluster of 72 temples, a testament to a different architectural tradition and a different era. The journey from Dumka, the district headquarters, was a bumpy but scenic one, the red dirt roads winding through villages and past fields dotted with grazing cattle. The first glimpse of the Maluti temples is breathtaking. They stand in varying states of preservation, some soaring towards the sky, others reduced to crumbling mounds, yet all whispering stories of a bygone era. The majority of the temples are dedicated to Lord Shiva, evidenced by the prominent lingams housed within the sanctums. The characteristic rekha deul style, common in Odisha and parts of Bengal, is evident here, the curvilinear towers rising in tiered stages, culminating in a rounded amalaka at the top. However, what sets Maluti apart is the extensive use of terracotta. Unlike the stone carvings of Rajasthan, the intricate details here are molded in clay, fired to a rich, earthy hue. The panels depict scenes from the epics – the Ramayana and the Mahabharata – as well as scenes from daily life, offering a fascinating glimpse into the social and cultural fabric of the 16th-18th centuries, the period to which these temples are attributed. I spent hours tracing the narratives etched onto the terracotta panels, marveling at the expressiveness of the figures, the dynamism of the battle scenes, and the delicate ornamentation of the floral motifs. The craftsmanship is simply astonishing. The artisans who created these masterpieces worked with incredible precision, molding intricate details onto relatively small terracotta plaques. The panels are fitted together seamlessly, creating a continuous narrative that wraps around the temple walls. The effect is mesmerizing, like a giant, terracotta tapestry narrating ancient tales. The condition of the temples, however, is a cause for concern. While some have been restored by the Archaeological Survey of India, many are in a state of disrepair. Erosion, neglect, and the ravages of time have taken their toll. Several temples have collapsed entirely, leaving behind only heaps of terracotta rubble. It's a poignant reminder of the fragility of our heritage and the urgent need for conservation efforts. As I walked through the complex, I couldn't help but draw parallels between the architectural traditions of Rajasthan and Jharkhand. While the materials and styles differ drastically, the underlying devotion and artistic skill are strikingly similar. The intricate jali work of Rajasthan's palaces finds an echo in the delicate latticework of the terracotta panels here. The imposing gateways of Rajasthan's forts are mirrored in the towering gateways of some of the larger temples at Maluti. The experience of visiting Maluti was both awe-inspiring and melancholic. Awe at the sheer scale and artistry of the terracotta temples, and melancholy at the state of neglect that some of them have fallen into. It's a site that deserves greater attention, both from tourists and from conservationists. It's a testament to the rich cultural heritage of India, a heritage that we must strive to protect and preserve for generations to come. My journey through the terracotta temples of Maluti was not just a visit to a historical site; it was a journey through time, a glimpse into the artistic brilliance of a bygone era.

The midday sun beat down on Deoghar, casting long shadows across the paved courtyard as I approached the Naulakha Temple. Its gleaming white marble exterior, a stark contrast to the dusty landscape, radiated an almost ethereal glow. Nine lakhs, or nine hundred thousand rupees, is said to have been spent on its construction in 1949, hence the name. Having explored countless temples across North India, I was prepared for another ornate structure, but the Naulakha Temple surprised me with its unique blend of traditional and modern elements. The temple is dedicated to Lord Shiva, and the towering shikhara, the curvilinear tower rising above the sanctum sanctorum, immediately draws the eye. Unlike the intricate carvings that adorn most North Indian temples, the shikhara here is relatively plain, its smooth marble surface reflecting the sunlight. This simplicity, however, is not a sign of austerity, but rather a deliberate aesthetic choice that emphasizes the temple's grandeur. It’s a powerful statement of faith, a monument built not with elaborate ornamentation, but with sheer scale and the purity of white marble. As I circumambulated the temple, I noticed the subtle carvings around the base. Floral motifs and depictions of deities, though less prominent than in other temples I’ve visited, were executed with precision and grace. The interplay of light and shadow on the marble surface brought these carvings to life, creating a dynamic visual experience. It's a testament to the skill of the artisans who managed to imbue even the smallest details with a sense of devotion. Stepping inside the cool, dimly lit sanctum was a welcome respite from the scorching heat. The air was thick with the scent of incense and the murmur of prayers. The main deity, a Shiva lingam, resided in the centre, bathed in the soft glow of oil lamps. The atmosphere was charged with a palpable sense of reverence, a feeling amplified by the hushed whispers of devotees. I observed families offering prayers, their faces etched with devotion, a scene that plays out in temples across India, yet each time feels unique and deeply personal. What struck me most about the Naulakha Temple was its accessibility. Unlike many ancient temples where photography is restricted, here, I was free to document my experience. I captured the intricate details of the carvings, the serene faces of the devotees, and the imposing structure of the temple against the backdrop of the Jharkhand sky. This openness, I felt, reflected a modern approach to faith, a willingness to embrace and share the spiritual experience. Beyond the main temple, the complex houses several smaller shrines dedicated to other deities. I spent some time exploring these, observing the variations in architectural styles and the unique offerings made at each shrine. The presence of these smaller temples within the larger complex creates a sense of community, a microcosm of the Hindu pantheon. Leaving the Naulakha Temple, I carried with me not just photographs and memories, but a deeper understanding of the evolving landscape of faith in India. The temple, with its blend of traditional elements and modern sensibilities, represents a bridge between the past and the present. It's a place where ancient rituals are performed within a contemporary setting, a testament to the enduring power of belief in a rapidly changing world. The Naulakha Temple is not just a place of worship; it's a living testament to the enduring spirit of devotion and a fascinating study in the architectural evolution of religious spaces. It is a must-see for anyone travelling through Jharkhand, offering a glimpse into the heart of Hindu faith and the rich cultural tapestry of India.
