Nagara Architecture Architecture in India
This collection documents 14 heritage sites throughout Bharat, representing profound expressions of Hindu civilization's architectural and spiritual heritage. These monuments exemplify the nagara architecture architectural tradition, with some maintaining unbroken traditions spanning millennia. Our comprehensive documentation, developed in collaboration with ASI archaeologists, conservation specialists, and scholarly institutions, preserves not merely physical structures but the sacred geometry, cosmological symbolism, and ritual spaces central to Dharmic worship. 2 hold UNESCO World Heritage recognition, acknowledging their universal significance to human civilization. Through royal patronage and community devotion, these structures embody the timeless principles of Bharatiya Sanskriti, connecting contemporary devotees to ancient traditions through stone, sculpture, and sacred spaces that continue to inspire reverence and wonder.
14 heritage sites with comprehensive documentation
Detailed architectural surveys and measurements
High-resolution photography and documentation
Average documentation completion: 80%
Total Sites:14
UNESCO Sites:2
ASI Protected:3
Top Category:Temple (14)
Top Period:British Colonial Period (3)
Avg. Documentation:80%
14
Total Sites
2
UNESCO Sites
3
ASI Protected
14
Featured
14 Sites Found

Featured
80% Documented
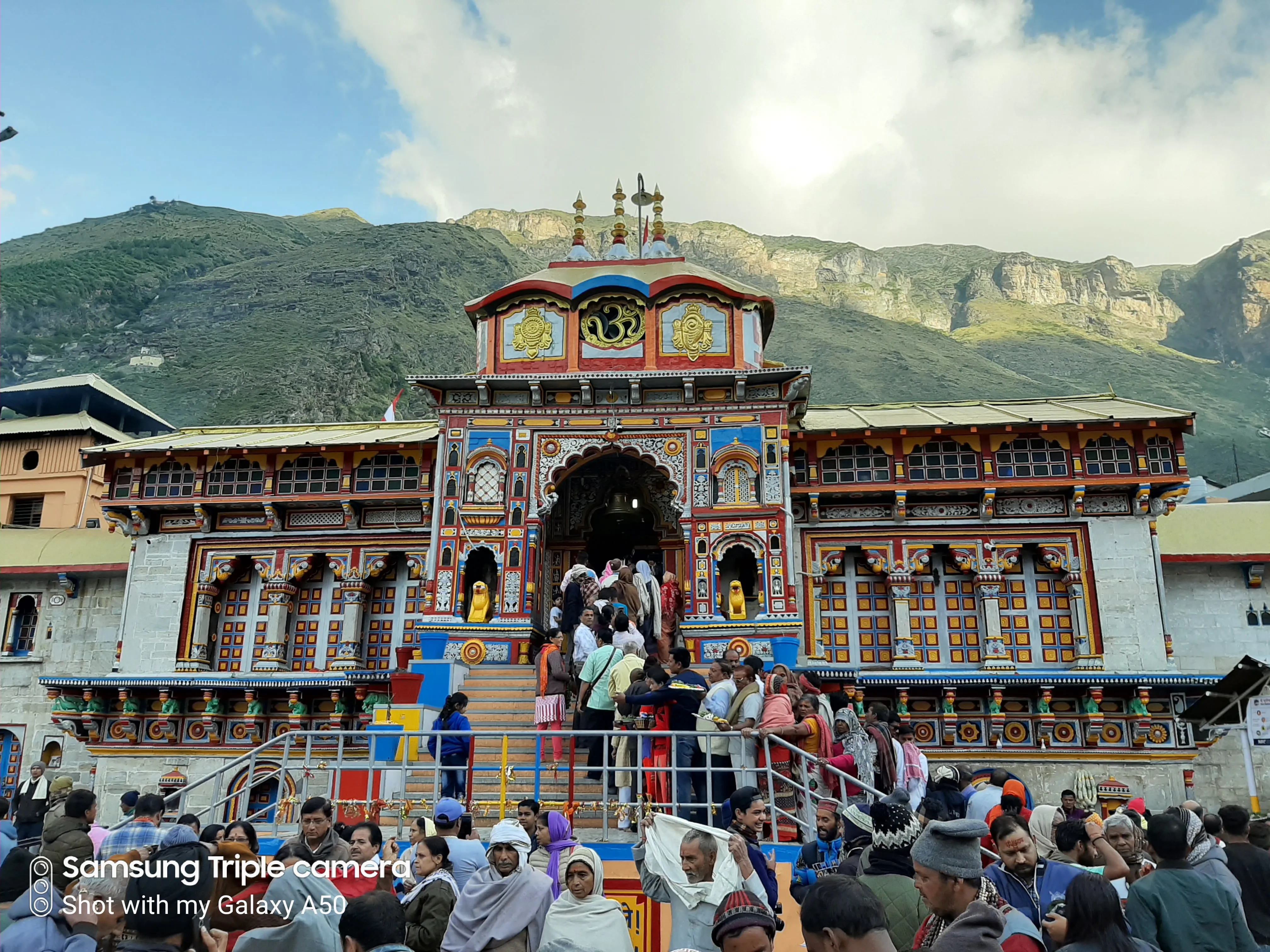
Badrinath Road, Chamoli, Badrinath (246422), Uttarakhand, India, Uttarakhand
The biting Himalayan air, thin and crisp, whipped prayer flags into a frenzy of colour against the backdrop of the snow-dusted Neelkanth peak. This is Badrinath, nestled within the formidable embrace of the Garhwal Himalayas, a place where the spiritual and the sublime converge. As I stood before the Badrinath Temple, the culmination of my journey to every UNESCO site in India, I felt a palpable shift, a sense of arrival not just at a destination, but at a nexus of faith and fortitude. The temple, dedicated to Lord Vishnu, isn't imposing in its scale like some of the South Indian behemoths I've documented. Instead, it exudes a quiet strength, a resilience honed by centuries of harsh weather and unwavering devotion. Its architecture, characteristic of the North Indian style, features a brightly coloured facade, dominated by an arched gateway crowned with a small cupola. The walls are relatively plain, save for intricate carvings around the windows and doorways, depicting scenes from Hindu mythology. What struck me most was the contrast: the vibrant, almost festive exterior against the stark, monochromatic landscape. It's as if the temple itself is a defiant burst of colour in a world of grey and white. Entering the sanctum sanctorum was an experience in sensory overload. The air, thick with the scent of incense and ghee, vibrated with the rhythmic chanting of priests. The dimly lit space, illuminated by flickering oil lamps, focused all attention on the black stone idol of Lord Vishnu, serenely seated in the padmasana pose. Unlike the elaborate rituals I've witnessed in other temples, the puja here felt intimate, personal. Perhaps it was the confined space, the close proximity to the deity, or the palpable devotion of the pilgrims, but I felt a connection, a sense of shared reverence that transcended the usual tourist experience. Beyond the main shrine, the temple complex houses several smaller shrines dedicated to various deities. I spent some time exploring these, each unique in its own right, each whispering tales of ancient legends and local beliefs. The Tapt Kund, a thermal spring located near the temple, is another highlight. Braving the near-freezing temperatures, I took a dip in the sulfur-rich waters, a ritual considered sacred by pilgrims. The experience, while invigorating, was a stark reminder of the harsh realities of life at this altitude. One of the most fascinating aspects of Badrinath is its connection to the surrounding landscape. The Alaknanda River, roaring past the temple, is considered sacred, and the surrounding peaks, each with its own mythological significance, form a natural amphitheater. I spent hours simply absorbing the scenery, trying to capture the essence of this place through my lens. The sheer scale of the mountains, the raw power of the river, and the quiet resilience of the temple created a visual symphony that resonated deep within me. My visit to Badrinath wasn't just about documenting another UNESCO site; it was a pilgrimage of sorts, a journey into the heart of the Himalayas, to a place where faith and nature intertwine. It was a humbling experience, a reminder of the enduring power of belief and the profound connection between humans and the natural world. As I descended from the heights of Badrinath, I carried with me not just photographs and memories, but a renewed appreciation for the rich tapestry of India's cultural and natural heritage. This is a place that stays with you, a place that calls you back, not just to witness its beauty, but to experience its soul.
Temple
North Indian Temple Style
Featured
Basukinath Road, Deoghar, Deoghar (814112), Jharkhand, India, Jharkhand
The air hummed with a low, constant thrum of devotion. A kaleidoscope of saffron, marigold, and crimson swirled around me as I stepped into the courtyard of Basukinath Dham, the revered Shiva temple nestled in the heart of Deoghar, Jharkhand. Having traversed the length and breadth of North India, exploring countless temples, I thought I was immune to the awe these sacred spaces inspire. Basukinath, however, proved me wrong. It wasn't just a temple; it was a living, breathing entity pulsating with the fervent energy of countless pilgrims. The main temple, dedicated to Lord Shiva in his Basukinath form, is a relatively modest structure compared to some of the grand edifices I've encountered. Its unassuming exterior, primarily white with splashes of vibrant colour from prayer flags and offerings, belies the spiritual weight it carries. The architecture is a blend of traditional Nagara style with regional influences. The shikhara, though not towering, possesses a distinct elegance, its curves softened by time and weather. Intricate carvings adorn the doorway, depicting scenes from Hindu mythology, their details worn smooth by the touch of millions of hands over centuries. The real spectacle, however, unfolds within the temple’s sanctum sanctorum. The queue, a vibrant tapestry of humanity, snaked its way through the courtyard, each face etched with anticipation and reverence. The air grew thick with the scent of incense and the rhythmic chanting of “Bol Bam,” the resonant mantra echoing the pilgrims’ arduous journey, many having walked miles carrying holy water from the Ganges. Witnessing this raw, unfiltered devotion was deeply moving. It wasn't just faith; it was a tangible, palpable force that permeated the very stones of the temple. Unlike the often-commercialized atmosphere of some North Indian temples, Basukinath retained a sense of authentic spirituality. The priests, though busy, performed their duties with a quiet dignity, their chants adding another layer to the symphony of devotion. The absence of aggressive vendors hawking trinkets and blessings was a welcome respite, allowing for a more immersive and introspective experience. Beyond the main temple, the complex houses several smaller shrines dedicated to various deities. I spent some time exploring these, observing the unique architectural nuances of each. One particular shrine, dedicated to Parvati, caught my attention. Its intricate terracotta carvings, depicting scenes of the goddess’s life, were remarkably well-preserved, showcasing the rich artistic heritage of the region. The atmosphere outside the temple was equally captivating. The narrow lanes leading to the main entrance were lined with stalls selling everything from religious paraphernalia to local delicacies. The aroma of freshly prepared prasad mingled with the earthy scent of incense, creating a sensory overload that was both overwhelming and exhilarating. I sampled some local sweets, their sweetness a perfect counterpoint to the spiritual intensity of the temple. As the sun began to set, casting long shadows across the courtyard, the temple took on an ethereal glow. The chanting intensified, the flickering lamps illuminating the faces of the devotees, creating a tableau of profound beauty. It was a moment of pure magic, a testament to the enduring power of faith. Leaving Basukinath Dham, I carried with me more than just memories and photographs. I carried a renewed appreciation for the spiritual heart of India, a heart that beats strongest in places like this, where faith transcends the mundane and connects humanity to something larger than itself. It's a place I would urge every traveller exploring North India to experience, not just as a tourist, but as a pilgrim, even if just for a fleeting moment.