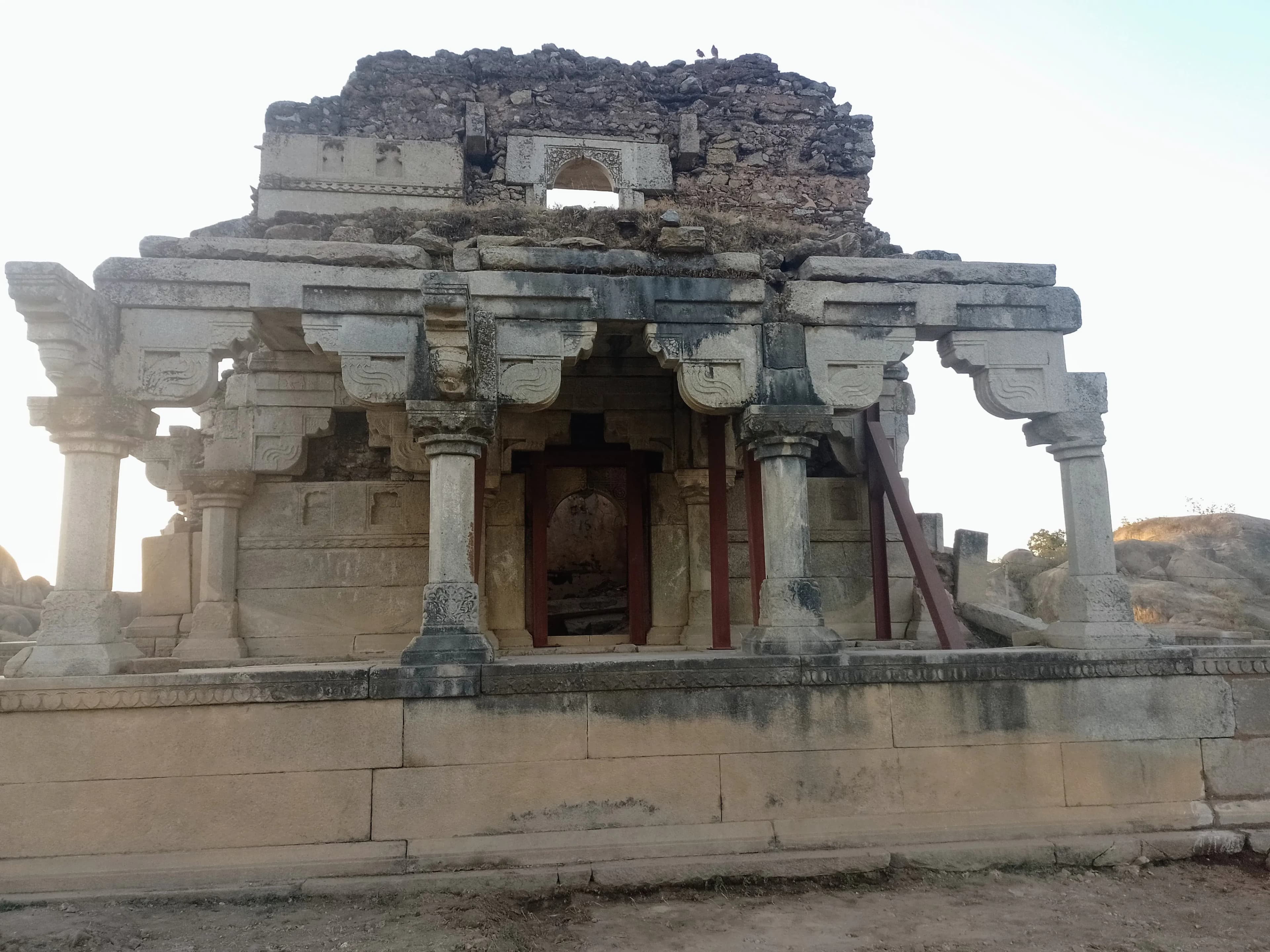

The midday sun beat down on the undulating Jharkhand landscape as I finally crested the hill, Navratangarh Fort rising before me like a forgotten sentinel. Having explored countless Mughal and Rajput forts across North India, I was intrigued to see what this tribal stronghold, nestled deep in Gumla district, had to offer. It certainly wasn't the imposing grandeur of a Mehrangarh or the intricate elegance of a Fatehpur Sikri, but Navratangarh possessed a raw, almost primal energy that immediately captivated me. The fort’s name, meaning “nine courtyards,” hints at a structured layout, but the reality is far more organic. While traces of nine distinct enclosures are discernible, nature has reclaimed much of the space, blurring the lines between architecture and wilderness. Massive, uncut laterite stones form the ramparts, their uneven surfaces softened by moss and clinging vines. Unlike the precisely dressed stones of northern forts, these felt ancient, whispering tales of a time long before mortar and meticulous planning. I stepped through a narrow, crumbling gateway, the rough stone scraping against my backpack. The first courtyard, the largest, was a surprisingly level expanse, now overgrown with scrub and wildflowers. Fragments of pottery littered the ground, a tangible reminder of the lives once lived within these walls. Local legend claims the fort was built by the Nagvanshi kings, who ruled this region for centuries. While historical evidence is scarce, the fort's construction style and strategic location certainly suggest a powerful, well-organized society. As I explored further, I discovered remnants of what might have been living quarters, storage areas, and even a small temple. The architecture was simple, functional, and deeply connected to the landscape. Narrow passages, carved directly into the laterite bedrock, connected the different sections of the fort. I paused at one such passage, the cool, damp air a welcome respite from the midday heat. Looking up, I could see the sky framed by the rough-hewn stone, a perfect example of how the builders incorporated the natural environment into their design. One of the most striking features of Navratangarh is its water management system. Several large, rock-cut cisterns are strategically placed throughout the fort, designed to collect rainwater. Even in the dry season, some of these cisterns still held water, a testament to the ingenuity of the Nagvanshi engineers. I imagined the fort bustling with activity, the cisterns brimming with life-sustaining water, a vital resource in this often-arid region. Climbing to the highest point of the fort, I was rewarded with panoramic views of the surrounding countryside. Rolling hills, dotted with villages and patches of forest, stretched as far as the eye could see. From this vantage point, it was easy to understand the strategic importance of Navratangarh. It commanded the surrounding area, offering a clear view of approaching enemies. My visit to Navratangarh wasn't about ticking off another fort on my list. It was an immersive experience, a journey into the heart of a forgotten kingdom. While the fort may lack the polished beauty of its northern counterparts, it possesses a unique charm, a raw authenticity that resonates deeply. It's a place where history whispers from the stones, where nature has reclaimed its domain, and where the spirit of a bygone era still lingers in the air. It's a reminder that India's heritage is not just confined to grand palaces and majestic tombs, but also exists in these hidden gems, waiting to be discovered by those willing to venture off the beaten path. And as I descended the hill, leaving the silent sentinel behind, I knew that Navratangarh, with its rugged beauty and whispered stories, would stay with me long after I left Jharkhand.