Temple
Late Medieval Period

Featured
80% Documented
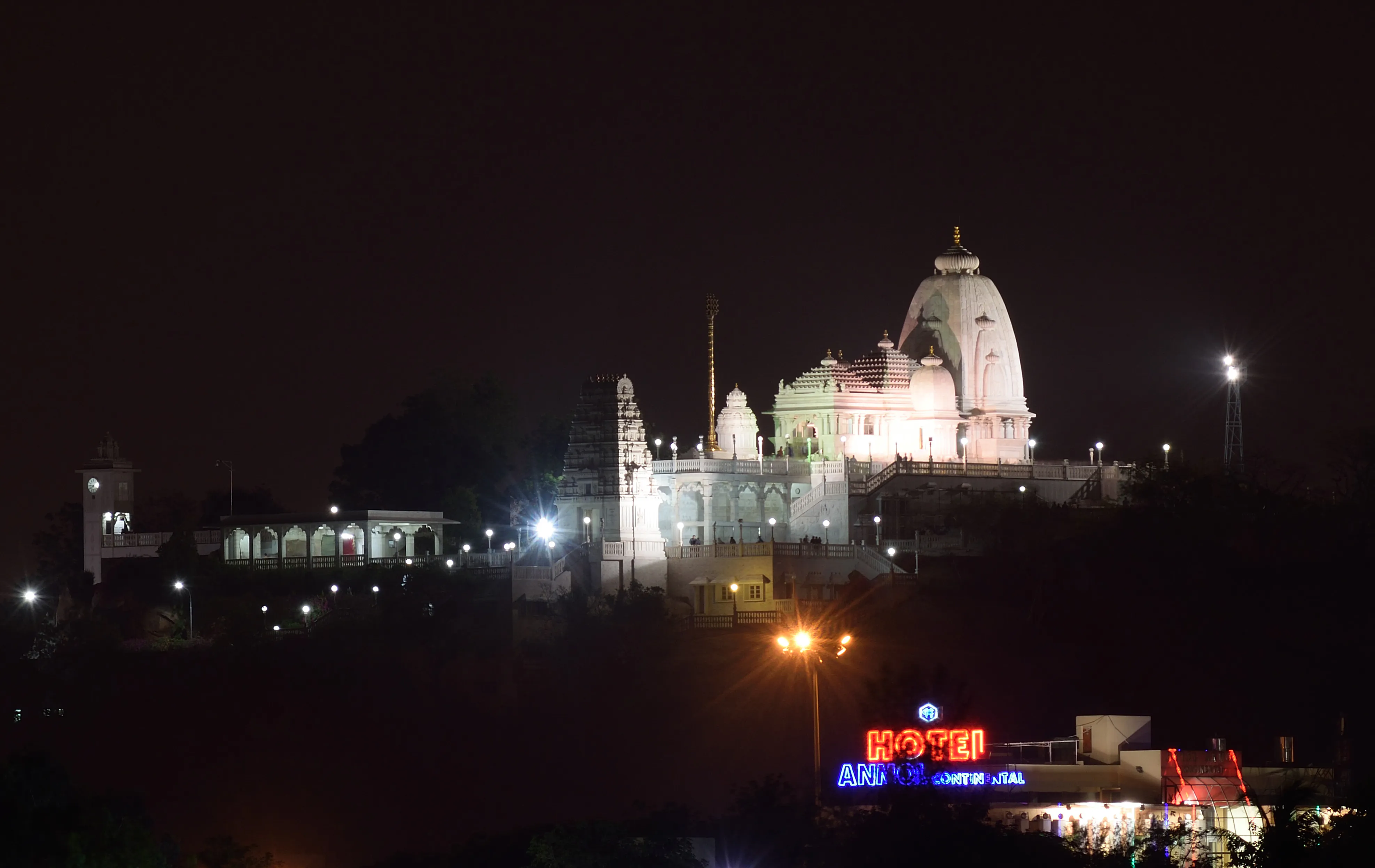
Hill Fort Rd, Khairatabad, Hyderabad (500004), Telangana, India, Telangana
The sun, a molten orb in the Hyderabad sky, cast a warm glow on the pristine white marble of the Birla Mandir. Having explored countless temples across North India, from the ancient stone carvings of Khajuraho to the spiritual serenity of the Golden Temple, I arrived at this southern edifice with a sense of anticipation, curious to see how it would compare. The climb up the Kala Pahad hill, on which the temple sits, offered panoramic views of the city sprawling below, a tapestry of old and new. The hustle and bustle faded as I ascended, replaced by a palpable sense of tranquility. The temple, dedicated to Lord Venkateswara, stands as a beacon of white against the azure sky. Its architecture, a blend of South Indian and Orissan styles, immediately struck me. Unlike the ornate and often overwhelming detail of many North Indian temples, the Birla Mandir exuded a sense of elegant simplicity. The towering shikharas, reminiscent of Odisha’s temple architecture, reached towards the heavens, their clean lines accentuated by the brilliant white marble. This marble, sourced from Rajasthan, is said to have been carved by skilled artisans, and the precision of their work is evident in every detail. Stepping inside the main sanctum, I was greeted by the imposing presence of the presiding deity, Lord Venkateswara. The atmosphere was hushed, reverent. The deity, a replica of the one at Tirupati, radiated a sense of profound peace. The absence of bells, a conscious decision by the temple’s founders, further enhanced the serene atmosphere, allowing for quiet contemplation. The soft chanting of hymns added another layer to the spiritual experience, creating a sense of timeless devotion. Exploring the temple complex, I noticed intricate carvings depicting scenes from the Mahabharata and Ramayana adorning the walls. These narratives, etched in stone, brought the epics to life, adding a layer of cultural richness to the architectural beauty. Unlike the vibrant colours that often dominate North Indian temple art, the carvings here relied on the play of light and shadow on the white marble to create a sense of depth and drama. I found myself drawn to the subtle nuances of the carvings, appreciating the skill and artistry involved in their creation. One aspect that particularly resonated with me was the temple's inclusive nature. Built by the Birla family, known for their philanthropic endeavors, the temple welcomes people of all faiths. This inclusivity, a hallmark of India's diverse spiritual landscape, felt particularly poignant in the current climate. Observing devotees from different backgrounds offering prayers and experiencing the shared sense of reverence reinforced the unifying power of faith. As the sun began to set, casting long shadows across the marble courtyard, I paused to take in the breathtaking view. The city lights twinkled below, a stark contrast to the serene atmosphere of the temple. The Birla Mandir, a testament to human devotion and architectural brilliance, stood as a silent sentinel, a beacon of peace amidst the urban sprawl. My journey through North India’s temples had prepared me for the grandeur and spirituality of this southern shrine, but the unique blend of architectural styles, the serene atmosphere, and the inclusive nature of the Birla Mandir offered a fresh perspective on India's rich tapestry of faith. Leaving the temple, I carried with me not just the memory of its stunning beauty, but also a renewed appreciation for the diverse expressions of spirituality that define India.
Temple
Modern Period

Featured
80% Documented
Ashutosh Chowdhury Avenue, Ballygunge, Kolkata (700019), West Bengal, India, West Bengal
The Kolkata skyline, a tapestry of colonial architecture and modern high-rises, is punctuated by a striking edifice of pristine white marble – the Birla Mandir. Having explored the basalt-carved caves and ancient temples of Maharashtra extensively, I was curious to experience this relatively modern temple dedicated to Lord Krishna and Radha. Stepping onto the grounds, I immediately felt a shift in atmosphere. The bustling city seemed to fade away, replaced by a sense of tranquility, amplified by the sheer expanse of the courtyard. The temple, built in the traditional Nagara style of North Indian temple architecture, is a magnificent sight. Unlike the cave temples of Ajanta and Ellora, where the rock itself forms the structure, here, every inch is meticulously crafted marble. The intricate carvings covering the temple walls are a testament to the artisans' skill. Depictions from the Bhagavad Gita and other Hindu scriptures unfold in detailed panels, narrating stories I’ve known since childhood, but seeing them rendered in this way felt fresh and inspiring. The shikharas, the towering curvilinear spires, reach towards the sky, their intricate detailing catching the light and creating a mesmerizing play of shadows. They reminded me of the shikharas of the Bhuleshwar Temple near Pune, albeit on a grander, more ornate scale. Entering the main sanctum, I was struck by the serene atmosphere. The idols of Radha and Krishna, adorned in vibrant silks and jewels, radiated a palpable sense of divinity. The air was thick with the scent of incense and the murmur of prayers, creating an immersive spiritual experience. Unlike the dimly lit interiors of many ancient temples in Maharashtra, the Birla Mandir was bathed in soft, natural light filtering through the large windows, illuminating the intricate carvings and adding to the sense of peace. I spent some time observing the devotees. Families, couples, and solitary individuals offered prayers with a quiet devotion. The diversity of the crowd was striking, a reflection of Kolkata's cosmopolitan nature. It was fascinating to witness the different ways people expressed their faith, from the elaborate rituals to the simple act of bowing their heads in reverence. This reminded me of the Kumbh Mela, where millions gather in faith, although here, the atmosphere was more intimate, more personal. The temple complex also houses a museum showcasing a collection of religious artifacts and scriptures. While smaller than the Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj Vastu Sangrahalaya in Mumbai, it offered a fascinating glimpse into Hindu mythology and iconography. I was particularly drawn to the miniature paintings depicting scenes from the Ramayana and Mahabharata, their vibrant colors and intricate details capturing the essence of these epic tales. As I walked through the manicured gardens surrounding the temple, I noticed a small pond with a fountain. The gentle sound of the water cascading over the rocks added to the sense of tranquility. It was a welcome respite from the city's noise and chaos. The gardens, unlike the rugged, natural landscapes surrounding the forts and caves of Maharashtra, were meticulously planned and maintained, offering a different kind of beauty. Leaving the Birla Mandir, I felt a sense of peace and rejuvenation. While the architectural style and the deities worshipped were different from what I was accustomed to in Maharashtra, the underlying spirit of devotion and reverence was the same. The experience reinforced the idea that faith, in its various forms, transcends geographical boundaries and cultural differences. The Birla Mandir, with its stunning architecture and serene atmosphere, stands as a testament to the enduring power of faith and a beautiful addition to India's rich tapestry of temples.
Temple
British Colonial Period

Featured
80% Documented
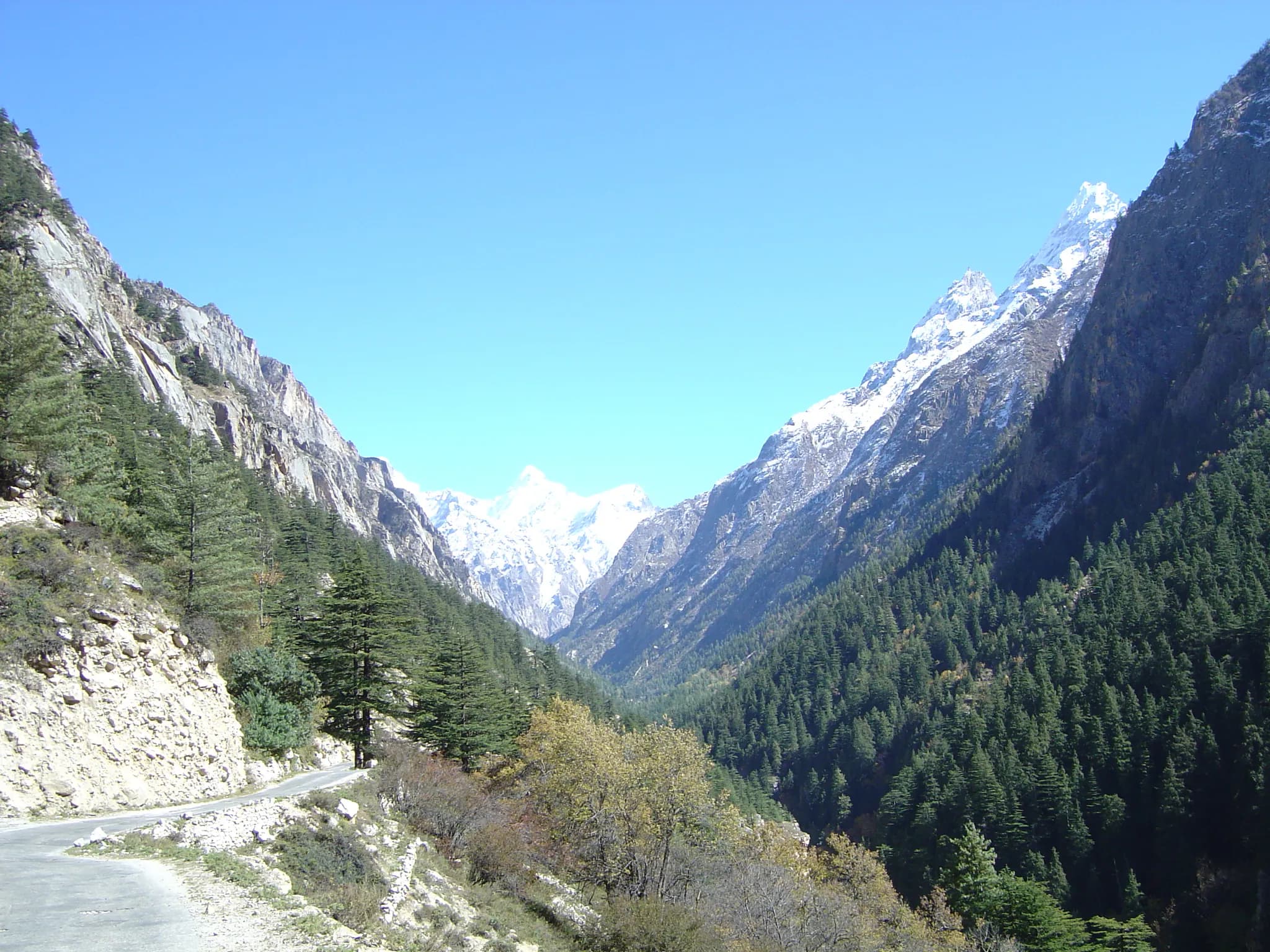
Golu Devta Temple Road, Almora, Chitai (263626), Uttarakhand, India, Uttarakhand
The crisp mountain air vibrated with the faint clang of countless bells. I stood before the Chitai Golu Devta Temple, nestled amidst the verdant hills of Almora, Uttarakhand, a place where faith takes a tangible, almost audible form. Unlike the ornate stone carvings and towering shikharas of many North Indian temples, Chitai Golu Devta presents a simpler, more rustic aesthetic. The main temple structure, while architecturally modest, is completely enveloped, almost suffocated, by a dense tapestry of bells. Thousands upon thousands of them, in every size imaginable, from tiny tinkling trinkets to hefty, resonant giants, hang from every available surface – the roof eaves, the doorways, the railings, even the branches of the surrounding trees. This visual symphony of bronze and brass, glinting in the Himalayan sunlight, is a testament to the unwavering faith of the devotees who offer these bells as symbols of their fulfilled wishes. The deity, Golu Devta, is a manifestation of Lord Shiva, revered as the dispenser of justice. This aspect is immediately apparent in the countless letters tied to the temple walls, each a whispered plea, a desperate hope, a heartfelt prayer for intervention. These letters, yellowed and weathered by time and elements, form a poignant narrative of human struggles, desires, and unwavering belief. They are not merely pieces of paper; they are tangible representations of the emotional weight carried by those who visit this sacred site. I spent a considerable amount of time photographing these letters, trying to capture not just their physical presence but also the silent stories they held within their folds. The temple complex itself is a multi-tiered structure, with the main shrine housing the deity at the center. The architecture is relatively simple, with sloping slate roofs and whitewashed walls, allowing the vibrant tapestry of bells to take center stage. The courtyard, paved with uneven stones worn smooth by countless footsteps, is always bustling with activity. Devotees offer prayers, tie their bells, and write their letters, their faces etched with a mixture of hope and reverence. The air is thick with the scent of incense and the murmur of prayers, creating an atmosphere that is both chaotic and deeply spiritual. What struck me most about Chitai Golu Devta was the palpable sense of connection between the devotees and the deity. This wasn't just a place of worship; it was a living, breathing testament to the power of faith. I observed a young girl carefully tying a small bell to a railing, her eyes closed in silent prayer. An elderly man, his face lined with years of experience, meticulously wrote a letter, his hand trembling slightly. A family, their faces beaming with joy, offered a large bell, its resonant clang echoing through the valley. Each act of devotion, however small, contributed to the unique energy of this place. As a heritage photographer, I'm often drawn to the grandeur and intricate details of ancient monuments. However, Chitai Golu Devta offered a different kind of beauty, a beauty born not of architectural prowess but of the sheer weight of human faith. The temple, in its relative simplicity, serves as a blank canvas for the vibrant tapestry of bells and letters, each a testament to the enduring power of belief. The experience was humbling, a reminder that sometimes, the most powerful stories are not etched in stone but whispered in the clang of a bell or written on a faded piece of paper. Leaving Chitai Golu Devta, I carried with me not just photographs but a profound sense of the human spirit's enduring capacity for hope and faith, resonating like the lingering chime of a thousand bells.
Temple
British Colonial Period

Featured
80% Documented
Gangotri, Uttarkashi, Gangotri (249135), Uttarakhand, India, Uttarakhand
The glacial chill of the Bhagirathi River, roaring just a few meters away, seemed to permeate the very stones of the Gangotri Temple. Standing before this pristine white structure, nestled amidst the towering Himalayas, I felt a palpable shift from the Dravidian temple architecture I'm so accustomed to in Chennai. Here, the simplicity and almost austere elegance of the Gangotri Temple spoke a different architectural language, a testament to the resilience of faith in this harsh, yet breathtaking landscape. Built in the 18th century by the Gorkha General Amar Singh Thapa, the temple lacks the elaborate ornamentation and towering gopurams that characterize South Indian temples. Its two-story structure, constructed primarily of granite, is relatively small in scale, yet its presence is magnified by the sheer grandeur of its surroundings. The sloping roof, clad in sheets of copper, is a distinct feature, a practical adaptation to the heavy snowfall this region experiences. This contrasts sharply with the granite and sandstone vimanas of the south, designed to withstand torrential monsoons. Entering the sanctum sanctorum, I was struck by the reverence that permeated the air. The deity, Goddess Ganga, is depicted in a silver palanquin, a stark departure from the intricately carved stone idols I'm familiar with. The simplicity of the iconography, however, seemed to amplify the spiritual energy within the temple. The lack of elaborate carvings within the sanctum allowed the focus to remain solely on the goddess, fostering a sense of direct connection with the divine. Stepping back outside, I began to appreciate the subtle nuances of the temple's design. The lack of extensive sculptural programs, common in Dravidian architecture, allows the natural beauty of the surrounding landscape to become an integral part of the temple experience. The snow-capped peaks, the roaring river, and the crisp mountain air all contribute to a sense of awe and reverence. This integration of the natural world with the built environment is a hallmark of Himalayan temple architecture, a stark contrast to the often self-contained temple complexes of the south. I observed a few pilgrims performing parikrama around the temple. The circumambulatory path, unlike the wide prakarams of Southern temples, was a simple, paved walkway. This again highlighted the emphasis on functionality and adaptation to the environment. The temple's design prioritizes accessibility and practicality, reflecting the challenging terrain and weather conditions. The use of granite for the temple's construction is also noteworthy. While granite is used in South Indian temples, particularly for the base and pillars, the extensive use of this material at Gangotri speaks to its local availability and durability in this mountainous region. The gleaming white granite, set against the backdrop of the grey mountains and the turquoise river, creates a visually stunning contrast. One aspect that particularly intrigued me was the absence of a dedicated mandapam or pillared hall, a ubiquitous feature in South Indian temples. This absence, I believe, stems from the climatic conditions. A large open hall would be impractical in a region that experiences heavy snowfall. The temple's design, therefore, prioritizes enclosed spaces for warmth and protection from the elements. My visit to the Gangotri Temple was a profound experience, offering a fresh perspective on sacred architecture. It underscored the fact that architectural styles are not merely aesthetic choices but are deeply intertwined with the environment, the local culture, and the practical needs of the community. While the Dravidian temples of my homeland celebrate ornamentation and intricate detail, the Gangotri Temple, in its elegant simplicity, embodies a different kind of beauty, a beauty born of resilience, adaptation, and a deep reverence for the natural world. It stands as a testament to the enduring power of faith, expressed through architecture that harmonizes with its surroundings, creating a sacred space that resonates with the very soul of the Himalayas.
Temple
British Colonial Period

Featured
80% Documented
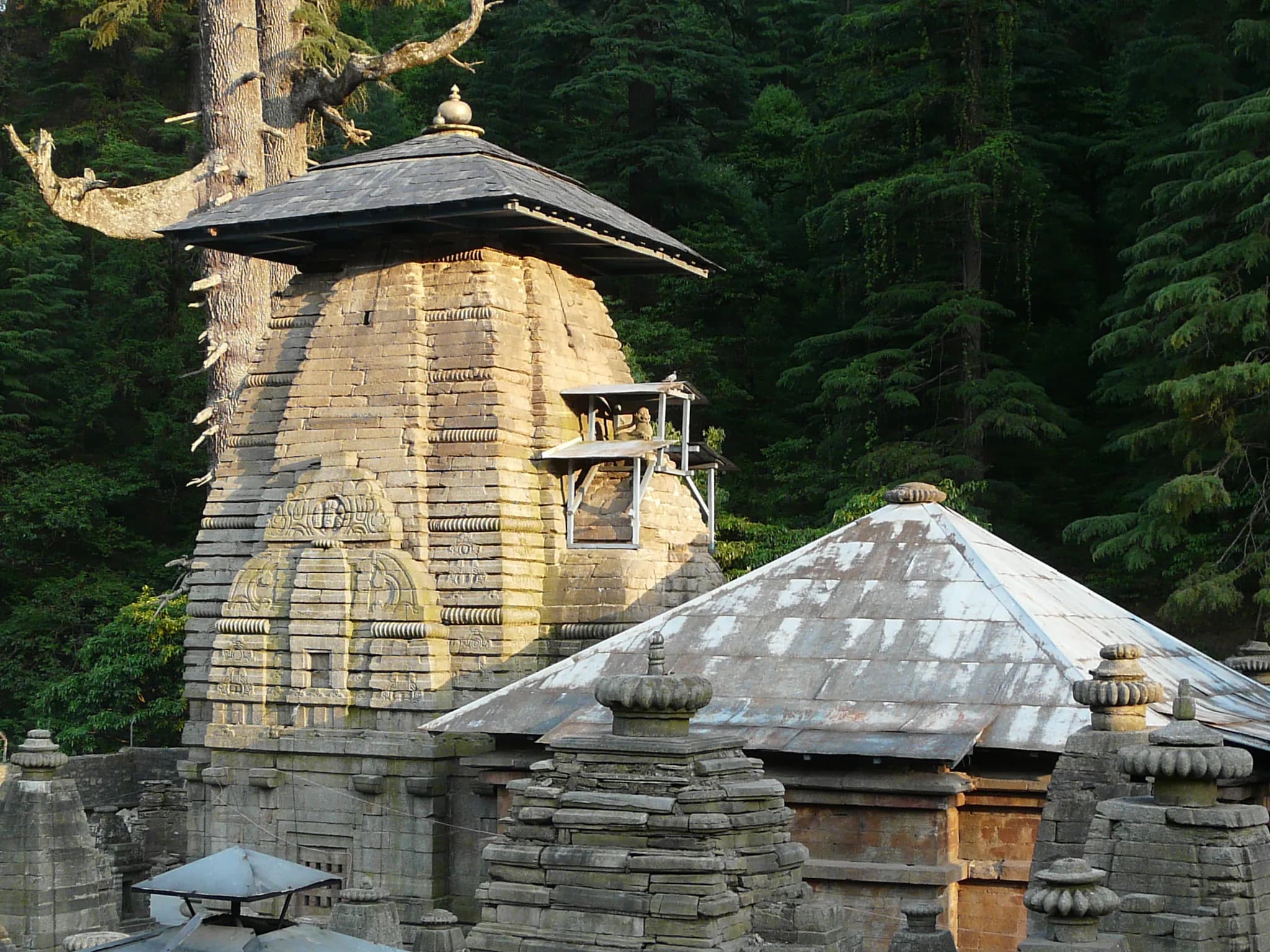
Jageshwar, Almora, Jageshwar (263634), Uttarakhand, India, Uttarakhand
The crisp mountain air of Uttarakhand carried the scent of pine and something older, something sacred. I stood at the entrance to the Jageshwar temple complex, a sprawling tapestry of over 124 stone temples nestled within a deodar forest. It wasn't simply a collection of structures; it felt like stepping into a living, breathing organism that had evolved organically over centuries. The Jageshwar group isn't a planned, symmetrical layout like Khajuraho or Modhera; it's a cluster, a family of shrines that have grown around each other, whispering stories of devotion and architectural ingenuity. My initial impression was one of subdued grandeur. Unlike the towering, imposing structures of South India, these temples were more intimate, their grey stone surfaces softened by moss and lichen. The majority of the temples belong to the Nagara style of North Indian architecture, characterized by a curvilinear shikhara, the tower above the sanctum. However, the shikharas here possess a distinct local flavour. They are taller and more slender than those found in, say, Odisha, giving them an almost ethereal quality against the backdrop of the Himalayas. Several temples, particularly the larger ones dedicated to Jageshwar (Shiva) and Mrityunjaya, exhibit the classic tiered structure of the shikhara, with miniature replicas of the main tower adorning each level, diminishing in size as they ascend towards the finial. I spent hours wandering through the complex, tracing the weathered carvings on the doorways and pillars. The intricate detailing, though eroded by time and the elements, still spoke volumes of the skill of the artisans. Recurring motifs included stylized lotuses, geometric patterns, and depictions of divine figures – Shiva, Parvati, and Ganesha being the most prominent. One particular panel, on a smaller shrine dedicated to Nandi, caught my attention. It depicted a scene from Shiva's marriage to Parvati, the figures rendered with a surprising dynamism, their expressions almost palpable despite the wear and tear. The main Jageshwar temple, dedicated to the eponymous deity, is the largest and arguably the most impressive. Its towering shikhara dominates the skyline of the complex, drawing the eye upwards. Inside the sanctum, a lingam, the aniconic representation of Shiva, resides in a dimly lit chamber, imbued with a palpable sense of reverence. The air was thick with the scent of incense and the murmur of prayers, a testament to the fact that this is not merely an archaeological site but a living place of worship. What struck me most about Jageshwar was the sense of continuity. The architectural styles evident here span several centuries, from the early Gupta period to the later medieval era. You can trace the evolution of the Nagara style, observing the subtle changes in the shikhara design, the ornamentation, and the layout of the temples. This layering of history, this palpable connection to the past, is what sets Jageshwar apart. It's not a static museum piece; it's a dynamic testament to the enduring power of faith and the artistry of generations of builders. As the sun began to dip behind the mountains, casting long shadows across the complex, I felt a profound sense of peace. Jageshwar is more than just a collection of temples; it's a sanctuary, a place where the whispers of the past mingle with the prayers of the present. It's a place that reminds us of the enduring power of human creativity and the timeless search for the divine. And it's a place that I, as a student of ancient Indian architecture, will carry with me, etched in my memory, for years to come.