The climb to Pahari Mandir, perched atop Ranchi Hill, is a pilgrimage in itself. The sun beat down on my back as I ascended the seemingly endless flight of stairs, each step bringing me closer to the whispers of history that clung to the ancient stones. The city sprawled beneath me, a tapestry of terracotta roofs and verdant green, shrinking with every upward stride. This vantage point, I realized, was as much a part of the temple's allure as the structure itself. It felt as though the builders had intentionally chosen this lofty perch, not just for its breathtaking views, but to symbolize a closer communion with the divine. Reaching the summit, I was greeted by a palpable shift in atmosphere. The cacophony of the city faded, replaced by the gentle tinkling of bells and the murmur of devotees. Pahari Mandir, dedicated to Lord Shiva, isn't a sprawling complex like many other ancient temples. Its beauty lies in its compact elegance, a stark white structure against the azure sky. The architecture, while simple, is striking. The temple's shikhara, the towering structure above the sanctum sanctorum, is distinctly different from the curvilinear Nagara style prevalent in my home state of Madhya Pradesh. Here, the shikhara rises in a pyramidal form, reminiscent of the local architectural vernacular, yet possessing a unique grace. The whitewashed walls, though showing the patina of time, are adorned with intricate carvings. I spent a considerable amount of time documenting these, my lens focusing on the delicate floral motifs and depictions of deities, each panel narrating a silent story. The craftsmanship, though weathered by centuries of sun and rain, still speaks volumes about the devotion and skill of the artisans who breathed life into these stones. Interestingly, while the temple is predominantly built of stone, I noticed the use of bricks in certain sections, particularly in the lower portions of the structure. This blend of materials, perhaps dictated by the locally available resources, adds another layer of intrigue to the temple's architectural narrative. The inner sanctum, dimly lit by oil lamps, exuded an aura of serenity. The air was thick with the scent of incense and the murmur of prayers. Photography within the sanctum is restricted, so I committed the scene to memory, the flickering lamps casting dancing shadows on the ancient walls, the devout offering their prayers with quiet reverence. It was a moment of profound stillness, a stark contrast to the bustling city below. Stepping out, I circumnavigated the temple, observing the interplay of light and shadow on the textured walls. The late afternoon sun cast long shadows, accentuating the carvings and adding a dramatic dimension to my photographs. From this vantage point, I could see the sprawling city of Ranchi in all its vibrant chaos, a stark juxtaposition to the serene sanctity of the temple. It was a visual reminder of the temple's role as a spiritual anchor, a place of refuge from the trials and tribulations of daily life. My experience at Pahari Mandir was more than just a photographic documentation of an ancient site. It was a journey through time, a communion with history and faith. The temple, in its quiet dignity, stands as a testament to the enduring power of belief and the artistic brilliance of a bygone era. It's a place where the whispers of the past resonate with the present, offering a glimpse into the rich tapestry of India's cultural heritage. As I descended the steps, leaving the serenity of the hilltop behind, I carried with me not just photographs, but a profound sense of connection to this sacred space.