Temple
Gurjara-Pratihara Period

Featured
85% Documented
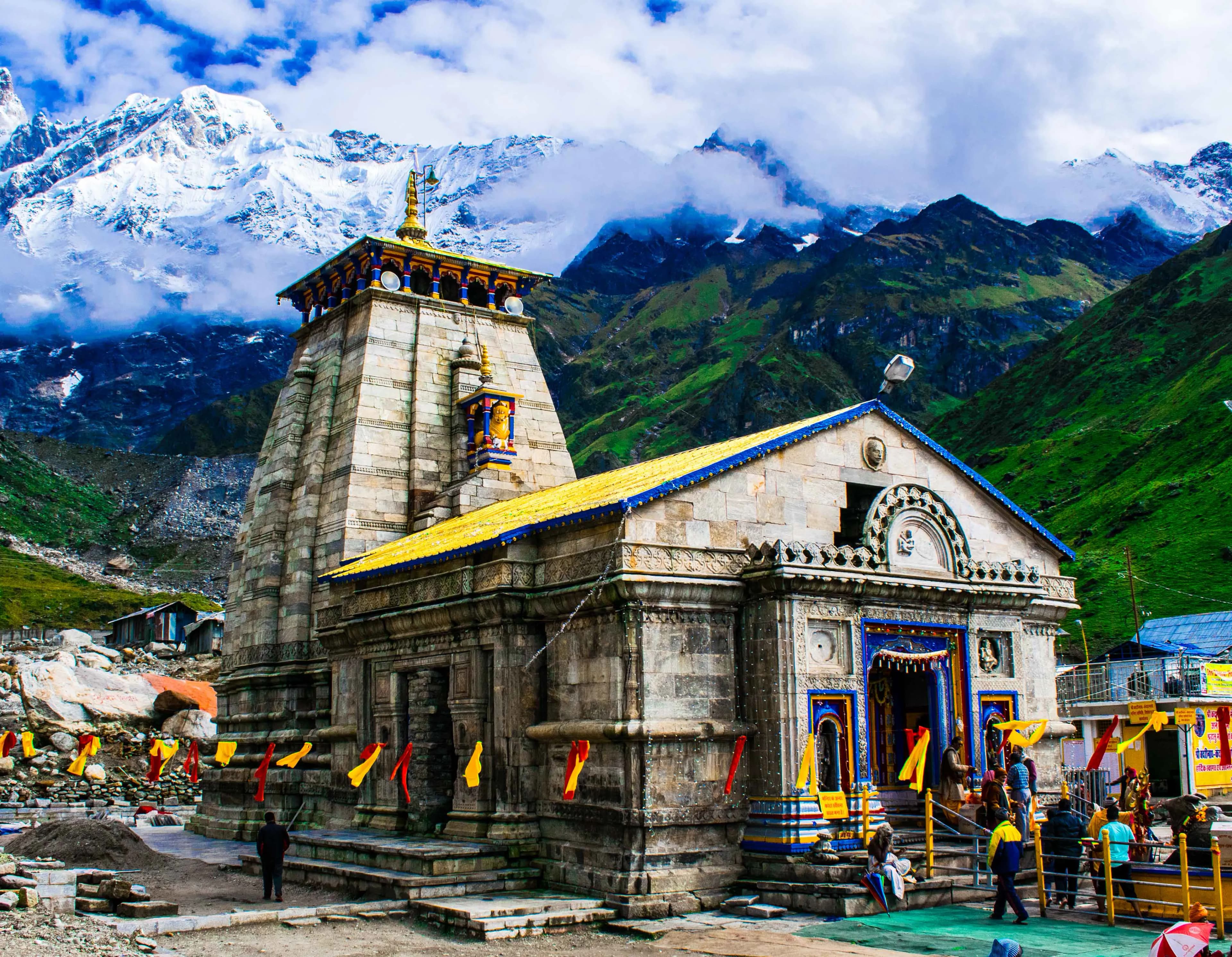
Kedarnath, Rudraprayag, Kedarnath (246445), Uttarakhand, India, Uttarakhand
The biting Himalayan wind whipped prayer flags into a frenzy around me, their vibrant colours a stark contrast to the grey, imposing stone of the Kedarnath Temple. Standing at an altitude of over 11,755 feet, surrounded by snow-capped peaks, the sheer resilience of this ancient structure took my breath away, even more so than the thin mountain air. My journey from Uttar Pradesh, traversing the winding roads and steep inclines, felt like a pilgrimage through time, connecting me to the deep spiritual roots of my own region. The temple, dedicated to Lord Shiva in his Kedarnath form, exudes an aura of timeless devotion. Its architecture, typical of the North Indian Himalayan style, is a testament to the ingenuity of the craftsmen who built it centuries ago. The thick, grey stone walls, built to withstand the harsh weather, are adorned with intricate carvings, weathered by time but still retaining a remarkable clarity. I ran my hand over the cool stone, tracing the outlines of deities and mythical creatures, feeling a palpable connection to the generations of pilgrims who had done the same. The main entrance, a relatively small wooden door, almost feels understated given the grandeur of the temple itself. Stepping inside, the dimly lit sanctum sanctorum offers a stark contrast to the bright exterior. The air is thick with the scent of incense and the murmur of prayers. The conical-shaped lingam, the symbolic representation of Lord Shiva, dominates the space, its dark, smooth surface worn smooth by centuries of reverence. I watched as devotees offered flowers, whispered prayers, and performed rituals, their faces etched with a profound sense of devotion. The energy within the sanctum is palpable, a blend of reverence, hope, and the quiet hum of spiritual energy. Outside, the temple complex is a bustling hub of activity. Priests perform rituals, pilgrims circumambulate the temple, and vendors sell religious paraphernalia. Despite the commercial activity, the atmosphere remains deeply spiritual. The backdrop of the majestic Himalayas, the constant chime of temple bells, and the palpable faith of the devotees create an environment unlike any other. What struck me most about Kedarnath was not just its religious significance, but also its historical and cultural context. Having studied the history of Uttar Pradesh, I recognized the influence of the region's architectural styles and religious practices in the temple's design and rituals. The intricate carvings, the use of specific materials, and the reverence for Lord Shiva all echoed the cultural landscape of my own homeland. It highlighted the interconnectedness of the Himalayan region and the flow of cultural and spiritual influences across these mountainous terrains. The 2013 floods, which devastated the region, left their mark on Kedarnath. While the temple itself miraculously survived, the surrounding area suffered significant damage. Evidence of the disaster is still visible, a stark reminder of the power of nature and the fragility of human endeavors. However, the resilience of the local community and the unwavering faith of the pilgrims are equally evident. The rebuilding efforts, the renewed influx of devotees, and the unwavering spirit of the place speak volumes about the enduring power of faith and the human capacity for recovery. As I descended from Kedarnath, the image of the temple, silhouetted against the snow-capped peaks, remained etched in my mind. The journey had been more than just a reporting assignment; it was a deeply personal experience. It was a journey into the heart of the Himalayas, a journey into the heart of faith, and a journey into the rich cultural tapestry of my own heritage. The echoes of chants, the scent of incense, and the feel of the ancient stone beneath my fingertips – these are the sensory memories I carry with me, a testament to the enduring power of Kedarnath.
Temple
Gurjara-Pratihara Period

UNESCO
Featured
80% Documented
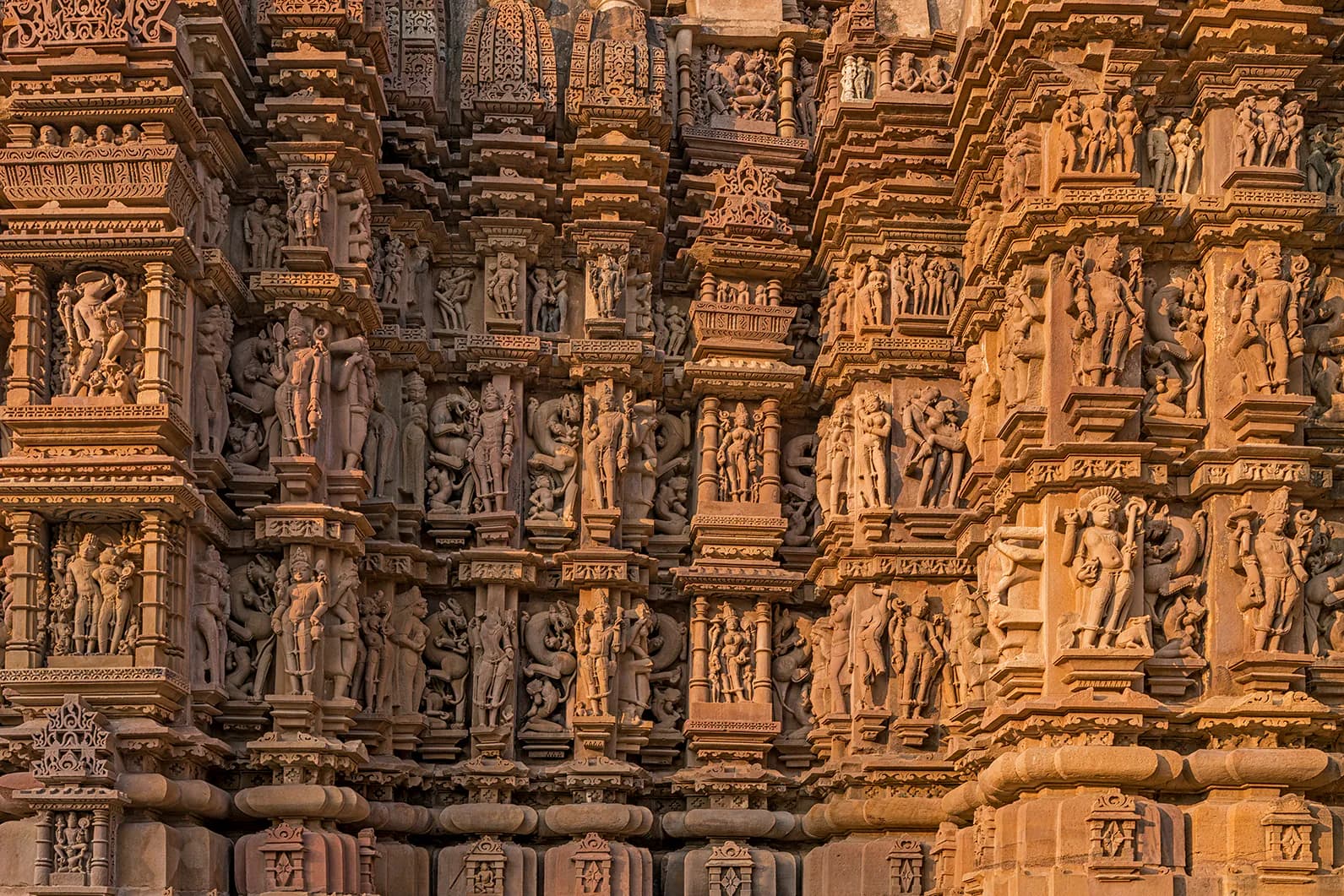
Khajuraho, Chhatarpur (471606), Madhya Pradesh, India, Madhya Pradesh
The first rays of dawn painted the sandstone a soft gold, illuminating the intricate carvings of the Kandariya Mahadeva Temple. Standing before this magnificent edifice, the largest of the Khajuraho group, I felt a palpable connection to the Chandela dynasty’s artistic zenith. Having explored countless temples across North India, from the snow-capped Himalayas to the plains of the Ganges, I can confidently say that Khajuraho holds a unique place, a testament to a time when art and spirituality were seamlessly interwoven. The sheer scale of the Kandariya Mahadeva is breathtaking. Its towering shikhara, a mountain of sculpted stone, reaches towards the heavens, a symbol of Mount Meru, the sacred abode of the gods. As I circumambulated the temple, my eyes traced the intricate friezes depicting celestial beings, mythical creatures, and scenes of everyday life. The level of detail is astonishing; every inch of the sandstone seems to pulsate with life. Noticeably, the erotic sculptures, often the focus of casual visitors, form only a small fraction of the overall artwork. They are integrated into the narrative, representing the cycle of creation and the celebration of life in all its forms. Moving beyond the Kandariya Mahadeva, I explored the western group of temples, each with its own distinct character. The Lakshmana Temple, dedicated to Vishnu, captivated me with its elegant proportions and the dynamic energy of its sculptures. I spent a considerable amount of time studying the narrative panels, deciphering the stories from the Ramayana and the Mahabharata etched into the stone. The sheer mastery of the Chandela sculptors is evident in the way they captured movement and emotion, breathing life into these ancient epics. The Chitragupta Temple, dedicated to Surya, the sun god, offered a different perspective. Its towering chariot, drawn by seven horses, is a powerful symbol of the sun’s journey across the sky. Inside, the sanctum houses a magnificent image of Surya, radiating an aura of divine power. The architectural style here subtly shifts, showcasing the evolution of the Chandela aesthetic over time. Venturing into the eastern group of temples, I found myself in a quieter, more intimate setting. The Parsvanatha Temple, a Jain temple, exudes a sense of serenity. Its polished sandstone surfaces gleam in the sunlight, reflecting the surrounding landscape. The intricate carvings here are more delicate, focusing on floral motifs and geometric patterns. The absence of the elaborate narratives found in the western group creates a different atmosphere, one of contemplation and inner peace. The Javari Temple, though smaller in scale, is a gem of architectural ingenuity. Its ornate doorway, adorned with celestial nymphs and intricate scrollwork, is a masterpiece of Chandela craftsmanship. I was particularly struck by the graceful curves and the delicate detailing of the sculptures, showcasing the artists' ability to manipulate the hard stone into forms of exquisite beauty. My exploration of Khajuraho wasn't just about admiring the architecture and sculptures. It was about experiencing the spirit of the place, imagining the artisans who toiled for decades to create these masterpieces, and the devotees who thronged these temples centuries ago. The air is thick with history, and as I walked through the temple grounds, I felt a profound sense of connection to India's rich cultural heritage. Khajuraho is more than just a collection of temples; it's a living testament to the artistic genius of a bygone era, a place that whispers stories of faith, devotion, and the celebration of life. It’s a must-see for anyone seeking to understand the depth and complexity of Indian art and history.
Temple
Chandela Period

Featured
80% Documented
Legship, West Sikkim, Geyzing (737111), Sikkim, India, Sikkim
The air hung thick with the scent of pine and damp earth as I climbed the final steps to the Kirateshwar Mahadev Temple. Nestled in the verdant foothills of the Himalayas, near Legship in West Sikkim, this temple doesn't boast the grandeur of some of India's more famous UNESCO sites, but it holds a quiet power, a palpable sense of history that resonated deeply within me. Unlike the meticulously preserved monuments I'd encountered elsewhere, Kirateshwar felt lived-in, a place of active worship woven into the fabric of the local community. The temple is dedicated to Lord Shiva, manifested here as Kirateshwar, the "Lord of the Kiratas," an ancient tribe believed to be the earliest inhabitants of the region. This connection to the land and its people is immediately apparent. The temple complex is situated at the confluence of the Rangit and Ratong rivers, a location considered sacred in Hindu mythology. The constant rush of the glacial waters provides a natural soundtrack to the spiritual atmosphere, a soothing counterpoint to the chanting of prayers. Architecturally, the temple is a blend of traditional Nepali and Hindu styles. The main structure, a two-tiered pagoda, is constructed primarily of wood, with intricately carved details adorning the eaves and pillars. Unlike the vibrant colours often seen in South Indian temples, Kirateshwar is more subdued. The dark wood, weathered by time and the elements, lends it an air of ancient wisdom, a sense of having witnessed centuries of devotion. I was particularly struck by the intricate carvings depicting mythological scenes and figures, each panel a testament to the skill of the artisans who created them. The roof, layered with intricately carved wooden shingles, sweeps upwards towards the sky, culminating in a golden pinnacle that catches the light. Inside the main sanctum, the atmosphere is hushed and reverent. Photography is restricted within the inner chamber, a rule I respected, allowing myself to fully absorb the spiritual energy of the space. The deity, a Shiva lingam, is bathed in the soft glow of oil lamps, the air thick with the fragrance of incense. Devotees offered prayers, their whispered chants adding to the sacred ambiance. It was a privilege to witness this intimate act of faith, a reminder of the enduring power of belief. Beyond the main temple, the complex sprawls across a sizable area, encompassing smaller shrines dedicated to various deities. I spent some time exploring these, each offering a unique glimpse into the rich tapestry of Hindu mythology. One shrine, dedicated to Goddess Durga, was particularly striking, with its vibrant red and gold decorations. The presence of these subsidiary shrines underscores the inclusive nature of Hinduism, its ability to embrace a multitude of deities and beliefs. My visit to Kirateshwar coincided with the annual Bala Chaturdashi festival, a significant event in the local calendar. Thousands of pilgrims from across Sikkim and neighbouring Nepal gather at the temple to offer prayers and perform rituals. The atmosphere was electric, a vibrant mix of devotion and celebration. Witnessing this festival firsthand was an unforgettable experience, a testament to the living heritage of this remarkable site. Kirateshwar Mahadev Temple is more than just a collection of stones and wood; it's a living testament to the enduring power of faith and the rich cultural heritage of the region. It's a place where the past and present intertwine, where the whispers of ancient legends mingle with the chants of contemporary devotees. While it may not be as visually spectacular as some of India's more famous UNESCO sites, its quiet power and profound spiritual significance left an indelible mark on my journey. It's a place I won't soon forget, a hidden gem nestled in the heart of the Himalayas.