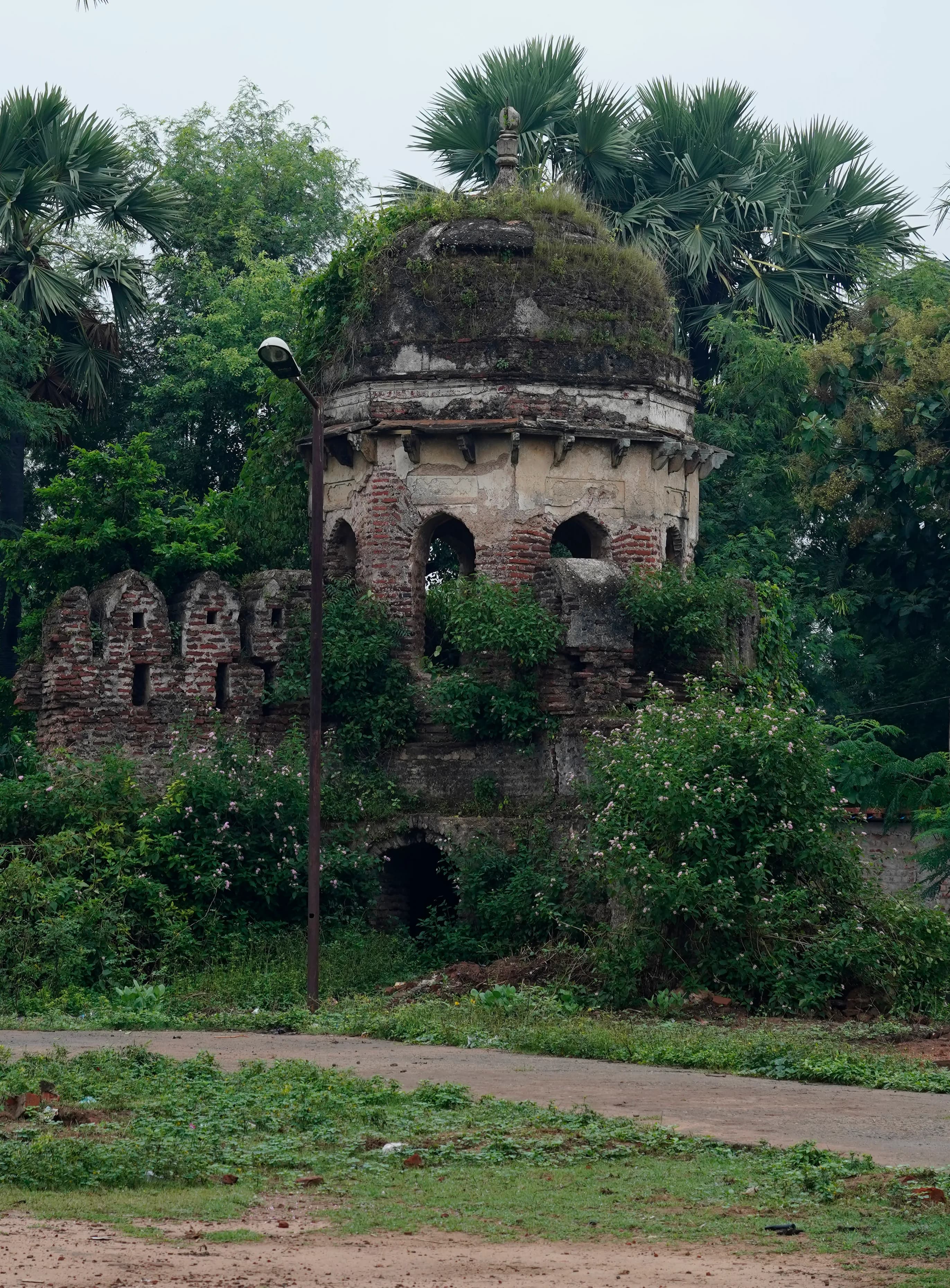

The imposing silhouette of Palamu Fort, rising from a forested plateau in Jharkhand’s Latehar district, held me captive long before I reached its weathered gates. The Chero dynasty, who ruled this region for centuries, left an indelible mark on this landscape, and the fort stands as a silent testament to their power and architectural prowess. My journey from Gujarat, a land rich in its own architectural heritage, had brought me here, eager to witness this relatively unexplored gem. The approach to the fort was a winding climb through dense Sal forests, a stark contrast to the arid landscapes I was accustomed to. The air, thick with the scent of damp earth and vegetation, buzzed with unseen life. This natural fortification, I realized, must have been a significant advantage for the Chero rulers. As I neared the fort, the three enormous gateways, the Ran Darwaza, the Nagpuri Darwaza, and the Pachwati Darwaza, came into view, each a formidable barrier in its own right. The weathered stone, a mix of granite and laterite, spoke of centuries of sun, wind, and rain. The Ran Darwaza, the main entrance, was particularly impressive, its massive archway flanked by two sturdy bastions. Stepping through the Ran Darwaza felt like stepping back in time. The sprawling complex within revealed a blend of architectural styles, reflecting the fort’s long and complex history. The influence of the Chero, Mughal, and even British periods was evident in the structures that remained. The Raja’s Palace, though now in ruins, still exuded a sense of grandeur. I could almost picture the opulent life that once thrived within its walls. The intricately carved stone brackets and pillars, though weathered and worn, hinted at the craftsmanship of a bygone era. I was particularly struck by the remnants of the vibrant murals that once adorned the palace walls, their faded colours still whispering stories of courtly life. The fort’s strategic location offered breathtaking panoramic views of the surrounding landscape. From the ramparts, I could see the undulating hills stretching as far as the eye could see, a tapestry of green punctuated by the occasional village. It was easy to understand why this location was chosen for the fort. The Chero rulers had a clear view of approaching enemies, giving them a significant tactical advantage. Within the fort complex, several temples dedicated to various deities stand as testaments to the religious beliefs of the rulers and the people. The most prominent among them is the Shiva temple, its shikhara rising above the other structures. The temple’s architecture, though simpler than the palace, possessed a quiet dignity. The worn stone steps leading to the sanctum sanctorum spoke of countless pilgrims who had sought solace within its walls. Exploring the fort’s extensive network of underground tunnels was a particularly intriguing experience. These tunnels, believed to have been used as escape routes during times of siege, were dark and damp, their air thick with the smell of earth. Walking through these narrow passageways, I felt a palpable sense of history, imagining the hurried footsteps of those who had once sought refuge within them. My visit to Palamu Fort was more than just a sightseeing trip; it was a journey through time. The fort’s weathered stones whispered stories of ambition, power, and resilience. It was a stark reminder of the impermanence of empires and the enduring power of human ingenuity. As I descended from the fort, the setting sun casting long shadows across the landscape, I carried with me not just photographs and memories, but a deeper understanding of the rich tapestry of Indian history and architecture. Palamu Fort, though often overlooked, deserves its place among the architectural marvels of India. It is a place that stays with you, its silent stories echoing long after you’ve left its imposing gates behind.