Temple
Ahom Period
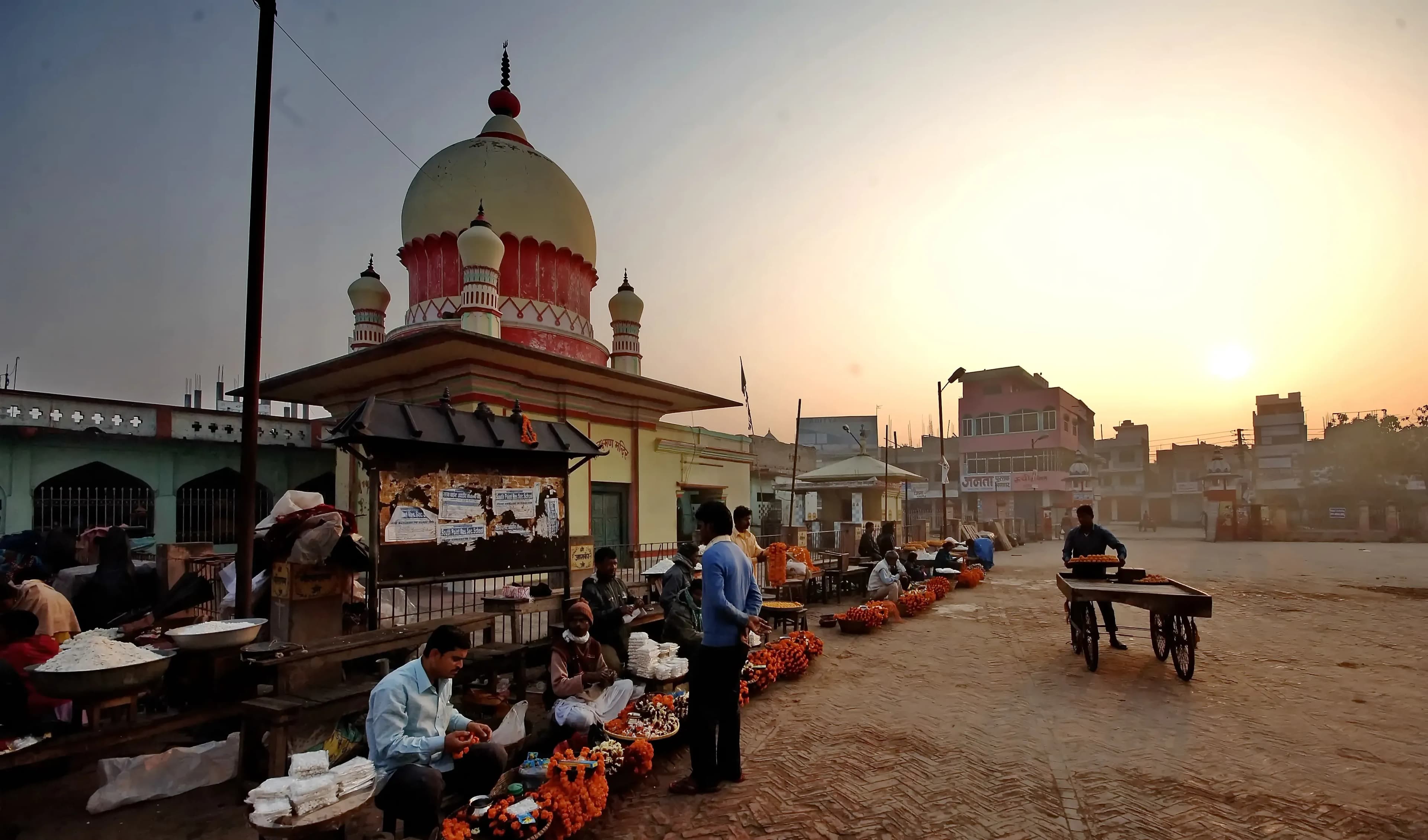

Featured
80% Documented
Baba Baidyanath Temple Road, Deoghar, Deoghar (814112), Jharkhand, India, Jharkhand
The midday sun beat down on Deoghar, casting long shadows across the paved courtyard as I approached the Naulakha Temple. Its gleaming white marble exterior, a stark contrast to the dusty landscape, radiated an almost ethereal glow. Nine lakhs, or nine hundred thousand rupees, is said to have been spent on its construction in 1949, hence the name. Having explored countless temples across North India, I was prepared for another ornate structure, but the Naulakha Temple surprised me with its unique blend of traditional and modern elements. The temple is dedicated to Lord Shiva, and the towering shikhara, the curvilinear tower rising above the sanctum sanctorum, immediately draws the eye. Unlike the intricate carvings that adorn most North Indian temples, the shikhara here is relatively plain, its smooth marble surface reflecting the sunlight. This simplicity, however, is not a sign of austerity, but rather a deliberate aesthetic choice that emphasizes the temple's grandeur. It’s a powerful statement of faith, a monument built not with elaborate ornamentation, but with sheer scale and the purity of white marble. As I circumambulated the temple, I noticed the subtle carvings around the base. Floral motifs and depictions of deities, though less prominent than in other temples I’ve visited, were executed with precision and grace. The interplay of light and shadow on the marble surface brought these carvings to life, creating a dynamic visual experience. It's a testament to the skill of the artisans who managed to imbue even the smallest details with a sense of devotion. Stepping inside the cool, dimly lit sanctum was a welcome respite from the scorching heat. The air was thick with the scent of incense and the murmur of prayers. The main deity, a Shiva lingam, resided in the centre, bathed in the soft glow of oil lamps. The atmosphere was charged with a palpable sense of reverence, a feeling amplified by the hushed whispers of devotees. I observed families offering prayers, their faces etched with devotion, a scene that plays out in temples across India, yet each time feels unique and deeply personal. What struck me most about the Naulakha Temple was its accessibility. Unlike many ancient temples where photography is restricted, here, I was free to document my experience. I captured the intricate details of the carvings, the serene faces of the devotees, and the imposing structure of the temple against the backdrop of the Jharkhand sky. This openness, I felt, reflected a modern approach to faith, a willingness to embrace and share the spiritual experience. Beyond the main temple, the complex houses several smaller shrines dedicated to other deities. I spent some time exploring these, observing the variations in architectural styles and the unique offerings made at each shrine. The presence of these smaller temples within the larger complex creates a sense of community, a microcosm of the Hindu pantheon. Leaving the Naulakha Temple, I carried with me not just photographs and memories, but a deeper understanding of the evolving landscape of faith in India. The temple, with its blend of traditional elements and modern sensibilities, represents a bridge between the past and the present. It's a place where ancient rituals are performed within a contemporary setting, a testament to the enduring power of belief in a rapidly changing world. The Naulakha Temple is not just a place of worship; it's a living testament to the enduring spirit of devotion and a fascinating study in the architectural evolution of religious spaces. It is a must-see for anyone travelling through Jharkhand, offering a glimpse into the heart of Hindu faith and the rich cultural tapestry of India.
Temple
Rajput Period

Featured
80% Documented
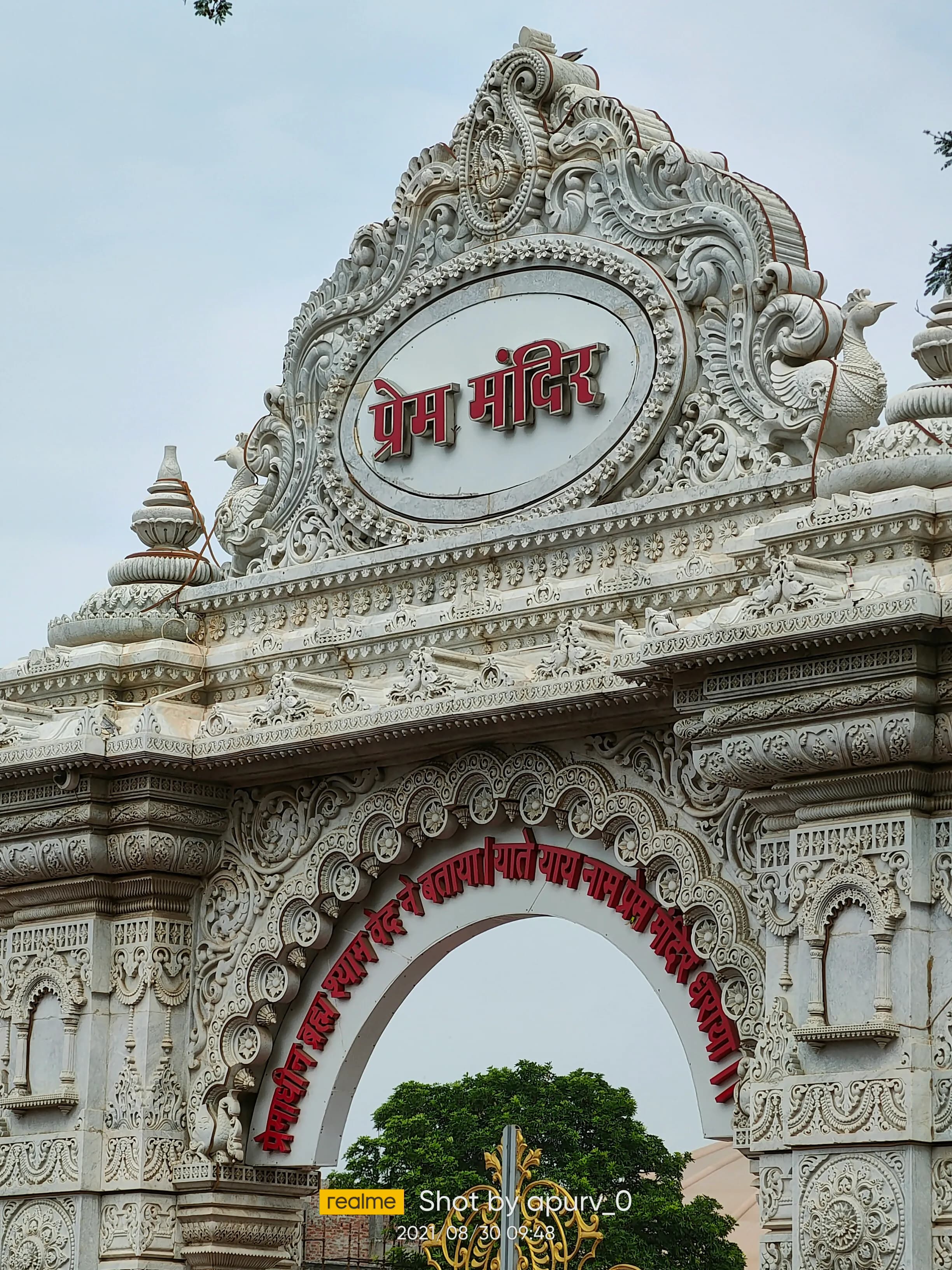
Parikrama Marg, Mathura, Vrindavan (281121), Uttar Pradesh, India, Uttar Pradesh
The air hummed with a palpable devotion, a tangible energy that enveloped me as I stepped onto the pristine marble expanse of Prem Mandir in Vrindavan. Having explored countless temples across North India, I thought I was immune to the sheer scale and grandeur of religious architecture, but Prem Mandir stopped me in my tracks. Bathed in the warm glow of the late afternoon sun, the temple, a relatively recent addition to Vrindavan's spiritual landscape, shimmered like a celestial palace descended to earth. The sheer scale is breathtaking. Towering white spires, intricately carved with depictions of Krishna's leelas, reach towards the sky, creating a skyline unlike any other in this holy city. Unlike the older, sandstone structures that characterize much of Vrindavan, Prem Mandir’s Italian marble construction gives it a unique, almost ethereal quality. The stone, imported from Italy, is polished to a high sheen, reflecting the sunlight and creating a dazzling spectacle. As I walked through the main gate, I was struck by the meticulous detailing. Every inch of the temple, from the towering shikharas to the delicate floral motifs adorning the walls, speaks of painstaking craftsmanship. The main temple structure is built on a raised platform, accessed by a broad flight of stairs. Circumambulating the main shrine, I noticed the intricate bas-relief panels depicting scenes from Krishna's life. These aren't mere carvings; they are narratives etched in stone, each panel telling a story with remarkable expressiveness. I paused at a depiction of the Rasa Lila, the divine dance of Krishna with the gopis, captivated by the fluidity of the figures and the sense of joyous movement captured in the static medium. One of the most striking features of Prem Mandir is the Govardhan Hill replica situated behind the main temple. This miniature mountain, crafted with impressive realism, is a testament to the devotion that fueled the temple's creation. Waterfalls cascade down its slopes, feeding a small lake at its base, creating a serene oasis within the bustling temple complex. Walking around the hill, I felt transported to the pastoral landscape of Braj, the region where Krishna is said to have spent his youth. As dusk settled, the temple underwent a magical transformation. Thousands of tiny lights embedded in the marble facade flickered to life, illuminating the intricate carvings and casting a warm, inviting glow over the entire complex. The light show, synchronized with devotional music, is a spectacle in itself, drawing gasps of admiration from the assembled devotees. The narrative of Krishna's life, projected onto the temple walls, added another layer to the experience, bringing the stories etched in stone to vibrant life. What truly sets Prem Mandir apart, however, is not just its architectural magnificence or the dazzling light show, but the palpable sense of serenity that pervades the atmosphere. Despite the crowds, a sense of peacefulness permeates the air. I observed families seated on the marble floors, lost in prayer, and groups of pilgrims chanting hymns with quiet devotion. The temple, despite its grandeur, feels remarkably intimate, a space where individuals can connect with their faith in their own way. Leaving Prem Mandir, I carried with me not just the memory of its architectural splendor, but also a renewed appreciation for the power of faith and devotion. It’s a testament to human ingenuity and artistic skill, a place where spirituality and artistry converge to create an experience that is both awe-inspiring and deeply moving. For anyone journeying through North India's spiritual heartland, Prem Mandir is an essential stop, a place to witness the enduring power of belief manifested in marble and light.