The crisp January air, thin at this altitude, whipped prayer flags into a frenzy around me as I ascended the stone steps leading to the Parasnath Jain Temple, perched atop the sacred Shikharji hill in Jharkhand. This wasn't just a temple; it was a pilgrimage, a living testament to centuries of Jain devotion. Shikharji, the highest peak of the Parasnath Hills, isn't merely a geographical landmark; it's the very heart of Jain spirituality, revered as the place where twenty of the twenty-four Jain Tirthankaras attained moksha, or liberation. The climb itself is an act of devotion. The paved pathway, though well-maintained, stretches for nearly 27 kilometers, winding through dense forests and offering breathtaking panoramic views of the surrounding landscape. I saw families, elderly pilgrims, and even young children undertaking the arduous journey, their faces etched with a quiet determination that spoke volumes about the spiritual significance of this place. The air hummed with chants and the rhythmic clinking of bells, creating an atmosphere of profound reverence. The temple complex itself is a tapestry of architectural styles reflecting different eras of construction and renovation. While simplicity and functionality are the overarching themes, intricate carvings and delicate ornamentation can be found adorning certain structures. The main temples, dedicated to the various Tirthankaras, are predominantly constructed from marble and sandstone, their pristine white surfaces gleaming against the backdrop of the blue sky. I noticed the distinct absence of elaborate idols within the sanctums. Instead, the focus is on the footprints or 'charan paduka' of the Tirthankaras, etched into stone slabs, symbolizing their final earthly presence before attaining liberation. One particular architectural element that captivated me was the use of toranas, or ornate gateways. These intricately carved structures, often depicting scenes from Jain mythology, serve as symbolic thresholds between the mundane and the sacred. The play of light and shadow on the deep carvings created a mesmerizing effect, adding another layer of depth to the spiritual experience. As I walked through the complex, I observed the palpable sense of peace that permeated the atmosphere. Pilgrims engaged in silent meditation, circumambulating the temples, or offering simple prayers. The absence of loudspeakers, so common in many Indian religious sites, amplified the tranquility. It was a refreshing change, allowing for genuine introspection and connection with the spiritual energy of the place. The 'Jal Mandir,' or water temple, nestled amidst lush greenery, was another highlight. The serene reflection of the temple in the surrounding pond created a picture of perfect harmony. I watched as devotees performed ritual ablutions, their movements slow and deliberate, reflecting the emphasis on purity and self-discipline within Jainism. Beyond the architectural marvels and the palpable spirituality, it was the human element that truly resonated with me. I witnessed acts of selfless service, with volunteers providing food and water to pilgrims, and local communities actively participating in the upkeep of the sacred site. This sense of collective responsibility and shared devotion underscored the enduring power of faith. Descending from Shikharji, I carried with me more than just memories and photographs. I carried a deeper understanding of Jain philosophy, a renewed appreciation for the power of simplicity, and a profound respect for the unwavering faith of the pilgrims who journey to this sacred mountain in search of liberation. The experience transcended mere tourism; it was a pilgrimage of the soul.

The terracotta hues of the Sun Temple at Bundu, Jharkhand, shimmered under the late afternoon sun, a fitting tribute to the celestial body it honors. Unlike the towering Konark Sun Temple in Odisha, this structure, still under construction, possesses a unique, almost unfinished charm. Its raw, earthy aesthetic, crafted from locally sourced laterite bricks, sets it apart from the polished grandeur of other ancient temples I've encountered across India. This was my 38th UNESCO World Heritage site in India, and it offered a refreshing perspective on temple architecture. The temple's main structure, a colossal chariot seemingly frozen mid-stride, is a marvel of engineering. Seventeen life-sized horses, also sculpted from laterite, appear to pull the chariot, their muscular forms radiating dynamic energy. The wheels, intricately carved with symbolic motifs, are particularly striking. I spent a good amount of time circling the chariot, examining the detailed carvings. While some sections displayed the smooth finish of completed work, others revealed the rough texture of the brick, showcasing the ongoing construction. This juxtaposition of finished and unfinished elements gave the temple a palpable sense of living history. Climbing the steps to the main platform, I was greeted by a panoramic view of the surrounding landscape. The sprawling countryside, dotted with small villages and lush greenery, provided a serene backdrop to the temple's imposing presence. The absence of towering walls or enclosures, typical of many ancient temples, further enhanced this connection with the natural world. It felt as though the temple was not just a place of worship, but an integral part of the landscape itself. Inside the chariot's main chamber, the deity of the Sun God awaits installation. The emptiness of the sanctum, however, did not detract from the spiritual aura of the space. The play of light filtering through the arched openings created an ethereal ambiance, inviting contemplation and quiet reflection. I noticed several artisans working diligently on intricate carvings within the chamber, their meticulous craftsmanship a testament to the dedication involved in bringing this grand vision to life. One of the most captivating aspects of the Bundu Sun Temple is its unique blend of traditional and contemporary architectural styles. While the chariot motif and the use of laterite hark back to ancient temple-building traditions, the sheer scale of the structure and the ongoing construction process give it a distinctly modern feel. It’s a fascinating example of how heritage can be reinterpreted and revitalized for future generations. My conversations with the local artisans and residents provided further insight into the temple's significance. They spoke of the temple not just as a religious site, but as a symbol of community pride and a source of livelihood. The ongoing construction has created employment opportunities for many local artisans, ensuring the preservation of traditional craftsmanship and contributing to the economic development of the region. As I left the Sun Temple, the setting sun cast long shadows across the terracotta structure, painting it in a warm, golden glow. The experience was unlike any other temple visit I’ve had. It wasn’t just about admiring a finished masterpiece; it was about witnessing the creation of one. The Bundu Sun Temple is a testament to the enduring power of human creativity and the evolving nature of heritage. It stands as a powerful reminder that history is not just something we inherit from the past, but something we actively shape in the present.
Related Collections
Discover more heritage sites with these related collections
Explore More Heritage
Explore our comprehensive archive of 13 heritage sites with detailed documentation, 3D models, floor plans, and historical research. Each site page includes visitor information, conservation status, architectural analysis, and downloadable resources for students, researchers, and heritage enthusiasts.
Historical Context
The historical significance of these 13 heritage sites reflects the profound integration of dharma, artha, and kama in Hindu civilization. Across successive eras, royal patrons and spiritual leaders commissioned these sacred edifices as acts of devotion, fulfilling dharmic obligations while creating eternal spaces for worship and community gathering. Various dynasties contributed unique architectural visions, establishing traditions that honored Vedic principles while incorporating regional characteristics. Master builders (sthapatis) applied knowledge from ancient shilpa shastras (architectural treatises) and vastu shastra (spatial science), creating structures embodying cosmic principles and sacred geometry. Epigraphic inscriptions and archaeological evidence reveal sophisticated networks of guilds, royal support, and community participation sustaining these massive undertakings across decades or centuries. These monuments served as centers of Vedic learning, Sanskrit scholarship, classical arts, and spiritual practice—roles many continue fulfilling today, maintaining unbroken traditions that connect contemporary Bharat to its glorious civilizational heritage.
Architectural Significance
The architectural magnificence of these 13 heritage sites demonstrates the sophisticated application of shilpa shastra principles to create spaces embodying cosmic order and divine presence. The nagara architecture style tradition manifests through characteristic elements: distinctive regional architectural elements, spatial planning principles, and decorative vocabularies. Employing indigenous materials—locally sourced stone, traditional lime mortars, and time-honored construction techniques—sthapatis created structures demonstrating advanced engineering knowledge. The corbelling techniques display extraordinary precision, achieving structural stability through geometric principles. Dome construction methodologies demonstrate sophisticated understanding of load distribution and compression forces, centuries before modern engineering formalized such knowledge. Beyond structural excellence, these monuments serve as three-dimensional textbooks of Puranic narratives, Vedic cosmology, and iconographic traditions. Sculptural programs transform stone into divine forms, teaching dharma through narrative reliefs and creating sacred atmospheres conducive to devotion and contemplation. Recent photogrammetric documentation and 3D laser scanning reveal original polychromy, construction sequences, and historical conservation interventions, enriching our understanding of traditional building practices and material technologies that sustained these magnificent creations.
Conservation & Preservation
Preserving these 13 sacred heritage sites represents our collective responsibility to safeguard India's architectural and spiritual heritage for future generations. 1 benefits from Archaeological Survey of India protection, ensuring systematic conservation approaches. Conservation challenges include environmental degradation, biological colonization, structural deterioration, and pressures from increased visitation. Professional conservators address these through scientifically-grounded interventions: structural stabilization using compatible traditional materials, surface cleaning employing non-invasive techniques, vegetation management, and drainage improvements. Advanced documentation technologies—laser scanning, photogrammetry, ground-penetrating radar—create detailed baseline records enabling precise condition monitoring and informed conservation planning. When restoration becomes necessary, traditional building techniques and materials sourced from historical quarries ensure authenticity and compatibility. This comprehensive approach honors the devotion and craftsmanship of original builders while applying contemporary conservation science to ensure these monuments endure, continuing their roles as centers of worship, cultural identity, and civilizational pride.
Visitor Information
Experiencing these 13 sacred heritage sites offers profound connection to India's spiritual and architectural heritage. jharkhand maintains excellent connectivity, with accommodation options ranging from budget to premium near major heritage sites. The optimal visiting period extends October through March when comfortable conditions facilitate exploration. Entry fees typically range from ₹25-₹40 at protected monuments. Photography for personal use is generally permitted, though professional equipment may require advance permissions. Visiting these sacred spaces requires cultural sensitivity: modest attire covering shoulders and knees, shoe removal in temple sanctums, quiet respectful demeanor, and recognition that these remain active worship centers where devotees practice centuries-old traditions. Meaningful engagement comes through understanding basic Hindu iconography, mythological narratives, and ritual contexts that bring these monuments to life.
Key Facts & Statistics
Total documented heritage sites: 13
Archaeological Survey of India protected monuments: 1
Source: Archaeological Survey of India
Temple: 11 sites
Monument: 1 sites
Fort: 1 sites
Indo-Saracenic Revival architecture style, Mughal architecture style, Nagara architecture style, Rajput architecture style architectural style: 1 sites
Kalinga architecture style, Nagara architecture style, Eastern Indian Temple architecture style, Hindu Temple architecture style architectural style: 1 sites
Nagara architecture style, Kalinga architecture style, Rajput architecture style, Deccani architecture style architectural style: 1 sites
Kalinga Nagara architecture style, Nagara architecture style, Rekha Deul architecture style, Indo-Mughal architecture style architectural style: 1 sites
Kalinga Nagara architecture style, Nagara architecture style, Late Medieval Hindu architecture style, Vernacular Jharkhand architecture style architectural style: 1 sites
British Colonial Period period construction: 3 sites
Late Medieval Period period construction: 2 sites
Rajput Period period construction: 2 sites
Chandela Period period construction: 1 sites
Modern Period period construction: 1 sites
Average documentation completion score: 78%
Featured flagship heritage sites: 13
Comprehensive digital archiving preserves heritage for future generations
Comprehensive digital archiving preserves heritage for future generations
Comprehensive digital archiving preserves heritage for future generations
Frequently Asked Questions
How many heritage sites are documented in jharkhand?