Temple
Contemporary Period

Featured
80% Documented
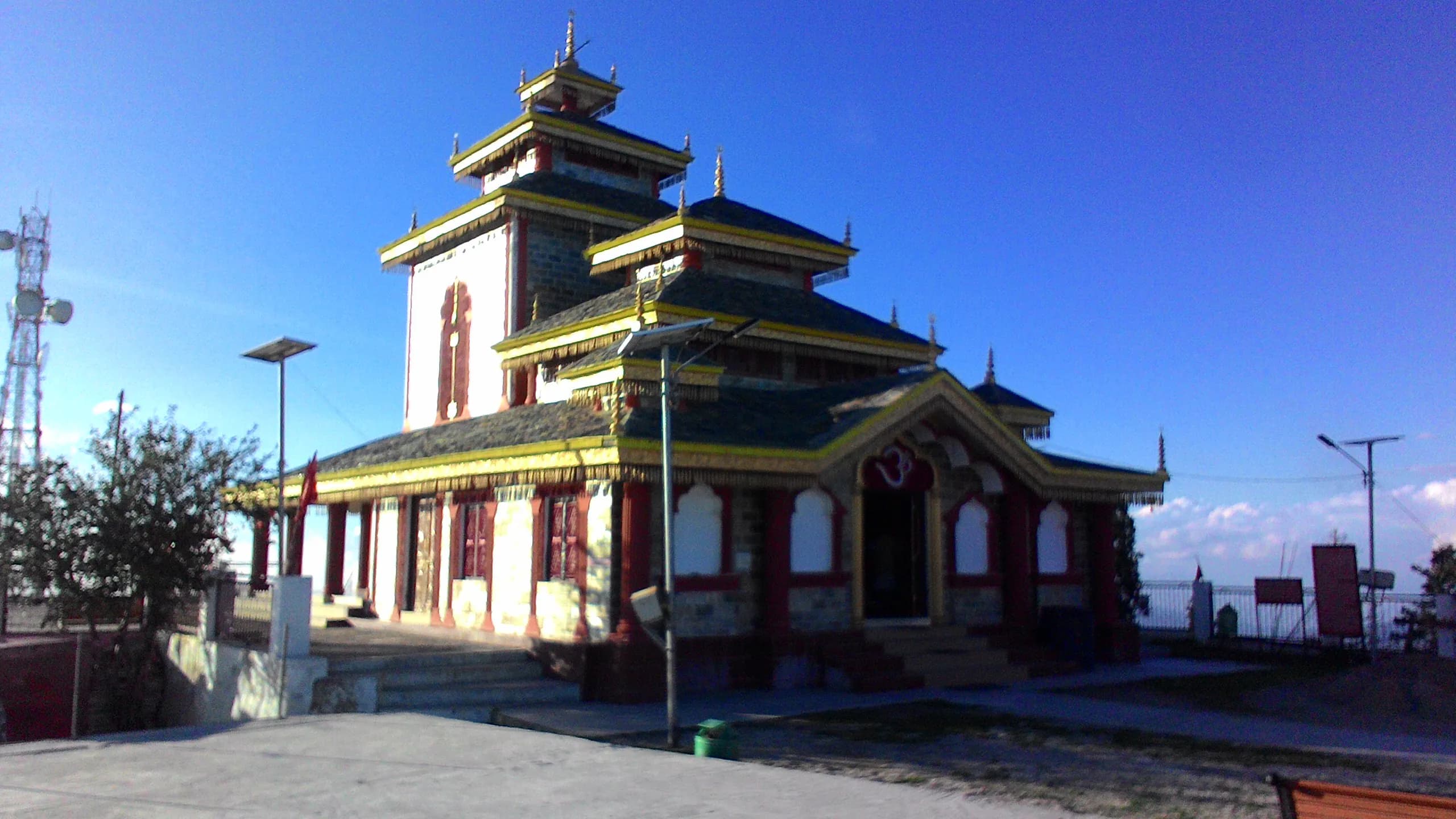
Surkanda Devi Road, Tehri Garhwal, Dhanaulti (249175), Uttarakhand, India, Uttarakhand
The crisp mountain air, scented with pine and a hint of woodsmoke, whipped around me as I ascended the final steps to Surkanda Devi Temple. Perched at an altitude of almost 10,000 feet in the Tehri Garhwal district of Uttarakhand, the temple commands a breathtaking panorama of the Himalayan peaks. It's a view that instantly justifies the arduous journey, a blend of winding roads and a steep, albeit scenic, climb. My camera, a constant companion, felt almost inadequate to capture the grandeur of the snow-capped giants against the azure sky. Surkanda Devi, dedicated to the goddess Sati, holds a profound significance in Hindu mythology. Local legend recounts this spot as the place where Sati's head fell after she self-immolated. This narrative imbues the location with a palpable sense of reverence, a quiet energy that hums beneath the surface of the bustling activity of pilgrims. The temple itself is relatively small, a stark contrast to the vastness of the landscape it inhabits. Its architecture is a simple yet elegant example of traditional Himalayan temple design. The main shrine, constructed of grey stone, features a sloping slate roof adorned with a golden trident, glinting in the sunlight. Unlike the ornate carvings found in many South Indian temples, the aesthetic here is one of understated beauty, allowing the natural surroundings to take center stage. I spent hours observing the intricate details. The stonework, though weathered by time and the elements, displayed a remarkable craftsmanship. The mortar, seemingly a simple mixture of lime and sand, had held the structure together for centuries, a testament to the ingenuity of the builders. Small brass bells, tied to the eaves, chimed melodiously in the wind, adding another layer to the sensory experience. Inside the sanctum sanctorum, photography is prohibited, a rule I respected. However, the memory of the dimly lit space, filled with the fragrance of incense and the murmur of prayers, remains vivid. The atmosphere was thick with devotion, a collective energy that transcended language and background. It was a privilege to witness this intimate expression of faith. Beyond the main shrine, the temple complex includes several smaller structures and open spaces. I noticed a series of small stone platforms, likely used for rituals. The surrounding walls were adorned with faded murals depicting scenes from Hindu mythology. These weathered paintings, though partially obscured by time, offered a glimpse into the rich artistic traditions of the region. I meticulously documented these fragments of history, hoping to preserve their stories through my lens. One of the most striking aspects of Surkanda Devi is the seamless integration of the built environment with the natural landscape. The temple seems to grow organically from the mountainside, a harmonious blend of human creation and nature's artistry. The panoramic views from the temple courtyard are simply mesmerizing. The rolling hills, blanketed in dense forests, stretch out as far as the eye can see, punctuated by the towering peaks of the Himalayas. As the sun began to dip below the horizon, casting long shadows across the valley, I felt a profound sense of peace. Surkanda Devi is more than just a temple; it's a sanctuary, a place where the spiritual and the natural converge. My experience here transcended the purely visual; it was a journey into the heart of the Himalayas, a testament to the enduring power of faith and the breathtaking beauty of the natural world. Leaving the temple, I carried with me not just photographs, but a deeper appreciation for the rich cultural and spiritual heritage of Uttarakhand.
Temple
Rajput Period

UNESCO
Featured
80% Documented
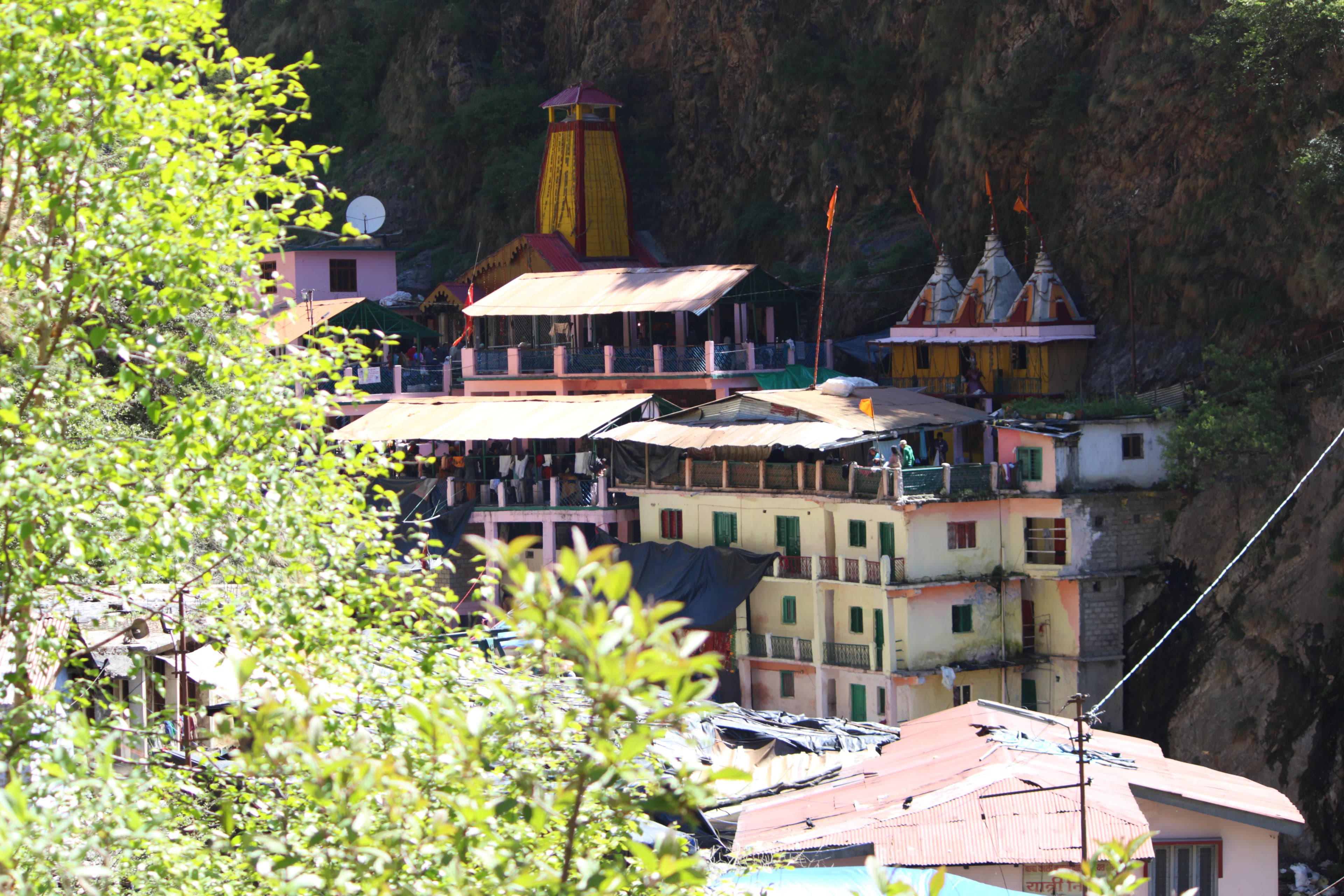
Kharsali, Uttarkashi, Yamunotri (249141), Uttarakhand, India, Uttarakhand
The biting Himalayan wind whipped around me, a stark contrast to the warmth radiating from the heart of Yamunotri. Here, nestled amidst snow-capped peaks in Uttarakhand's Uttarkashi district, stands the modest yet magnificent Yamunotri Temple, the source of the revered Yamuna River. My journey from the sun-drenched landscapes of Gujarat to this icy abode of the Goddess Yamuna was a pilgrimage not just of faith, but of architectural discovery. The temple, constructed primarily of granite, stands as a testament to resilience against the harsh elements. Its simple, almost austere design, is a departure from the ornate temples I'm accustomed to back home. The stark white facade, punctuated by a vibrant orange roof, creates a striking visual against the backdrop of grey mountains and verdant pine forests. The structure is relatively small, almost intimate, allowing devotees to feel a close connection with the deity. I noticed the meticulous craftsmanship in the granite blocks, fitted together with precision, a feat considering the challenging terrain and weather conditions. The absence of elaborate carvings, common in Gujarati temples, allows the natural beauty of the stone to shine through. The temple’s resilience is evident; it has withstood centuries of harsh winters, avalanches, and earthquakes, each time being rebuilt with unwavering devotion. Inside the sanctum sanctorum resides the black marble idol of Goddess Yamuna, radiating a serene aura. The energy within the temple is palpable, a blend of reverence and the raw power of nature. Unlike the bustling temple complexes of Gujarat, Yamunotri offers a sense of quiet contemplation. The focus remains solely on the Goddess and the sacred source of the Yamuna. Just a few meters away from the temple, bubbling from the mountainside, is the actual source of the Yamuna – the Yamunotri glacier. Witnessing this glacial stream, the birthplace of a river that nourishes millions, was a profoundly moving experience. The icy water, even at its source, held a surprising warmth. Devotees were taking a holy dip in the nearby Surya Kund, a thermal spring where they also boil rice and potatoes as prasad, a ritual I observed with fascination. The juxtaposition of the icy river and the boiling hot spring is a testament to the fascinating interplay of nature's forces. The trek to the temple itself is an architectural marvel of a different kind. The paved pathway, though steep in parts, is a testament to human ingenuity and perseverance. The route is dotted with small shrines and rest stops, offering glimpses of local architecture and providing respite to weary pilgrims. I observed the clever use of local materials like wood and stone in these structures, blending seamlessly with the surrounding landscape. One particular architectural element that caught my eye was the use of dry stone walling along the trek. These walls, built without mortar, are a testament to the ingenuity of the local communities. They serve as retaining walls, preventing landslides and protecting the pathway. The intricate patterns formed by the carefully placed stones are a testament to the aesthetic sensibilities of the builders. As I descended from Yamunotri, I carried with me not just the memory of a sacred pilgrimage, but also a deep appreciation for the unique architectural heritage of the Himalayas. The Yamunotri Temple, in its simplicity and resilience, stands as a powerful symbol of faith and human connection with nature. It is a stark contrast to the architectural exuberance of my homeland, yet equally captivating. The experience reinforced the understanding that architecture, in its diverse forms, reflects the spirit of a place and its people. The quiet strength of Yamunotri's architecture spoke volumes, a silent testament to the enduring power of faith and the awe-inspiring beauty of the Himalayas.