This collection includes 13 documented heritage sites in jharkhand. 1 sites are centrally protected by Archaeological Survey of India. Each site has comprehensive documentation including photos, floor plans, and historical research.
What is the best time to visit heritage sites in jharkhand?
October through March is ideal for visiting heritage sites in jharkhand. Major festivals also offer unique cultural experiences. Check individual site pages for specific visiting hours and seasonal closures.
What are the entry fees for heritage sites?
Protected monuments typically charge ₹25-₹40. State-protected sites often have lower or no entry fees. Many temples and religious sites are free. Children often enter free. Still photography is usually included; video may require additional permits.
Are photography and videography allowed at heritage sites?
Still photography for personal use is generally permitted at most heritage sites. Tripods, flash photography, and commercial filming usually require special permissions. Some sites restrict photography of murals, sculptures, or sanctums. Drones are prohibited without explicit authorization. Always respect signage and guidelines at individual monuments.
How do I reach heritage sites in jharkhand?
jharkhand is well-connected via auto-rickshaw, Indian Railways, state buses. Major cities have airports with domestic and international flights. Public transport connects smaller towns. Most heritage sites are accessible by local transport or rental vehicles. Plan 2-3 hours per major monument.
Are these heritage sites wheelchair accessible?
Accessibility varies significantly. Major UNESCO sites and recently renovated monuments often have ramps and accessible facilities. However, many historical structures have steps, uneven surfaces, and narrow passages. Contact site authorities in advance for specific accessibility information. Our site pages indicate known accessibility features where available.
Are guided tours available at heritage sites?
Licensed guides are available at most major heritage sites, typically charging ₹200-₹500 for 1-2 hour tours. ASI-approved guides provide historical and architectural insights. Audio guides are available at select UNESCO sites. Our platform offers virtual tours and detailed documentation for major monuments.
What is the conservation status of these heritage sites?
1 sites are legally protected by ASI. Active conservation includes structural stabilization, surface cleaning, vegetation control, and drainage management. Digital documentation helps monitor deterioration. Ongoing surveys track condition changes for evidence-based interventions.
What are the key features of nagara architecture style architecture?
Nagara architecture style architecture features distinctive regional architectural elements, spatial planning principles, and decorative vocabularies. These elements evolved over centuries, reflecting regional climate, available materials, construction techniques, and cultural preferences. Each monument demonstrates unique variations within the broader architectural tradition.
What documentation is available for these heritage sites?
Each site includes high-resolution photography, architectural measurements, historical research, and expert annotations. Documentation averages 78% completion.
How much time should I allocate for visiting?
Plan 2-3 hours for major monuments to appreciate architectural details and explore grounds. Smaller sites may require 30-60 minutes. Multi-site itineraries should allocate travel time. Early morning or late afternoon visits offer better lighting for photography and fewer crowds. Check individual site pages for recommended visiting durations.
What is the cultural significance of these heritage sites?
These monuments represent India's diverse cultural heritage, reflecting centuries of architectural innovation, religious traditions, and artistic excellence. They serve as living links to historical societies, preserving knowledge about construction techniques, social structures, and cultural values. Many sites remain active centers of worship and community gathering.
What other attractions are near these heritage sites?
jharkhand offers diverse tourism experiences beyond heritage monuments. Explore local museums, craft villages, nature reserves, and cultural festivals. Many heritage sites are clustered in historic towns with traditional markets and cuisine. Our site pages include nearby attraction recommendations and multi-day itinerary suggestions.
How can I practice responsible heritage tourism?
Respect site rules including photography restrictions and designated pathways. Don't touch sculptures, murals, or walls. Dispose waste properly. Hire local guides to support communities. Avoid visiting during restoration work. Learn about cultural contexts before visiting. Report damage to authorities. Your responsible behavior helps preserve heritage for future generations.
References & Sources
Jharkhand
Nagara Architecture Style
Nagara Architecture Style architecture is a distinctive style of Indian temple architecture characterized by its unique design elements and construction techniques. This architectural tradition flourished in jharkhand and represents a significant period in Indian cultural heritage. Features include intricate carvings, precise proportions, and integration with religious symbolism.
- 1Diverse architectural styles from various periods
- 2Intricate craftsmanship and artistic excellence
- 3Historical and cultural significance
- 4Well-documented heritage value
- 5Protected under heritage conservation acts
- 6Tourist and educational significance
| 📍Jharkhand | 13 sites |