Temple
Rajput Period
Related Collections
Discover more heritage sites with these related collections
Explore More Heritage
Explore our comprehensive archive of 14 heritage sites with detailed documentation, 3D models, floor plans, and historical research. Each site page includes visitor information, conservation status, architectural analysis, and downloadable resources for students, researchers, and heritage enthusiasts.
Historical Context
The historical significance of these 14 heritage sites reflects the profound integration of dharma, artha, and kama in Hindu civilization. Across successive eras, royal patrons and spiritual leaders commissioned these sacred edifices as acts of devotion, fulfilling dharmic obligations while creating eternal spaces for worship and community gathering. Various dynasties contributed unique architectural visions, establishing traditions that honored Vedic principles while incorporating regional characteristics. Master builders (sthapatis) applied knowledge from ancient shilpa shastras (architectural treatises) and vastu shastra (spatial science), creating structures embodying cosmic principles and sacred geometry. Epigraphic inscriptions and archaeological evidence reveal sophisticated networks of guilds, royal support, and community participation sustaining these massive undertakings across decades or centuries. These monuments served as centers of Vedic learning, Sanskrit scholarship, classical arts, and spiritual practice—roles many continue fulfilling today, maintaining unbroken traditions that connect contemporary Bharat to its glorious civilizational heritage.
Architectural Significance
The architectural magnificence of these 14 heritage sites demonstrates the sophisticated application of shilpa shastra principles to create spaces embodying cosmic order and divine presence. The nagara architecture tradition manifests through characteristic elements: distinctive regional architectural elements, spatial planning principles, and decorative vocabularies. Employing indigenous materials—locally sourced stone, traditional lime mortars, and time-honored construction techniques—sthapatis created structures demonstrating advanced engineering knowledge. The corbelling techniques display extraordinary precision, achieving structural stability through geometric principles. Dome construction methodologies demonstrate sophisticated understanding of load distribution and compression forces, centuries before modern engineering formalized such knowledge. Beyond structural excellence, these monuments serve as three-dimensional textbooks of Puranic narratives, Vedic cosmology, and iconographic traditions. Sculptural programs transform stone into divine forms, teaching dharma through narrative reliefs and creating sacred atmospheres conducive to devotion and contemplation. Recent photogrammetric documentation and 3D laser scanning reveal original polychromy, construction sequences, and historical conservation interventions, enriching our understanding of traditional building practices and material technologies that sustained these magnificent creations.
Conservation & Preservation
Preserving these 14 sacred heritage sites represents our collective responsibility to safeguard Bharat's architectural and spiritual heritage for future generations. 3 benefit from Archaeological Survey of India protection, ensuring systematic conservation approaches. Conservation challenges include environmental degradation, biological colonization, structural deterioration, and pressures from increased visitation. Professional conservators address these through scientifically-grounded interventions: structural stabilization using compatible traditional materials, surface cleaning employing non-invasive techniques, vegetation management, and drainage improvements. Advanced documentation technologies—laser scanning, photogrammetry, ground-penetrating radar—create detailed baseline records enabling precise condition monitoring and informed conservation planning. When restoration becomes necessary, traditional building techniques and materials sourced from historical quarries ensure authenticity and compatibility. This comprehensive approach honors the devotion and craftsmanship of original builders while applying contemporary conservation science to ensure these monuments endure, continuing their roles as centers of worship, cultural identity, and civilizational pride.
Visitor Information
Experiencing these 14 sacred heritage sites offers profound connection to Bharat's spiritual and architectural heritage. Planning visits across multiple sites benefits from understanding regional connectivity and seasonal considerations. The optimal visiting period extends from October through March when pleasant temperatures facilitate comfortable exploration. Entry fees typically range from ₹25-40 for Indian nationals and ₹250-600 for international visitors at ASI-protected monuments. Photography for personal use is generally permitted, though professional equipment may require advance permissions. Visiting these sacred spaces requires cultural sensitivity: modest attire covering shoulders and knees, shoe removal in temple sanctums, quiet respectful demeanor, and recognition that these remain active worship centers where devotees practice centuries-old traditions. Meaningful engagement comes through understanding basic Hindu iconography, mythological narratives, and ritual contexts that bring these monuments to life.
Key Facts & Statistics
•
Total documented heritage sites: 14
•
UNESCO World Heritage Sites: 2
Source: UNESCO World Heritage Centre
•
ASI centrally protected monuments: 3
Source: Archaeological Survey of India
•
Temple: 14 sites
•
Nagara Architecture, Hindu Temple, Curvilinear towers, ornate carvings architectural style: 2 sites
•
Nagara architecture, Hindu temple, North Indian curvilinear towers architectural style: 1 sites
•
Nagara architecture, Hindu temple, Curvilinear towers, ornate carvings architectural style: 1 sites
•
Nagara Architecture, North Indian Temple, Curvilinear towers, ornate carvings. architectural style: 1 sites
•
Nagara Architecture, Northern Indian, Tall curving towers architectural style: 1 sites
•
British Colonial Period period construction: 3 sites
•
Rajput Period period construction: 3 sites
•
Gurjara-Pratihara Period period construction: 2 sites
•
Chandela Period period construction: 1 sites
•
Ahom Period period construction: 1 sites
•
Average documentation completion score: 80%
•
Featured flagship heritage sites: 14
•
Comprehensive digital archiving preserves heritage for future generations
•
Comprehensive digital archiving preserves heritage for future generations
•
Comprehensive digital archiving preserves heritage for future generations
•
Comprehensive digital archiving preserves heritage for future generations
Frequently Asked Questions
How many heritage sites are documented in India?
This collection includes 14 documented heritage sites across India. Of these, 2 are UNESCO World Heritage Sites. 3 sites are centrally protected by ASI. Each site has comprehensive documentation including photos, floor plans, and historical research.
What is the best time to visit heritage sites in India?
October to March is ideal for visiting heritage sites in India, with pleasant temperatures (15-25°C) and minimal rainfall. Avoid May-June (peak summer) and July-September (monsoon season). Major festivals also offer unique cultural experiences. Check individual site pages for specific visiting hours and seasonal closures.
What are the entry fees for heritage sites?
ASI-protected monuments charge ₹25-₹40 for Indian nationals and ₹250-₹600 for foreign tourists. State-protected sites often have lower or no entry fees. Many temples and religious sites are free. Children under 15 typically enter free. Still photography is usually included; video may require additional permits.
Are photography and videography allowed at heritage sites?
Still photography for personal use is generally permitted at most heritage sites. Tripods, flash photography, and commercial filming usually require special permissions. Some sites restrict photography of murals, sculptures, or sanctums. Drones are prohibited without explicit authorization. Always respect signage and guidelines at individual monuments.
Are these heritage sites wheelchair accessible?
Accessibility varies significantly. Major UNESCO sites and recently renovated monuments often have ramps and accessible facilities. However, many historical structures have steps, uneven surfaces, and narrow passages. Contact site authorities in advance for specific accessibility information. Our site pages indicate known accessibility features where available.
Are guided tours available at heritage sites?
Licensed guides are available at most major heritage sites, typically charging ₹200-₹500 for 1-2 hour tours. ASI-approved guides provide historical and architectural insights. Audio guides are available at select UNESCO sites. Our platform offers virtual tours and detailed documentation for major monuments.
What is the conservation status of these heritage sites?
3 sites are legally protected by ASI. Active conservation includes structural stabilization, surface cleaning, vegetation control, and drainage management. Digital documentation helps monitor deterioration. Ongoing surveys track condition changes for evidence-based interventions.
What are the key features of nagara architecture architecture?
Nagara architecture architecture features distinctive regional architectural elements, spatial planning principles, and decorative vocabularies. These elements evolved over centuries, reflecting regional climate, available materials, construction techniques, and cultural preferences. Each monument demonstrates unique variations within the broader architectural tradition.
What documentation is available for these heritage sites?
Each site includes high-resolution photography, architectural measurements, historical research, and expert annotations. Documentation averages 80% completion.
How much time should I allocate for visiting?
Plan 2-3 hours for major monuments to appreciate architectural details and explore grounds. Smaller sites may require 30-60 minutes. Multi-site itineraries should allocate travel time. Early morning or late afternoon visits offer better lighting for photography and fewer crowds. Check individual site pages for recommended visiting durations.
What is the cultural significance of these heritage sites?
These monuments represent India's diverse cultural heritage, reflecting centuries of architectural innovation, religious traditions, and artistic excellence. They serve as living links to historical societies, preserving knowledge about construction techniques, social structures, and cultural values. Many sites remain active centers of worship and community gathering.
How can I practice responsible heritage tourism?
Respect site rules including photography restrictions and designated pathways. Don't touch sculptures, murals, or walls. Dispose waste properly. Hire local guides to support communities. Avoid visiting during restoration work. Learn about cultural contexts before visiting. Report damage to authorities. Your responsible behavior helps preserve heritage for future generations.
References & Sources
[3]
🎨
StyleNagara Architecture
What is Nagara Architecture Architecture?
Nagara Architecture architecture is a distinctive style of Indian temple architecture characterized by its unique design elements and construction techniques. This architectural tradition flourished in India and represents a significant period in Indian cultural heritage. Features include intricate carvings, precise proportions, and integration with religious symbolism.
Period:
6th-18th century CEPrimary Region:
South IndiaTotal Sites:
0 documentedCategory:
VariousKey Characteristics
- 1Diverse architectural styles from various periods
- 2Intricate craftsmanship and artistic excellence
- 3Historical and cultural significance
- 4Well-documented heritage value
- 5Protected under heritage conservation acts
- 6Tourist and educational significance
Distribution by State
| 📍Uttarakhand | 7 sites |
| 📍Jharkhand | 2 sites |
| 📍Madhya Pradesh | 1 sites |
| 📍Sikkim | 1 sites |
| 📍Uttar Pradesh | 1 sites |
| 📍West Bengal | 1 sites |
| 📍Telangana | 1 sites |